
Concept explainers
a.
To find the intervals on which the function is increasing by using analytical method.
a.
Answer to Problem 12RE
The function
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is
Calculation:
The function is increasing when
Below is the graph of
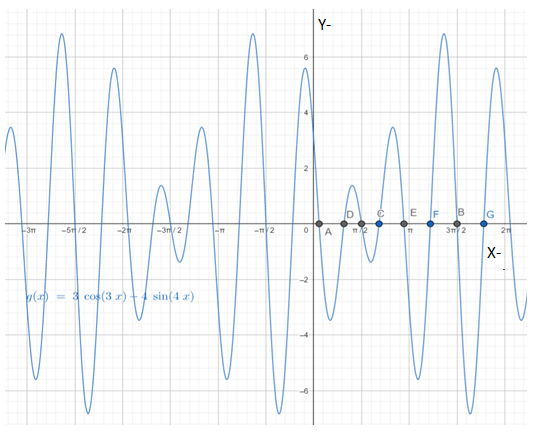
From graph it can be observed that there are total eight critical points that is
Now ,put
Therefore
Now ,put
Therefore
Now ,put
Therefore
Now ,put
Therefore
Now ,put
Therefore
Now ,put
Therefore
Now ,put
Therefore
Now ,put
Therefore
hence, the function
b.
To find the intervals on which the function is decreasing by using analytical method.
b.
Answer to Problem 12RE
The function
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is
Calculation:
The function is decreasing when
Below is the graph of
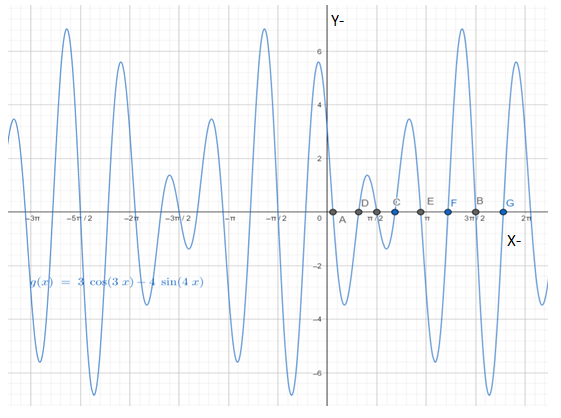
From graph it can be observed that there are total eight critical points that is
Now ,put
Therefore
Now ,put
Therefore
Now ,put
Therefore
Now ,put
Therefore
Now ,put
Therefore
Now ,put
Therefore
Now ,put
Therefore
Now ,put
Therefore
hence, the function
c.
To find the intervals on which the function is concave up by using analytical method.
c.
Answer to Problem 12RE
The function
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is
Calculation:
The graph of a twice differentiable function
Concave up on any interval where
Since,
First derivative :
Second derivative :
below is the graph of
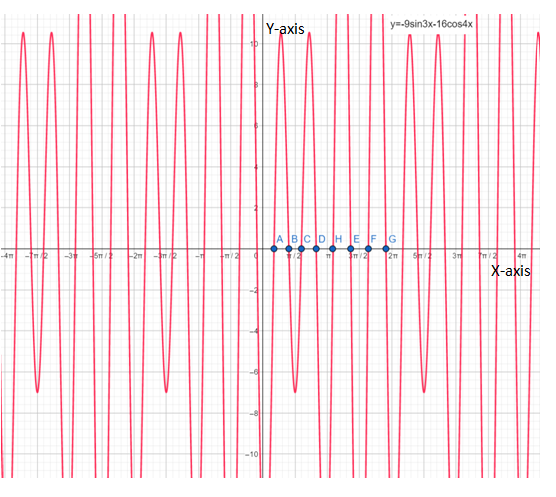
From graph it is clear that , there are total eight critical points that are
Now, put
Therefore,
Now, put
Therefore,
Now, put
Therefore,
Now, put
Therefore,
Now, put
Therefore,
Now, put
Therefore,
Now, put
Therefore,
Now, put
Therefore,
Now, put
Therefore,
Hence, the function
d.
To find the intervals on which the function is concave down by using analytical method.
d.
Answer to Problem 12RE
The function
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is
Calculation:
The graph of a twice differentiable function
Concave up on any interval where
Since,
First derivative :
Second derivative :
below is the graph of
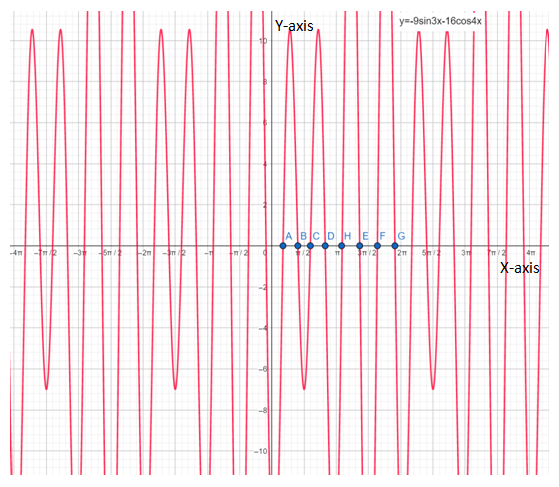
From graph it is clear that , there are total eight critical points that are
Now, put
Therefore,
Now, put
Therefore,
Now, put
Therefore,
Now, put
Therefore,
Now, put
Therefore,
Now, put
Therefore,
Now, put
Therefore,
Now, put
Therefore,
Now, put
Therefore,
Hence, the function
e.
To find any local extreme values.
e.
Answer to Problem 12RE
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is
Calculation:
Below is the graph of
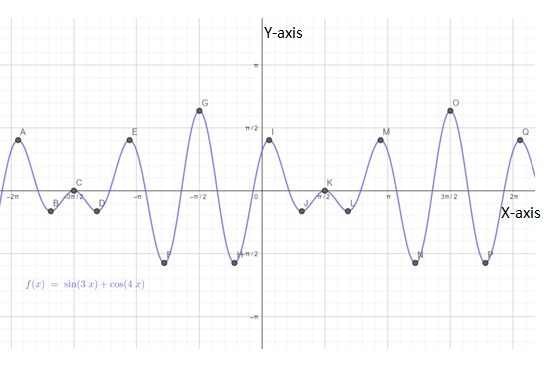
From graph it is clear that
f.
To find inflections points.
f.
Answer to Problem 12RE
The inflection points are
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is
Calculation:
Inflection point of any function is a point where the graph of function has a tangent line and where the concavity changes.
Since, the intervals in which function is concave up are
The intervals in which function is concave down are
Therefore, the inflection points are
Chapter 5 Solutions
Calculus 2012 Student Edition (by Finney/Demana/Waits/Kennedy)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Calculus, Single Variable: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Precalculus Enhanced with Graphing Utilities (7th Edition)
Single Variable Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition) - Standalone book
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





