
Concept explainers
ABC, implementation, ethics. (CMA, adapted) Plum Electronics, a division of Berry Corporation, manufactures two large-screen television models: the Mammoth, which has been produced since 2013 and sells for $990, and the Maximum, a newer model introduced in early 2015 that sells for $1,254. Based on the following income statement for the year ended November 30, 2017, senior management at Berry have decided to concentrate Plum’s marketing resources on the Maximum model and to begin to phase out the Mammoth model because Maximum generates a much bigger operating income per unit.
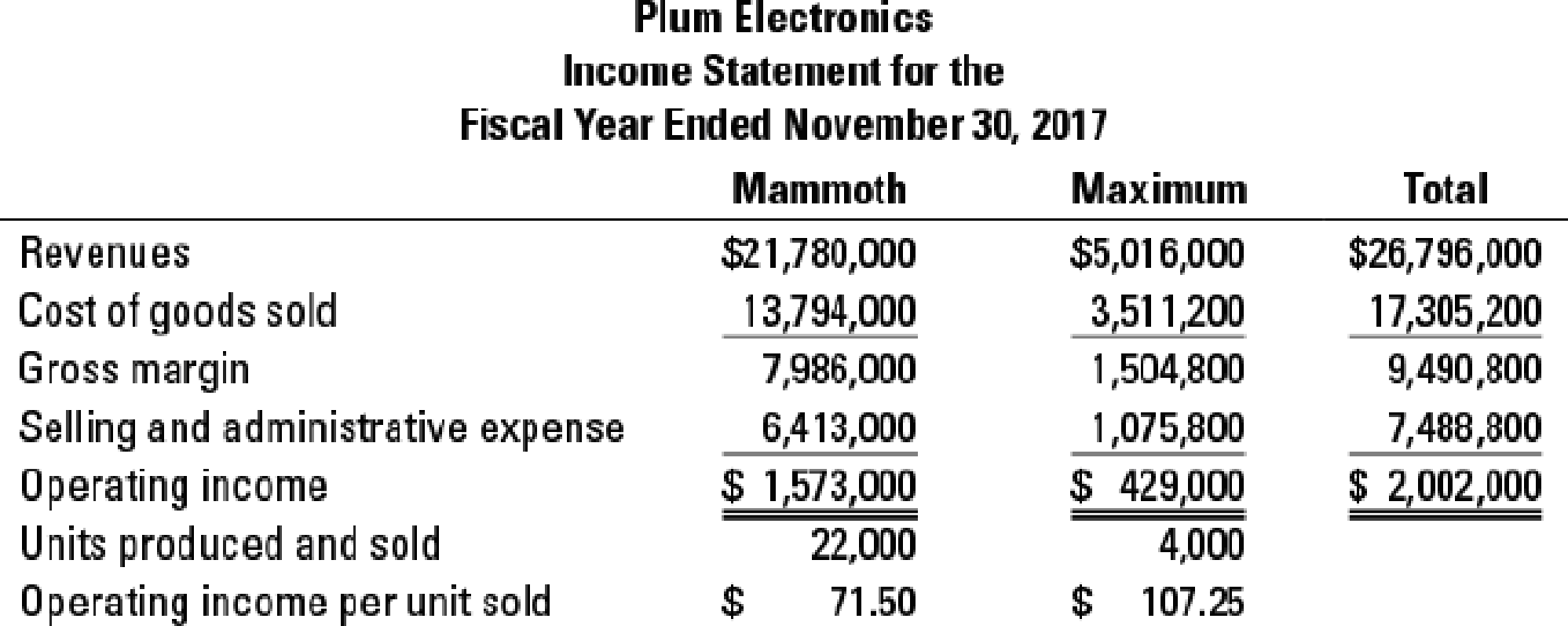
Details for cost of goods sold for Mammoth and Maximum are as follows:
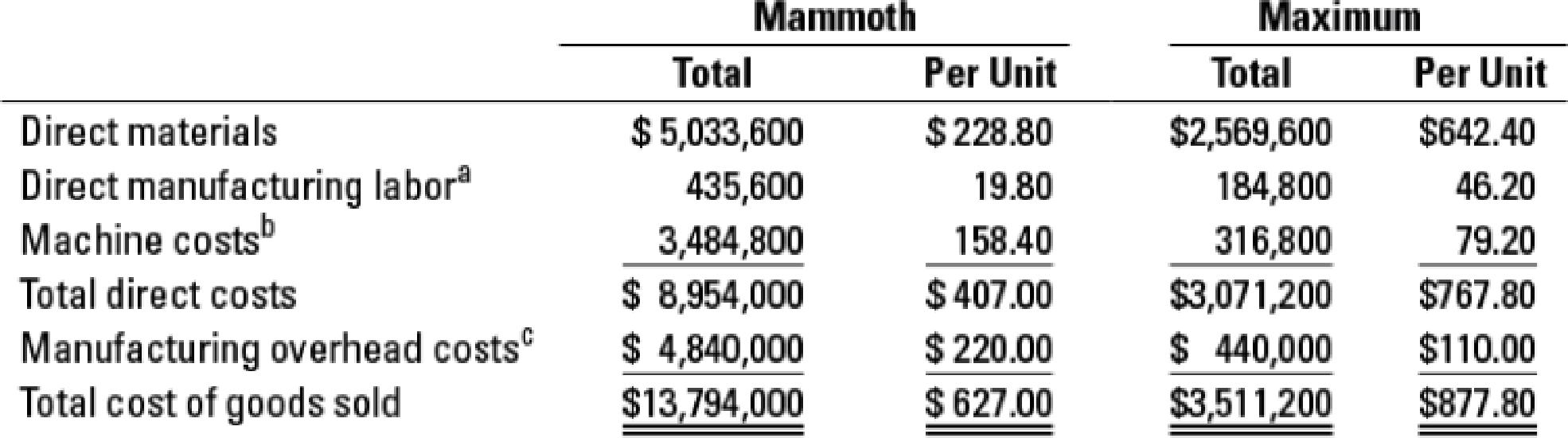
a Mammoth requires 1.5 hours per unit and Maximum requires 3.5 hours per unit. The direct
b Machine costs include lease costs of the machine, repairs, and maintenance. Mammoth requires 8 machine-hours per unit and Maximum requires 4 machine-hours per unit. The machine-hour rate is $19.80 per hour.
c Manufacturing overhead costs are allocated to products based on machine-hours at the rate of $27.50 per hour.
Plum’s controller, Steve Jacobs, is advocating the use of activity-based costing and activity-based management and has gathered the following information about the company’s manufacturing overhead costs for the year ended November 30, 2017.
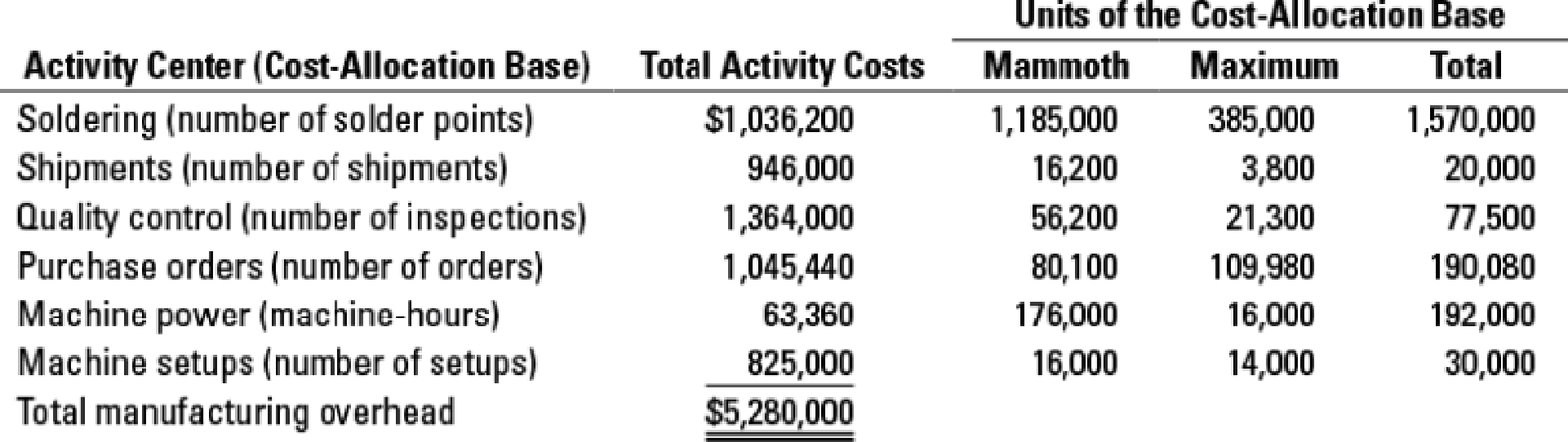
After completing his analysis, Jacobs shows the results to Charles Clark, the Plum division president. Clark does not like what he sees. “If you show headquarters this analysis, they are going to ask us to phase out the Maximum line, which we have just introduced. This whole costing stuff has been a major problem for us. First Mammoth was not profitable and now Maximum.
“Looking at the ABC analysis, I see two problems. First, we do many more activities than the ones you have listed. If you had included all activities, maybe your conclusions would be different. Second, you used number of setups and number of inspections as allocation bases. The numbers would be different had you used setup-hours and inspection-hours instead. I know that measurement problems precluded you from using these other cost-allocation bases, but I believe you ought to make some adjustments to our current numbers to compensate for these issues. I know you can do better. We can’t afford to phase out either product.” Jacobs knows that his numbers are fairly accurate. As a quick check, he calculates the profitability of Maximum and Mammoth using more and different allocation bases. The set of activities and activity rates he had used results in numbers that closely approximate those based on more detailed analyses. He is confident that headquarters, knowing that Maximum was introduced only recently, will not ask Plum to phase it out. He is also aware that a sizable portion of Clark’s bonus is based on division revenues. Phasing out either product would adversely affect his bonus. Still, he feels some pressure from Clark to do something.
- 1. Using activity-based costing, calculate the gross margin per unit of the Maximum and Mammoth models.
Required
- 2. Explain briefly why these numbers differ from the gross margin per unit of the Maximum and Mammoth models calculated using Plum’s existing simple costing system.
- 3. Comment on Clark’s concerns about the accuracy and limitations of ABC.
- 4. How might Plum find the ABC information helpful in managing its business?
- 5. What should Steve Jacobs do in response to Clark’s comments?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 5 Solutions
Horngren's Cost Accounting, Student Value Edition (16th Edition)
- Megaphone Corporation produces a molded plastic casing, M&M101, for many cell phones currently on the market. Summary data from its 2017 income statement are as follows:Revenues $5,000,000 Variable costs 3,250,000 Fixed costs 1,890,000 Operating income $ (140,000) Joshua Kirby, Megaphone’s president, is very concerned about Megaphone Corporation’s poor profitability. He asks Leroy Gibbs, production manager, and Tony DiNunzo, controller, to see if there are ways to reduce costs. After 2 weeks, Leroy returns with a proposal to reduce variable costs to 55% of revenues by reducing the costs Megaphone currently incurs for safe disposal of wasted plastic. Tony is concerned that this would expose the company to potential environmental liabilities. He tells Leroy, “We would need to estimate some of these potential environmental costs and include them in…arrow_forwardMegaphone Corporation produces a molded plastic casing, M&M101, for many cell phones currently on the market. Summary data from its 2017 income statement are as follows:Revenues $5,000,000 Variable costs 3,250,000 Fixed costs 1,890,000 Operating income $ (140,000) Joshua Kirby, Megaphone’s president, is very concerned about Megaphone Corporation’s poor profitability. He asks Leroy Gibbs, production manager, and Tony DiNunzo, controller, to see if there are ways to reduce costs. After 2 weeks, Leroy returns with a proposal to reduce variable costs to 55% of revenues by reducing the costs Megaphone currently incurs for safe disposal of wasted plastic. Tony is concerned that this would expose the company to potential environmental liabilities. He tells Leroy, “We would need to estimate some of these potential environmental costs and include them in…arrow_forwardMegaphone Corporation produces a molded plastic casing, M&M101, for many cell phones currently on the market. Summary data from its 2017 income statement are as follows:Revenues $5,000,000 Variable costs 3,250,000 Fixed costs 1,890,000 Operating income $ (140,000) Joshua Kirby, Megaphone’s president, is very concerned about Megaphone Corporation’s poor profitability. He asks Leroy Gibbs, production manager, and Tony DiNunzo, controller, to see if there are ways to reduce costs. After 2 weeks, Leroy returns with a proposal to reduce variable costs to 55% of revenues by reducing the costs Megaphone currently incurs for safe disposal of wasted plastic. Tony is concerned that this would expose the company to potential environmental liabilities. He tells Leroy, “We would need to estimate some of these potential environmental costs and include them in…arrow_forward
- Ethics, CVP analysis. Megaphone Corporation produces a molded plastic casing, M&M101, formany cell phones currently on the market. Summary data from its 2017 income statement are as follows:Revenues $5,000,000Variable costs 3,250,000Fixed costs 1,890,000Operating income $ (140,000)Joshua Kirby, Megaphone’s president, is very concerned about Megaphone Corporation’s poor profitability.He asks Leroy Gibbs, production manager, and Tony DiNunzo, controller, to see if there are ways toreduce costs.After 2 weeks, Leroy returns with a proposal to reduce variable costs to 55% of revenues by reducingthe costs Megaphone currently incurs for safe disposal of wasted plastic. Tony is concerned that this wouldexpose the company to potential environmental liabilities. He tells Leroy, “We would need to estimate someof these potential environmental costs and include them in our analysis.” “You can’t do that,” Leroy replies.“We are not violating any laws. There is some possibility that we may have to…arrow_forwardAt the beginning of the last quarter of 20x1, Youngston, Inc., a consumer products firm, hired Maria Carrillo to take over one of its divisions. The division manufactured small home appliances and was struggling to survive in a very competitive market. Maria immediately requested a projected income statement for 20x1. In response, the controller provided the following statement: After some investigation, Maria soon realized that the products being produced had a serious problem with quality. She once again requested a special study by the controllers office to supply a report on the level of quality costs. By the middle of November, Maria received the following report from the controller: Maria was surprised at the level of quality costs. They represented 30 percent of sales, which was certainly excessive. She knew that the division had to produce high-quality products to survive. The number of defective units produced needed to be reduced dramatically. Thus, Maria decided to pursue a quality-driven turnaround strategy. Revenue growth and cost reduction could both be achieved if quality could be improved. By growing revenues and decreasing costs, profitability could be increased. After meeting with the managers of production, marketing, purchasing, and human resources, Maria made the following decisions, effective immediately (end of November 20x1): a. More will be invested in employee training. Workers will be trained to detect quality problems and empowered to make improvements. Workers will be allowed a bonus of 10 percent of any cost savings produced by their suggested improvements. b. Two design engineers will be hired immediately, with expectations of hiring one or two more within a year. These engineers will be in charge of redesigning processes and products with the objective of improving quality. They will also be given the responsibility of working with selected suppliers to help improve the quality of their products and processes. Design engineers were considered a strategic necessity. c. Implement a new process: evaluation and selection of suppliers. This new process has the objective of selecting a group of suppliers that are willing and capable of providing nondefective components. d. Effective immediately, the division will begin inspecting purchased components. According to production, many of the quality problems are caused by defective components purchased from outside suppliers. Incoming inspection is viewed as a transitional activity. Once the division has developed a group of suppliers capable of delivering nondefective components, this activity will be eliminated. e. Within three years, the goal is to produce products with a defect rate less than 0.10 percent. By reducing the defect rate to this level, marketing is confident that market share will increase by at least 50 percent (as a consequence of increased customer satisfaction). Products with better quality will help establish an improved product image and reputation, allowing the division to capture new customers and increase market share. f. Accounting will be given the charge to install a quality information reporting system. Daily reports on operational quality data (e.g., percentage of defective units), weekly updates of trend graphs (posted throughout the division), and quarterly cost reports are the types of information required. g. To help direct the improvements in quality activities, kaizen costing is to be implemented. For example, for the year 20x1, a kaizen standard of 6 percent of the selling price per unit was set for rework costs, a 25 percent reduction from the current actual cost. To ensure that the quality improvements were directed and translated into concrete financial outcomes, Maria also began to implement a Balanced Scorecard for the division. By the end of 20x2, progress was being made. Sales had increased to 26,000,000, and the kaizen improvements were meeting or beating expectations. For example, rework costs had dropped to 1,500,000. At the end of 20x3, two years after the turnaround quality strategy was implemented, Maria received the following quality cost report: Maria also received an income statement for 20x3: Maria was pleased with the outcomes. Revenues had grown, and costs had been reduced by at least as much as she had projected for the two-year period. Growth next year should be even greater as she was beginning to observe a favorable effect from the higher-quality products. Also, further quality cost reductions should materialize as incoming inspections were showing much higher-quality purchased components. Required: 1. Identify the strategic objectives, classified by the Balanced Scorecard perspective. Next, suggest measures for each objective. 2. Using the results from Requirement 1, describe Marias strategy using a series of if-then statements. Next, prepare a strategy map. 3. Explain how you would evaluate the success of the quality-driven turnaround strategy. What additional information would you like to have for this evaluation? 4. Explain why Maria felt that the Balanced Scorecard would increase the likelihood that the turnaround strategy would actually produce good financial outcomes. 5. Advise Maria on how to encourage her employees to align their actions and behavior with the turnaround strategy.arrow_forwardMaxwell Company produces a variety of kitchen appliances, including cooking ranges and dishwashers. Over the past several years, competition has intensified. In order to maintainand perhaps increaseits market share, Maxwells management decided that the overall quality of its products had to be increased. Furthermore, costs needed to be reduced so that the selling prices of its products could be reduced. After some investigation, Maxwell concluded that many of its problems could be traced to the unreliability of the parts that were purchased from outside suppliers. Many of these components failed to work as intended, causing performance problems. Over the years, the company had increased its inspection activity of the final products. If a problem could be detected internally, then it was usually possible to rework the appliance so that the desired performance was achieved. Management also had increased its warranty coverage; warranty work had been increasing over the years. David Haight, president of Maxwell Company, called a meeting with his executive committee. Lee Linsenmeyer, chief engineer; Kit Applegate, controller; and Jeannie Mitchell, purchasing manager, were all in attendance. How to improve the companys competitive position was the meetings topic. The conversation of the meeting was recorded as seen on the following page: DAVID: We need to find a way to improve the quality of our products and at the same time reduce costs. Lee, you said that you have done some research in this area. Would you share your findings? LEE: As you know, a major source of our quality problems relates to the poor quality of the parts we acquire from the outside. We have a lot of different parts, and this adds to the complexity of the problem. What I thought would be helpful would be to redesign our products so that they can use as many interchangeable parts as possible. This will cut down the number of different parts, make it easier to inspect, and cheaper to repair when it comes to warranty work. My engineering staff has already come up with some new designs that will do this for us. JEANNIE: I like this idea. It will simplify the purchasing activity significantly. With fewer parts, I can envision some significant savings for my area. Lee has shown me the designs so I know exactly what parts would be needed. I also have a suggestion. We need to embark on a supplier evaluation program. We have too many suppliers. By reducing the number of different parts, we will need fewer suppliers. And we really dont need to use all the suppliers that produce the parts demanded by the new designs. We should pick suppliers that will work with us and provide the quality of parts that we need. I have done some preliminary research and have identified five suppliers that seem willing to work with us and assure us of the quality we need. Lee may need to send some of his engineers into their plants to make sure that they can do what they are claiming. DAVID: This sounds promising. Kit, can you look over the proposals and their estimates and give us some idea if this approach will save us any money? And if so, how much can we expect to save? KIT: Actually, I am ahead of the game here. Lee and Jeannie have both been in contact with me and have provided me with some estimates on how these actions would affect different activities. I have prepared a handout that includes an activity table revealing what I think are the key activities affected. I have also assembled some tentative information about activity costs. The table gives the current demand and the expected demand after the changes are implemented. With this information, we should be able to assess the expected cost savings. Additionally, the following activity cost data are provided: Purchasing parts: Variable activity cost: 30 per part number; 20 salaried clerks, each earning a 45,000 annual salary. Each clerk is capable of processing orders associated with 100 part numbers. Inspecting parts: Twenty-five inspectors, each earning a salary of 40,000 per year. Each inspector is capable of 2,000 hours of inspection. Reworking products: Variable activity cost: 25 per unit reworked (labor and parts). Warranty: Twenty repair agents, each paid a salary of 35,000 per year. Each repair agent is capable of repairing 500 units per year. Variable activity costs: 15 per product repaired. Required: 1. Compute the total savings possible as reflected by Kits handout. Assume that resource spending is reduced where possible. 2. Explain how redesign and supplier evaluation are linked to the savings computed in Requirement 1. Discuss the importance of recognizing and exploiting internal and external linkages. 3. Identify the organizational and operational activities involved in the strategy being considered by Maxwell Company. What is the relationship between organizational and operational activities?arrow_forward
- B' Manufacturing Company manufactures and sells parts for various musical gadgets. The followinginformation to a single part which is used in the production of a wind instrument. The business earned operating Income of $220,000 in 2019, when production was 3,000 units and the president of Darius is underpressure from shareholders to increase operating income in 2020 and is therefore considering the implementation of strategies mainly geared at increasing revenues and or decreasing variable costs. Data forvariable cost per unit and total fixed costs were as follows:Variable expenses per unit: Direct Material --$58Direct Labour-- $74Variable Manufacturing Overhead --$48Fixed expenses: Fixed Manufacturing Overhead --$215,000Fixed Selling Costs-- $65,000Fixed Administrative Costs -- $160,000Required:1) Compute the selling price per unit in 2019, using the equation method. 2) Given the sales of 3,000 units and the selling price calculated in (a), prepare a contribution margin income…arrow_forwardCarniTrin is a manufacturer of Carnival costumes in a highly competitive market. Thecompany's management team is seeking guidance on the use of financial performancemeasures to identify the key drivers of the company's financial performance and develop astrategy to improve it.The following data relate to the company for the year 2022: In its clothing division, the company has $6,000,000 invested in assets. After-taxoperating income from sales of clothing in 2022 is $900,000. Income for the clothingdivision has grown steadily over the last few years. The cosmetics division has $14,000,000 invested in assets and an after-tax operatingincome in 2022 of $1,900,000. The weighted-average cost of capital for CarniTrin is 10% and the 2021’s after-taxreturn on investment for each division was 15%. The general manager of CarniTrin has asserted that in the future, managers shouldhave their compensation structure aligned with their performance measures with nofixed salaries. However, the…arrow_forwardCarniTrin is a manufacturer of Carnival costumes in a highly competitive market. Thecompany's management team is seeking guidance on the use of financial performancemeasures to identify the key drivers of the company's financial performance and develop astrategy to improve it. The following data relate to the company for the year 2022: In its clothing division, the company has $6,000,000 invested in assets. After-taxoperating income from sales of clothing in 2022 is $900,000. Income for the clothingdivision has grown steadily over the last few years. The cosmetics division has $14,000,000 invested in assets and an after-tax operatingincome in 2022 of $1,900,000. The weighted-average cost of capital for CarniTrin is 10% and the 2021’s after-taxreturn on investment for each division was 15%. The general manager of CarniTrin has asserted that in the future, managers shouldhave their compensation structure aligned with their performance measures with nofixed salaries.…arrow_forward
- CarniTrin is a manufacturer of Carnival costumes in a highly competitive market. Thecompany's management team is seeking guidance on the use of financial performancemeasures to identify the key drivers of the company's financial performance and develop astrategy to improve it. The following data relate to the company for the year 2022: In its clothing division, the company has $6,000,000 invested in assets. After-taxoperating income from sales of clothing in 2022 is $900,000. Income for the clothingdivision has grown steadily over the last few years. The cosmetics division has $14,000,000 invested in assets and an after-tax operatingincome in 2022 of $1,900,000. The weighted-average cost of capital for CarniTrin is 10% and the 2021’s after-taxreturn on investment for each division was 15%. The general manager of CarniTrin has asserted that in the future, managers shouldhave their compensation structure aligned with their performance measures with nofixed salaries. However, the…arrow_forwardAt the end of 2021, Mejorar Company implemented a low-cost strategy to improve its competitive position. Its objective was to become the low-cost producer in its industry. A Balanced Scorecard was developed to guide the company toward this objective. To lower costs, Mejorar undertook a number of improvement activities such as JIT production, total quality management, and activity-based management. Now, after two years of operation, the president of Mejorar wants some assessment of the achievements. To help provide this assessment, the following information on one product has been gathered: 1. Compute the following measures for 2021 and 2023: a. actual velocity and cycle time (2021 and 2023) (My question: In the book it stated that Actual Velocity (# units produced/time) and Cycle Time (time/# units produced) However, which one is per hour and per minute Or maybe I wrong let me know?) b. Percentage of total revenue from new customers (2021 and 2023) (assume one unit per customer) c.…arrow_forwardCarniTrin is a manufacturer of Carnival costumes in a highly competitive market. The company's management team is seeking guidance on the use of financial performance measures to identify the key drivers of the company's financial performance and develop a strategy to improve it. The following data relate to the company for the year 2022: In its clothing division, the company has $6,000,000 invested in assets. After-tax operating income from sales of clothing in 2022 is $900,000. Income for the clothing division has grown steadily over the last few years. The cosmetics division has $14,000,000 invested in assets and an after-tax operating income in 2022 of $1,900,000. The weighted-average cost of capital for CarniTrin is 10% and the 2021’s after-tax return on investment for each division was 15%. The general manager of CarniTrin has asserted that in the future, managers should have their compensation structure aligned with their performance measures with no fixed salaries. However,…arrow_forward
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning


