
Concept explainers
Methods of Cost Analysis: Account Analysis, Simple and Multiple Regression Using a Spreadsheet (Appendix A)
Caiman Distribution Partners is the Brazilian distribution company of a U.S. consumer products firm. Inflation in Brazil has made bidding and budgeting difficult for marketing managers trying to penetrate some of the country’s rural regions. The company expects to distribute 450,000 cases of products in Brazil next month. The controller has classified operating costs (excluding costs of the distributed product) as follows:
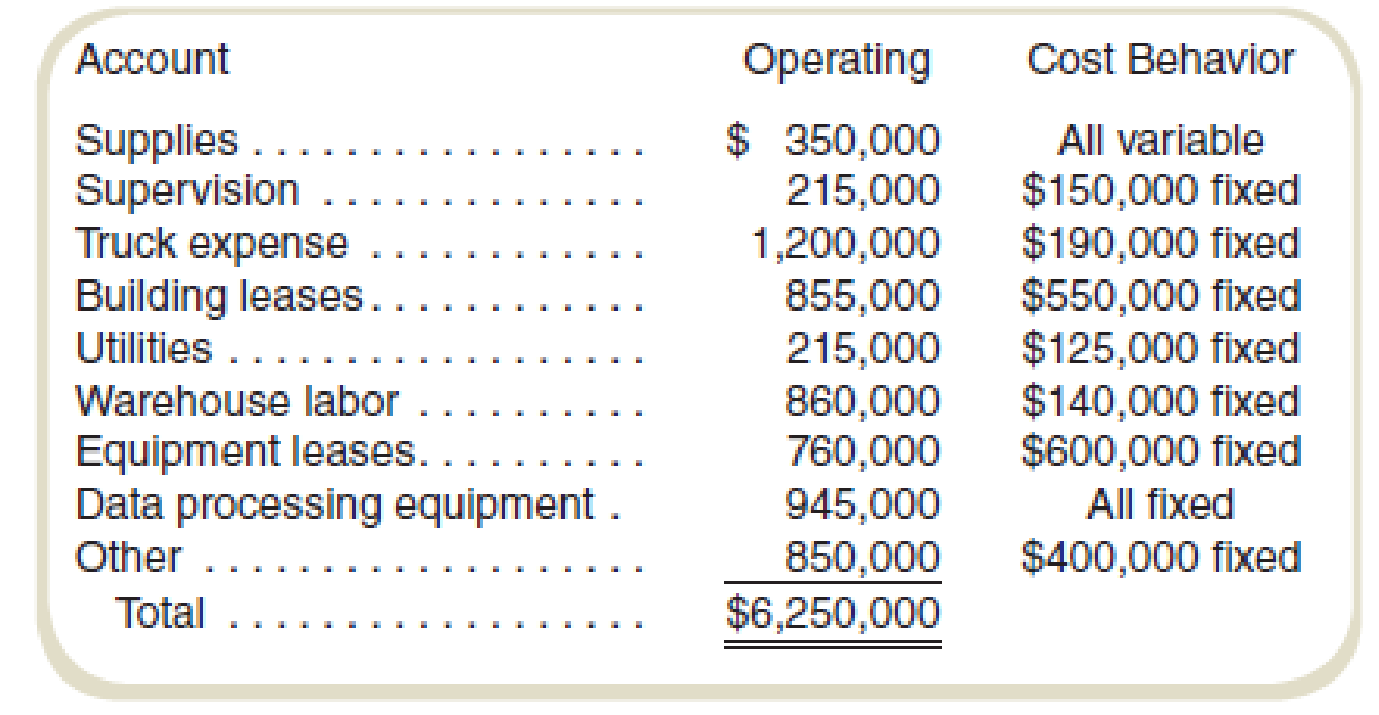
Although overhead costs were related to revenues throughout the company, the experience in Brazil suggested to the managers that they should incorporate information from a published index of Brazilian prices in the distribution sector to
Following instructions from the corporate offices, the controller’s office in Brazil collected the following information for monthly operations from last year:
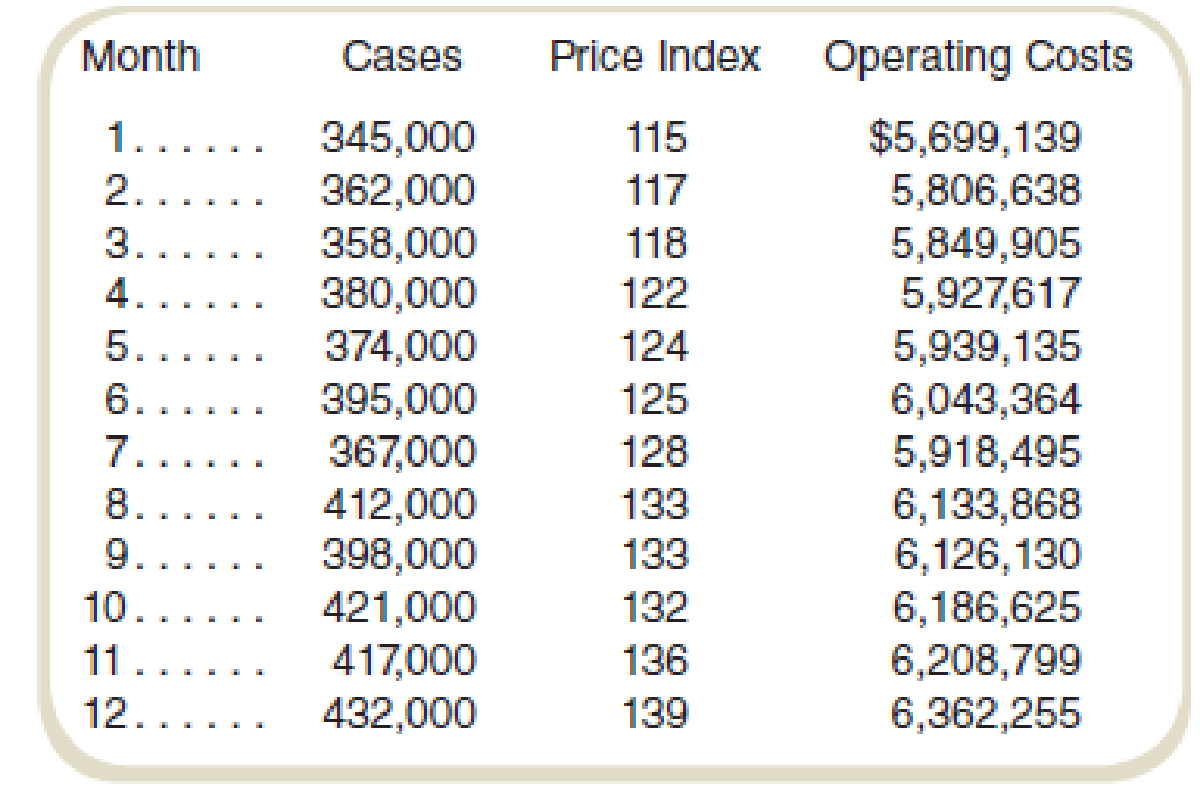
These data are considered representative for both past and future operations in Brazil.
Required
- a. Prepare an estimate of operating costs assuming that 450,000 cases will be shipped next month based on the controller’s analysis of accounts.
- b. Use the high-low method to prepare an estimate of operating costs assuming that 450,000 cases will be shipped next month.
- c. Prepare an estimate of operating costs assuming that 450,000 cases will be shipped next month by using the results of a simple regression of operating costs on cases shipped.
- d. Prepare an estimate of operating costs assuming that 450,000 cases will be shipped next month by using the results of a multiple regression of operating costs on cases shipped and the price level. Assume a price level of 145 for next month.
- e. Make a recommendation to the managers about the most appropriate estimate given the circumstances.
a.
Prepare an estimate of operating costs assuming that 450,000 cases will be shipped next month based on the controller’s analysis of accounts.
Explanation of Solution
Operating cost:
Operating cost is the total cost of the production. It includes direct and indirect cost of the production. Operating profit is calculated by deducting the operating cost from the revenue of the business.
Calculate the estimated overhead cost:
Thus, the estimated overhead cost is $6,250,000.
Working note 1:
Calculate the variable cost per unit:
Working note 2:
Prepare a schedule to show the allocation of fixed and variable cost:
| Particulars |
Operating cost (a) |
Fixed cost (b) |
Variable cost |
| Supplies | $350,000 | $0 | $350,000 |
| Supervision | $215,000 | $150,000 | $65,000 |
| Truck expenses | $1,200,000 | $190,000 | $1,010,000 |
| Building lease | $855,000 | $550,000 | $305,000 |
| Utilities | $215,000 | $125,000 | $90,000 |
| Warehouse labor | $860,000 | $140,000 | $720,000 |
| Equipment lease | $760,000 | $600,000 | $160,000 |
| Data processing equipment | $945,000 | $945,000 | $0 |
| Other | $850,000 | $400,000 | $450,000 |
| Total cost | $6,250,000 | $3,100,000 | $3,150,000 |
Table: (1)
b.
Use the high-low method to prepare an estimate of operating costs assuming that 450,000 cases will be shipped next month.
Explanation of Solution
High-low cost method:
High-low cost method helps in separating the fixed and variable cost from the total cost. It is calculated by comparing the highest and lowest level of activities and the cost of these activities.
Show the cost equation of fixed and variable cost with the overhead cost:
Thus, the cost equation is
Working note 1:
Calculate the fixed cost:
Calculate the highest and lowest activity:
| Particular | Cases | Cost |
| Highest activity | 432,000 | $6,362,255 |
| Lowest activity | 345,000 | $5,699,139 |
Table: (2)
Working note 2:
Calculate the variable cost (unit) with the help of high-low cost method:
Working note 3:
Calculate the variable cost ($) with the help of high-low cost method:
c.
Prepare an estimate of operating costs assuming that 450,000 cases will be shipped next month by using the results of a simple regression of operating costs on cases shipped.
Explanation of Solution
Regression analysis:
Regression analysis is used to show the relationship between the cost and the activity. It is used to estimate the cost at various level of activity.
The most important step in the calculation of regression analysis is to establish a logical relationship between the cost and the activity. The activity (independent variable) is placed on the right-hand side and the cost (dependent variable) is placed on the left-hand side of the graph.
Calculate the regression analysis to compute the cost equation:
| Regression Statistics | ||||||||
| Multiple R | 0.980345 | |||||||
| R Square | 0.961076 | |||||||
| Adjusted R Square | 0.957184 | |||||||
| Standard Error | 39850.14 | |||||||
| Observations | 12 | |||||||
| ANOVA | ||||||||
| Df | SS | MS | F | Significance F | ||||
| Regression | 1 | 3.92E+11 | 3.92E+11 | 246.9132 | 2.24E-08 | |||
| Residual | 10 | 1.59E+10 | 1.59E+09 | |||||
| Total | 11 | 4.08E+11 | ||||||
| Coefficients | Standard Error | t Stat | P-value | Lower 95% | Upper 95% | Lower 95.0% | Upper 95.0% | |
| Intercept | 3411468 | 166203 | 20.52591 | 1.66E-09 | 3041145 | 3781791 | 3041145 | 3781791 |
| X Variable 1 | 6.707649 | 0.426873 | 15.71347 | 2.24E-08 | 5.756518 | 7.658781 | 5.756518 | 7.658781 |
Table: (3)
The regression analysis of the company provides the following details:
Calculate the cost equation:
Put the values in the cost equation:
Thus, the operating cost equation is:
d.
Prepare an estimate of operating costs assuming that 450,000 cases will be shipped next month by using the results of multiple regression of operating costs on cases shipped and the price level.
Explanation of Solution
Regression analysis:
Regression analysis is used to show the relationship between the cost and the activity. It is used to estimate the cost at various level of activity.
The most important step in the calculation of regression analysis is to establish a logical relationship between the cost and the activity. The activity (independent variable) is placed on the right-hand side, and the cost (dependent variable) is placed on the left-hand side of the graph.
| SUMMARY OUTPUT | ||||||||
| Regression Statistics | ||||||||
| Multiple R | 0.990475 | |||||||
| R Square | 0.981042 | |||||||
| Adjusted R Square | 0.976829 | |||||||
| Standard Error | 29315.83 | |||||||
| Observations | 12 | |||||||
| ANOVA | ||||||||
| df | SS | MS | F | Significance F | ||||
| Regression | 2 | 4E+11 | 2E+11 | 232.8623 | 1.78E-08 | |||
| Residual | 9 | 7.73E+09 | 8.59E+08 | |||||
| Total | 11 | 4.08E+11 | ||||||
| Coefficients | Standard Error | t Stat | P-value | Lower 95% | Upper 95% | Lower 95.0% | Upper 95.0% | |
| Intercept | 3176995 | 144048.2 | 22.05509 | 3.83E-09 | 2851136 | 3502855 | 2851136 | 3502855 |
| X Variable 1 | 8857.728 | 2877.157 | 3.078639 | 0.013169 | 2349.147 | 15366.31 | 2349.147 | 15366.31 |
| X Variable 2 | 4.418915 | 0.807028 | 5.475543 | 0.000392 | 2.593292 | 6.244539 | 2.593292 | 6.244539 |
Table: (4)
The regression analysis of the company provides the following details:
Calculate the cost equation:
Put the values in the cost equation:
Thus, the operating cost equation is
e.
Make a recommendation to the managers about the most appropriate estimate given the circumstances.
Explanation of Solution
Recommendation to the manager:
The multiple regressions seem to be more useful as per the adjusted R2. But the inclusion of price index may not be dependent on the cost of the product instead on the growth of the business. So correlating the price with the cost will not be very useful.
Simple regression is easy to compute, and it shows the clear relationship between the cost and the revenue so it should be considered for the cost estimation.
Thus, management should consider the simple regression for the cost estimation.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF COST ACCOUNTING
- Aldovar Company produces a variety of chemicals. One division makes reagents for laboratories. The divisions projected income statement for the coming year is: Required: 1. Compute the contribution margin per unit, and calculate the break-even point in units. (Note: Round answer to the nearest unit.) Calculate the contribution margin ratio and use it to calculate the break-even sales revenue. (Note: Round contribution margin ratio to four decimal places, and round the break-even sales revenue to the nearest dollar.) 2. The divisional manager has decided to increase the advertising budget by 250,000. This will increase sales revenues by 1 million. By how much will operating income increase or decrease as a result of this action? 3. Suppose sales revenues exceed the estimated amount on the income statement by 1,500,000. Without preparing a new income statement, by how much are profits underestimated? 4. Compute the margin of safety based on the original income statement. 5. Compute the degree of operating leverage based on the original income statement. If sales revenues are 8% greater than expected, what is the percentage increase in operating income? (Note: Round operating leverage to two decimal places.)arrow_forwardDecision on accepting additional business A manager of Varden Sporting Goods Company is considering accepting an order from an overseas customer. This customer has requested an order for 20,000 dozen golf balls at a price of 22 per dozen. The variable cost to manufacture a dozen golf balls is 18 per dozen. The full cost is 25 per dozen. Varden has a normal selling price of 35 per dozen. Vardens plant has just enough excess capacity on the second shift to make the overseas order. What are some considerations in accepting or rejecting this order?arrow_forwardKatayama Company produces a variety of products. One division makes neoprene wetsuits. The divisions projected income statement for the coming year is as follows: Required: 1. Compute the contribution margin per unit, and calculate the break-even point in units. Repeat, using the contribution margin ratio. 2. The divisional manager has decided to increase the advertising budget by 140,000 and cut the average selling price to 200. These actions will increase sales revenues by 1 million. Will this improve the divisions financial situation? Prepare a new income statement to support your answer. 3. Suppose sales revenues exceed the estimated amount on the income statement by 612,000. Without preparing a new income statement, determine by how much profits are underestimated. 4. How many units must be sold to earn an after-tax profit of 1.254 million? Assume a tax rate of 34 percent. (Round your answer up to the next whole unit.) 5. Compute the margin of safety in dollars based on the given income statement. 6. Compute the operating leverage based on the given income statement. (Round to three significant digits.) If sales revenues are 20 percent greater than expected, what is the percentage increase in profits?arrow_forward
- Refer to Cornerstone Exercise 3.4 for data on Dohini Manufacturing Companys purchasing cost and number of purchase orders. The controller for Dohini Manufacturing ran regression on the data, and the coefficients shown by the regression program are: Required: 1. Construct the cost formula for the purchasing activity showing the fixed cost and the variable rate. 2. If Dohini Manufacturing Company estimates that next month will have 430 purchase orders, what is the total estimated purchasing cost for that month? (Round your answer to the nearest dollar.) 3. What if Dohini Manufacturing wants to estimate purchasing cost for the coming year and expects 5,340 purchase orders? What will estimated total purchasing cost be? (Round your answer to the nearest dollar.) What is the total fixed purchasing cost? Why doesnt it equal the fixed cost calculated in Requirement 1?arrow_forwardBolger and Co. manufactures large gaskets for the turbine industry. Bolgers per-unit sales price and variable costs for the current year are as follows: Bolgers total fixed costs aggregate to 360,000. Bolgers labor agreement is expiring at the end of the year, and management is concerned about the effects of a new labor agreement on its break-even point in units. The controller performed a sensitivity analysis to ascertain the estimated effect of a 10-per-unit direct labor increase and a 10,000 reduction in fixed costs. Based on these data, the break-even point would: a. decrease by 1,000 units. b. decrease by 125 units. c. increase by 375 units. d. increase by 500 units.arrow_forwardCost Classification, Income Statement Gateway Construction Company, run by Jack Gateway, employs 25 to 30 people as subcontractors for laying gas, water, and sewage pipelines. Most of Gateways work comes from contracts with city and state agencies in Nebraska. The companys sales volume averages 3 million, and profits vary between 0 and 10% of sales. Sales and profits have been somewhat below average for the past 3 years due to a recession and intense competition. Because of this competition, Jack constantly reviews the prices that other companies bid for jobs. When a bid is lost, he analyzes the reasons for the differences between his bid and that of his competitors and uses this information to increase the competitiveness of future bids. Jack believes that Gateways current accounting system is deficient. Currently, all expenses are simply deducted from revenues to arrive at operating income. No effort is made to distinguish among the costs of laying pipe, obtaining contracts, and administering the company. Yet all bids are based on the costs of laying pipe. With these thoughts in mind, Jack looked more carefully at the income statement for the previous year (see below). First, he noted that jobs were priced on the basis of equipment hours, with an average price of 165 per equipment hour. However, when it came to classifying and assigning costs, he needed some help. One thing that really puzzled him was how to classify his own 114,000 salary. About half of his time was spent in bidding and securing contracts, and the other half was spent in general administrative matters. Required: 1. Classify the costs in the income statement as (1) costs of laying pipe (production costs), (2) costs of securing contracts (selling costs), or (3) costs of general administration. For production costs, identify direct materials, direct labor, and overhead costs. The company never has significant work in process (most jobs are started and completed within a day). 2. Assume that a significant driver is equipment hours. Identify the expenses that would likely be traced to jobs using this driver. Explain why you feel these costs are traceable using equipment hours. What is the cost per equipment hour for these traceable costs?arrow_forward
- The controller for Dohini Manufacturing Company felt that the number of purchase orders alone did not explain the monthly purchasing cost. He knew that nonstandard orders (for example, one requiring an overseas supplier) took more time and effort. He collected data on the number of nonstandard orders for the past 12 months and added that information to the data on purchasing cost and total number of purchase orders. Multiple regression was run on the above data; the coefficients shown by the regression program are: Required: 1. Construct the cost formula for the purchasing activity showing the fixed cost and the variable rate. 2. If Dohini Manufacturing Company estimates that next month will have 430 total purchase orders and 45 nonstandard orders, what is the total estimated purchasing cost for that month? (Round your answer to the nearest dollar.) 3. What if Dohini Manufacturing wants to estimate purchasing cost for the coming year and expects 5,340 purchase orders and 580 nonstandard orders? What will estimated total purchasing cost be? What is the total fixed purchasing cost? Why doesnt it equal the fixed cost calculated in Requirement 2? (Round your answers to the nearest dollar.)arrow_forwardA company has prepared the following statistics regarding its production and sales at different capacity levels. Total costs: 1. At what point is break-even reached in sales dollars? In units? (Hint: Use the capacity level to determine the number of units.) 2. If the company is operating at 60% capacity, should it accept an offer from a customer to buy 10,000 units at 3 per unit?arrow_forwardIncome Statements under Absorption and Variable Costing In the coming year, Kalling Company expects to sell 28,700 units at 32 each. Kallings controller provided the following information for the coming year: Required: 1. Calculate the cost of one unit of product under absorption costing. 2. Calculate the cost of one unit of product under variable costing. 3. Calculate operating income under absorption costing for next year. 4. Calculate operating income under variable costing for next year.arrow_forward
- Total cost method of product pricing Based on the data presented in Exercise 17, assume that Smart Stream Inc. uses the total cost method of applying the cost-plus approach to product pricing. A. Determine the total costs and the total cost amount per unit for the production and sale of 10,000 cellular phones. B. Determine the total cost markup percentage (rounded to two decimal places) for cellular phones. C. Determine the selling price of cellular phones. (Round markup to the nearest dollar.)arrow_forwardVariable-Costing and Absorption-Costing Income Borques Company produces and sells wooden pallets that are used for moving and stacking materials. The operating costs for the past year were as follows: During the year, Borques produced 200,000 wooden pallets and sold 204,300 at 9 each. Borques had 8,200 pallets in beginning finished goods inventory; costs have not changed from last year to this year. An actual costing system is used for product costing. Required: 1. What is the per-unit inventory cost that is acceptable for reporting on Borquess balance sheet at the end of the year ? How many units are in ending inventory? What is the total cost of ending inventory? 2. Calculate absorption-costing operating income. 3. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION What would the per-unit inventory cost be under variable costing? Does this differ from the unit cost computed in Requirement 1? Why? 4. Calculate variable-costing operating income. 5. Suppose that Borques Company had sold 196,700 pallets during the year. What would absorption-costing operating income have been? Variable-costing operating income?arrow_forwardA new product is being designed by an engineering team at Golem Security. Several managers and employees from the cost accounting department and the marketing department are also on the team to evaluate the product and determine the cost using a target costing methodology. An analysis of similar products on the market suggests a price of $132.00 per unit. The company requires a profit of 0.20 of selling price. How much is the target cost per unit? Round to two decimal places.arrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





