
Concept explainers
A large sheet has charge density
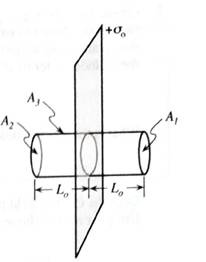
1. On the diagram at right indicate the location of the charge enclosed by the Gaussian cylinder.
In terms of
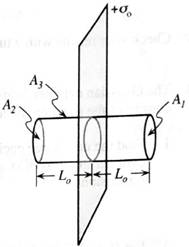
2. Sketch the electric field lines on both sides of the sheet.
Does the Gaussian cylinder affect the field lines or the charge distribution? Explain.
3. Let
How do the magnitudes of
How do the magnitudes of the areas of the ends of the Gaussian surface compare?
4. Through which of the surfaces
Write an expression for the net electric flux
Use the relationships between the electric fields
5. Gauss’ law
What is the electric field at the left end of the cylinder?
Does the electric field near a large sheet of charge depend on the distance from the sheet? Use your results above to justify your answer.
Is your answer consistent with the electric field lines you sketched in part 2?
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 5 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (4th Edition)
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Applied Physics (11th Edition)
The Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals (2nd Edition)
- Examine the summary on page 780. Why are conductors and charged sources with linear symmetry, spherical symmetry, and planar symmetry categorized as special cases rather than major concepts or underlying principles?arrow_forwardA disk of radius 0.10 m is oriented with its normal vector n at 30 degrees to a unform electric field E vector of a magnitude of 2.0x10^3 N/C. What is the electric flux through the disk? (Provide the complete details for the Illustrated Diagram - inside the box, Given, Required, Equation, Solution, and Answer)arrow_forwardA thin rod is bent into a circular arc that subtends an angle 2θ of a circle centered at P. A total charge, Q, is distributed uniformly over the full rod. Let the positive x direction be towards the right of the page, and the positive y direction is towards the top of the page. In Cartesian unit-vector format, what is the electric field at P?arrow_forward
- A solid ball of radius rb has a uniform charge density ρ. What is the magnitude of the electric field E(r)E( at a distance r>rb from the center of the ball? What is the magnitude of the electric field E(E(r) at a distance r<rb from the center of the ball? Let E(r) represent the electric field due to the charged ball throughout all of space. Which of the following statements about the electric field are true?arrow_forwardA solid conducting sphere of radius R has a uniform charge distribution, with a density = Ps * r / R where Ps is a constant and r the distance from the center of the sphere. Prove a) the total charge on the sphere is Q = πPsR ^ 3 b) the electric field of the sphere is given by E = (1 / 4πε0) * (Q / R ^ 4) * (r ^ 2)arrow_forwardAn infinitely long conducting cylindrical rod with a positive charge λ per unit length is surrounded by a conducting cylindrical shell (which is also infinitely long) with a charge per unit length of −2λ and radius r1, as shown in the figure. A) What is E(r), the radial component of the electric field between the rod and cylindrical shell as a function of the distance r from the axis of the cylindrical rod? Express your answer in terms of λ, r, and ϵ0 the permittivity of free space. B) What is σ inner, the surface charge density (charge per unit area) on the inner surface of the conducting shell? C) What is σ outer, the surface charge density on the outside of the conducting shell? (Recall from the problem statement that the conducting shell has a total charge per unit length given by −2λ D) What is the radial component of the electric field, E(r), outside the shell?arrow_forward
- A cylinder of diameter 1.72 m is in a region where the electric field is as shown in the figure below. If E1 = 38.0 N/C and E2 = 20.1 N/C, what is the net flux through the two end faces of the cylinder? Note that the diagram is not to scale. N · m2/Carrow_forwardConsider two thin disks, of negligible thickness, of radius R oriented perpendicular to the x axis such that the x axis runs through the center of each disk. The disk centered at x=0 has positive charge density η, and the disk centered at x=a has negative charge density −η, where the charge density is charge per unit area. What is the magnitude E of the electric field at the point on the x axis with x coordinate a/2? Express your answer in terms of η, R, a, and the permittivity of free space ϵ0.arrow_forwardA conducting sphere of radiusais placed at the origin surrounded by a spherical conductingshell of inner radiusband outer radiusc. The sphere carries a charge of−3Qwhile the outershell is charged to 2Q. Use Gauss Law to find E of the following: c) inside the shell (b < r < c) d) outside the shell (r > c)arrow_forward
- A cylinder of diameter 1.72 m is in a region where the electric field is as shown in the figure below. If E1 = 42.4 N/C and E2 = 23.1 N/C, what is the net flux through the two end faces of the cylinder? Note that the diagram is not to scale.arrow_forwardA charge of 87.6 pCpC is uniformly distributed on the surface of a thin sheet of insulating material that has a total area of 47.2 cm2cm2. A Gaussian surface encloses a portion of the sheet of charge. If the flux through the Gaussian surface is 5.70 N⋅m2/CN⋅m2/C, what area of the sheet is enclosed by the Gaussian surface? Express your answer with the appropriate units.arrow_forwardA slab of insulating material has thickness 2d and is oriented so that its faces are parallel to the yz-plane and given by the planes x=d and x=−d . The y- and z-dimensions of the slab are very large compared to d and may be treated as essentially infinite. The slab has a uniform positive charge density ρ . Part B Using Gauss's law, find the magnitude of the electric field due to the slab at the points 0≤x ≤d . Express your answer in terms of the variables ρ , x , d , and ϵ 0 . Part C What is the direction of the electric field due to the slab at the points 0≤x ≤d ? What is the direction of the electric field due to the slab at the points ? Part D Using Gauss's law, find the magnitude of the electric field due to the slab at the points x≥d . Express your answer in terms of the variables ρ , x , d , and ϵ 0 . Part E What is the direction of the electric field due to the slab at the points x≥d ?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
