
Concept explainers
Alternative cost flows
Montoure Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following calendar-year purchases and sales transactions. (For specific identification, units sold consists of 600 units from beginning inventory, 300 from the February 10 purchase, 200 from the March 13 purchase, 50 from the August 21 purchase, and 250 from the September 5 purchase.)
| Date | Activities | Units Acquired at Cost | Units Sold at Retail |
| Jan. 1 | Beginning inventory..... | 600 units @ $45.00 per unit | |
| Feb. 10 | Purchase.................... | 400 units @ $42.00 per unit | |
| Mar. 13 | Purchase.................... | 200 units @ $27.00 per unit | |
| Mar. 15 | Sales....................... | 800 units @ $ 75.00 per unit | |
| Aug. 21 | Purchase................. | 100 units @ $50.00 per unit | |
| Sep. 5 | Purchase.................... | 500 units @ $46.00 per unit | |
| Sep.10 | Sales....................... | 600 units @ $75.00 per unit | |
| Total....................... | 1,800 units | 1,400 units |
Required
- 1. Compute cost of goods available for sale and the number of units available for sale.
- 2. Compute the number of units in ending inventory.
- 3. Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, (c) weighted average, and (d) specific identification (Round all amounts to cents.)
- 4. Compute gross profit earned by the company for each of the four costing methods in part 3.
- 5. If the company’s manager earns a bonus based on a percent of gross profit, which method of inventory costing will the manager likely prefer?
1.
Ascertain the cost of goods available for sale, and the number of units available for sales.
Explanation of Solution
Ascertain the cost of goods available for sale, and the number of units available for sales as follows:
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Beginning balance | 600 | 45 | 27,000 |
| Add: Purchases | |||
| February 10 | 400 | 42 | 16,800 |
| March 13 | 200 | 27 | 5,400 |
| August 21 | 100 | 50 | 5,000 |
| September 5 | 500 | 46 | 23,000 |
| Total Goods available for Sale | 1,800 | 77,200 |
Table (1)
Therefore, the number of units available for sales is 1,800 units, and the cost of goods available for sale is $77,200.
2.
Ascertain the number of units in ending inventory.
Explanation of Solution
Ascertain the number of units in ending inventory as follows:
| Details | Number of Units |
| Total Goods available for Sale | 1,800 |
| Less: Sales: | |
| March 15 | 800 |
| September 10 | 600 |
| Ending Inventory | 400 |
Table (2)
Therefore, the number of units in ending inventory is 400.
3.
Ascertain the cost assigned to ending inventory under (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, (c) weighted average, and (d) specific identification.
Explanation of Solution
Perpetual inventory system: The method or system of maintaining, recording, and adjusting the inventory perpetually throughout the year, is referred to as perpetual inventory system.
First-in-First-Out (FIFO): In this method, items purchased initially are sold first. So, the value of the ending inventory consist the recent cost for the remaining unsold items.
Last-in-First-Out (LIFO): In this method, items purchased recently are sold first. So, the value of the ending inventory consist the initial cost for the remaining unsold items.
Weighted-average Cost Method: In this method, the inventories are priced at the average rate of goods available for sales.
Specific identification method: Specific identification method identifies the cost of each item in ending inventory by separating purchases. In this method, the value of ending inventory is computed based on the lower of cost or market value.
Ascertain the cost assigned to ending inventory under (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, (c) weighted average, and (d) specific identification as follows:
(a) FIFO
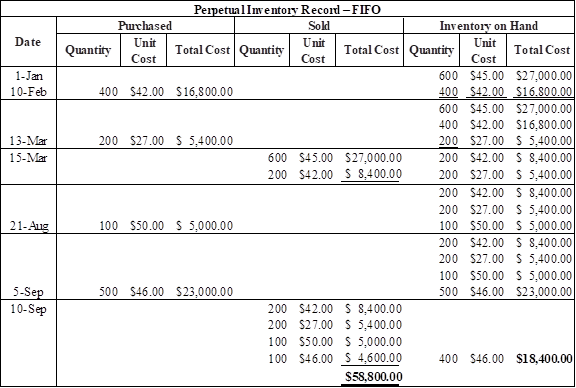
Table (3)
Therefore, the cost of ending inventory under FIFO is $18,400.
(b) LIFO

Table (4)
Therefore, the cost of ending inventory under LIFO is $18,000.
(c) Weighted average method:
Refer working note 1 and 2 for calculation of weighted average cost

Table (5)
Therefore, the cost of ending inventory under weighed average method is $17,760.
Working note:
Calculate the weighted average cost of inventory after March 13purchase
Calculate the weighted average cost of inventory after September 5 purchase
(d) Specific identification method:
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Cost of goods available for sale (refer table 1) | 77,200 | ||
| Less: Cost of goods sold | |||
| Beginning inventory | 600 | 45 | 27,000 |
| February 10 | 300 | 42 | 12,600 |
| March 13 | 200 | 27 | 5,400 |
| August 21 | 50 | 50 | 2,500 |
| September 5 | 250 | 46 | 11,500 |
| Ending inventory | 18,200 |
Table (6)
Therefore, the cost of ending inventory under specific identification method is $18,200.
4.
Ascertain the gross profit earned by the company for the each of the given methods.
Explanation of Solution
Ascertain the gross profit earned by the company for the each of the given methods as follows:
| Particulars | FIFO | LIFO | Specific Identification | Weighted Average |
| Sales | $ 105,000 | $ 105,000 | $105,000 | $ 105,000 |
| Less: Cost of goods sold | $ 58,800 | $ 59,200 | $ 59,000 | $ 59,440 |
| Gross profit | $ 46,200 | $ 45,800 | $46,000 | $ 45,560 |
Table (7)
5.
Identify the inventory method which is preferred by the manager, if company’s manger earns a bonus based on a percent of gross profit.
Explanation of Solution
Identify the inventory method which is preferred by the manager, if company’s manger earns a bonus based on a percent of gross profit as follows:
In this case, gross profit under FIFO method ($46,200) is more than the other three methods. Hence, the manager of Company would likely to prefer the FIFO method.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Principles of Financial Accounting.
- Inventory Costing Methods VanderMeer Inc. reported the following information for the month of February: During February, VanderMeer sold 140 units. The company uses a periodic inventory system. Required What is the value of ending inventory and cost of goods sold for February under the following assumptions: Of the 140 units sold, 55 cost $20, 35 cost $22, 45 cost $23, and 5 cost $24. FIFO LIFO Weighted averagearrow_forwardComparison of Inventory Costing Methods—Periodic System Bitten Companys inventory records show 600 units on hand on October 1 with a unit cost of $5 each. The following transactions occurred during the month of October: All expenses other than cost of goods sold amount to $3,000 for the month. The company uses an estimated tax rate of 30% to accrue monthly income taxes. Required Prepare a chart comparing cost of goods sold and ending inventory using the periodic system and the following costing methods: What does the Total column represent? Prepare income statements for each of the three methods. Will the company pay more or less tax if it uses FIFO rather than LIFO? How much more or less?arrow_forwardInventory Costing Methods Crandall Distributors uses a perpetual inventory system and has the following data available for inventory, purchases, and sales for a recent year. Required: 1. Compute the cost of ending inventory and the cost of goods sold using the specific identification method. Assume the ending inventory is made up of 40 units from beginning inventory, 30 units from Purchase 1, 80 units from Purchase 2, and 40 units from Purchase 3. 2. Compute the cost of ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the FIFO inventory costing method. 3. Compute the cost of ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the LIFO inventory costing method. 4. Compute the cost of ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the average cost inventory costing method. ( Note: Use four decimal places for per-unit calculations and round all other numbers to the nearest dollar.) 5. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Compare the ending inventory and cost of goods sold computed under all four methods. What can you conclude about the effects of the inventory costing methods on the balance sheet and the income statement?arrow_forward
- LIFO perpetual inventory The beginning inventory for Dunne Co. and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period are shown in Problem 6-1B. Instructions 1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of goods sold data in a perpetual inventory record similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 4, using the last-in, first-out method. 2. Determine the total sales, the total cost of goods sold, and the gross profit from sales for the period. 3. Determine the ending inventory cost on June 30.arrow_forwardCOST ALLOCATION AND LOWER-OF-COST-OR-MARKET Hall Companys beginning inventory and purchases during the fiscal year ended December 31, 20--, were as follows: There are 1,100 units of inventory on hand on December 31. REQUIRED 1. Calculate the total amount to be assigned to the ending inventory and cost of goods sold on December 31 under each of the following methods: (a) FIFO (b) LIFO (c) Weighted-average (round calculations to two decimal places) 2. Assume that the market price per unit (cost to replace) of Halls inventory on December 31 was 16. Calculate the total amount to be assigned to the ending inventory on December 31 under each of the following methods: (a) FIFO lower-of-cost-or-market (b) Weighted-average lower-of-cost-or-market 3. Prepare required entries to apply: (a) FIFO lower-of-cost-or-market (b) Weighted-average lower-of-cost-or-marketarrow_forwardCommunication Golden Eagle Company began operations on April 1 by selling a single product. Data on purchases and sales for the year are as follows: Purchases: Sales: The president of the company, Connie Kilmer, has asked for your advice on which inventory cost flow method should be used for the 32,000-unit physical inventory that was taken on December 31. The company plans to expand its product line in the future and uses the periodic inventory system. Write a brief memo to Ms. Kilmer comparing and contrasting the LIFO and FIFO inventory cost flow methods and their potential impacts on the companys financial statements.arrow_forward
- Alternative Inventory Methods Park Companys perpetual inventory records indicate the following transactions in the month of June: Required: 1. Compute the cost of goods sold for June and the inventory at the end of June using each of the following cost flow assumptions: a. FIFO b. LIFO c. Average cost (Round unit costs to 3 decimal places and other amounts to the nearest dollar.) 2. Next Level Why are the cost of goods sold and ending inventory amounts different for each of the three methods? What do these amounts tell us about the purchase price of inventory during the year? 3. Next Level Which method produces the most realistic amount for net income? For inventory? Explain your answer. 4. Next Level If Park uses IFRS, which of the previous alternatives would be acceptable and why?arrow_forwardCalculate the cost of goods sold dollar value for A65 Company for the month, considering the following transactions under three different cost allocation methods and using perpetual inventory updating. Provide calculations for first-in, first-out (FIFO).arrow_forwardInventory Costing Methods On June 1, Welding Products Company had a beginning inventory of 210 cases of welding rods that had been purchased for S88 per case. Welding Products purchased 1,150 cases at a cost of $95 per case on June 3. On June 19, the company purchased another 950 cases at a cost of $112 per case. Sales data for the welding rods are: Welding Products uses a perpetual inventory system, and the sales price of the welding rods was $130 per case. Required: 1. Compute the cost of ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the FIFO method. 2. Compute the cost of ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the LIFO method. 3. Compute the cost of ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the average cost method. ( Note: Use four decimal places for per-unit calculations and round all other numbers to the nearest dollar.) 4. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Assume that operating expenses are $21,600 and Welding Products has a 30% tax rate. How much will the cash paid for income taxes differ among the three inventory methods? 5. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Compute Welding Products' gross profit ratio (rounded to two decimal places) and inventory turnover ratio (rounded to three decimal places) under each of the three inventory costing methods. How would the choice of inventory costing method affect these ratios?arrow_forward
- On January 1 of Year 1, Dorso Company adopted the dollar-value LIFO method of inventory costing. Dorsos December 31 ending inventory records are as follows: Year 1: Current cost, 20,000; Index, 100 Year 2: Current cost, 33,600; Index, 120 Using the dollar-value LIFO method, compute Dorsos December 31 ending inventory for Year 2.arrow_forwardFIFO perpetual inventory The beginning inventory at Dunne Co. and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period ending June 30 are as follows: Instructions 1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of goods sold data in a perpetual inventory record similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 3, using the first-in, first-out method. 2. Determine the total sales and the total cost of goods sold for the period. Journalize the entries in the sales and cost of goods sold accounts. Assume that all sales were on account. 3. Determine the gross profit from sales for the period. 4. Determine the ending inventory cost on June 30. 5. Based upon the preceding data, would you expect the ending inventory using the last-in, first-out method to be higher or lower?arrow_forwardCalculate the cost of goods sold dollar value for B74 Company for the sale on November 20, considering the following transactions under three different cost allocation methods and using perpetual inventory updating. Provide calculations for (a) first-in, first-out (FIFO); (b) last-in, first-out (LIFO); and (c) weighted average (AVG).arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





