
Concept explainers
- (a) Water flows through a shower head steadily at a rate of 10 L/min. An electric resistance heater placed in the water pipe heats the water from 16 to 43°C. Taking the density of water to be 1 kg/L, determine the electric power input to the heater in kW and the rate of entropy generation during this process in kW/K.
FIGURE P7–209
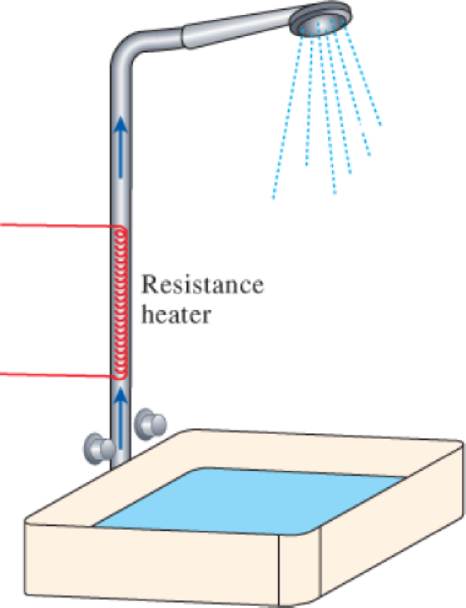
- (b) In an effort to conserve energy, it is proposed to pass the drained warm water at a temperature of 39°C through a heat exchanger to preheat the incoming cold water. If the heat exchanger has an effectiveness of 0.50 (that is, it recovers only half of the energy that can possibly be transferred from the drained water to incoming cold water), determine the electric power input required in this case and the reduction in the rate of entropy generation in the resistance heating section.
a)
The electric power input to the heater and the rate of entropy generation during the process.
Answer to Problem 209RP
The electric power input to the heater is
The rate of entropy generation during the process is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the energy balance of steady flow system.
Here, rate of net energy transfer in to the control volume is
Write the expression to calculate the mass flow rate
Here, density of water at room temperature is
Write the expression for the entropy balance equation of the system for steady flow process.
Here, rate of net entropy in is
Conclusion:
There is only one exit and one inlet, write the equation for the mass balance of steady flow system as,
Here, mass flow rate of water at inlet is
The rate of change in internal energy of system inside the system is zero at steady state,
Substitute 0 for
Here, electric power input to the heater is
From Table A-3 “Properties of common liquids, solids and foods”, the value for the density
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the electric power input to the heater is
Substitute
Since, water is incompressible substance,
Here, rate of entropy generation at stage 1 is
Substitute
Thus, the rate of entropy generation during the process is
b)
The electric power input required and the reduction in the rate of entropy generation in the resistance heating section.
Answer to Problem 209RP
The electric power input required is
The reduction in the rate of entropy generation in the resistance heating section is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression to calculate the energy saved
Here, effectiveness of heat exchanger is
Write the expression to calculate the required electric power
Here, electric power input to the heater is
Write the expression to calculate the temperature at which the cold water leaves heat exchanger.
Here, the energy saved is
Write the expression to calulate the entropy generation at stage 2.
Here, rate of entropy generation at stage 2 is
Write the expression to calculate the reduction in the rate of entropy generation within the heating section
Here, reduction in the rate of entropy generation is
Conclusion:
Substitute 0.5 for
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the reduction in the rate of entropy generation in the resistance heating section is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
- Refrigerant-134a enters a compressor as a saturated vapor at 160 kPa at a rate of 0.03 m3 /s and leaves at 800 kPa. The power input to the compressor is 10 kW. If the surroundings at 20°C experience an entropy increase of 0.008 kW/K, determine the exit temperature of the refrigerant.arrow_forwardRefrigerant-134a at 140 kPa and –10°C is compressed by an adiabatic 1.3-kW compressor to an exit state of 700 kPa and 60°C. Neglecting the changes in kinetic and potential energies, determine the volume flow rate of the refrigerant at the compressor inlet in L/min.arrow_forwardSteam flows steadily through an adiabatic turbine. The inlet conditions of the steam are 10MPa, 400°C, and 100 m/s, and the exit conditions are 10 kPa, 88 percent quality, and 50m/s. The mass flow rate of the steam is 18 kg/s. Determine (a) the change in kinetic energy,(b) the power output, and (c) the turbine inlet area.arrow_forward
- Steam enters a turbine steadily at 7 MPa and 600°C with a velocity of 60 m/s and leaves at 25 kPa with a quality of 95 percent. A heat loss of 20 kJ/kg occurs during the process. The inlet area of the turbine is 150 cm2 , and the exit area is 1400 cm2. Determine the power output.arrow_forwardWater flows through a shower head steadily at a rate of 10 L/min. An electric resistance heater placed in the water pipe heats the water from 16 to 43°C. Taking the density of water to be 1 kg/L, determine the electric power input to the heater in kW and the rate of entropy generation during this process in kW/K.arrow_forwardRefrigerant-134a enters a compressor as a saturated vapor at 160 kPa at a rate of 0.03 m3 /s and leaves at 800 kPa. The power input to the compressor is 10 kW. If the surroundings at 20°C experience an entropy increase of 0.008 kW/K, determine the rate of heat loss from the compressor.arrow_forward
- Steam enters a turbine steadily at 7 MPa and 600°C with a velocity of 60 m/s and leaves at 25 kPa with a quality of 95 percent. A heat loss of 20 kJ/kg occurs during the process. The inlet area of the turbine is 150 cm2 , and the exit area is 1400 cm2. Determine the exit velocity.arrow_forwardSteam enters a turbine steadily at 7 MPa and 600°C with a velocity of 60 m/s and leaves at 25 kPa with a quality of 95 percent. A heat loss of 20 kJ/kg occurs during the process. The inlet area of the turbine is 150 cm2 , and the exit area is 1400 cm2. Determine the mass flow rate of the steam.arrow_forwardSteam enters a turbine steadily at a flow rate of 1 kg/s at 7 MPa and 500 degrees and exits as saturated steam at 40 kPa. If there is a heat loss of 10 kW from the turbine, what will be the power produced by the turbine?arrow_forward
- Steam enters a turbine steadily at 7 MPa and 600°C with a velocity of 60 m/s and leaves at 25 kPa with a quality of 95 percent. A heat loss of 20 kJ/kg occurs during the process. The inlet area of the turbine is 150 cm2, and the exit area is 1400 cm2. Determine (a) the mass flow rate of the steam, (b) the exit velocity, and (c) the power output.arrow_forwardThe exhaust nozzle of a jet engine expands air at 300 kPa and 180°C adiabatically to 100 kPa. Determine the air velocity at the exit when the inlet velocity is low and the nozzle isentropic efficiency is 93 percent.arrow_forwardAir enters a compressor at ambient conditions of 100 kPa and 20°C at a rate of 6.2 m3 /s with a low velocity and exits at 900 kPa, 60°C, and 80 m/s. The compressor is cooled by cooling water that experiences a temperature rise of 10°C. The isothermal efficiency of the compressor is 70 percent. Determine the mass flow rate of the cooling water.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





