
Concept explainers
The 10-ft cable AB is attached to two collars as shown. The collar at A can slide freely along the rod; a stop attached to the rod prevents the collar at B from moving on the rod. Neglecting the effect of friction and the weight of the collars, determine the distance a.
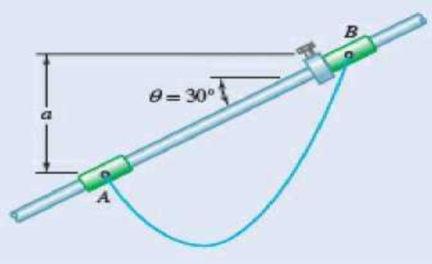
Fig. P7.147
Find the distance a.
Answer to Problem 7.147P
The distance a is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of the cable AB is
The value of angle
The collar at A is slides freely and the collar at B is prevented from the moving.
Calculation:
Show the free-body diagram of the cable assembly as in Figure 1.
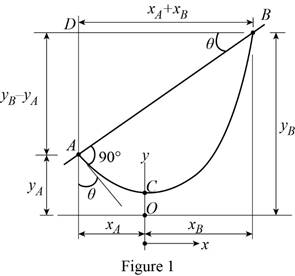
Refer the Equation 7.16 in the textbook.
Write the equation of the catenary cable as follows;
Differentiate the equation with x;
The slope at point A is;
The length of the portion AC is as follows:
The length of the portion CB is as follows:
Find the distance
Substitute 10 ft for L,
Find the distance
Find the distance
Consider the triangle ABD;
Find the value of
Find the distance a using the relation.
Use the trial and error procedure to find the value of a.
Consider the value of c and for the given value of
Trial 1:
Consider a trial value of 1.60 ft for c.
Substitute 1.60 ft for c and
Substitute 1.60 ft for c and 2.107 ft for
Substitute 1.60 ft for c and 2.107 ft for
Substitute 1.60 ft for c and 3.541 ft for
Substitute 2.107 ft for
The calculated value of
Trial 2:
Consider a trial value of 1.70 ft for c.
Substitute 1.70 ft for c and
Substitute 1.70 ft for c and 2.239 ft for
Substitute 1.70 ft for c and 2.239 ft for
Substitute 1.70 ft for c and 3.622 ft for
Substitute 2.239 ft for
The calculated value of
Trial 3:
Consider a trial value of 1.803 ft for c.
Substitute 1.803 ft for c and
Substitute 1.803 ft for c and 2.374 ft for
Substitute 1.803 ft for c and 2.374 ft for
Substitute 1.803 ft for c and 3.694 ft for
Substitute 2.374 ft for
The calculated value of
Therefore, the value of c is 1.803 ft.
Substitute 3.606 ft for
Therefore, the distance a is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
CE 99 STATICS-W/ACCESS (LL) >IP<
- A block with weight W is pulled up a plane forming an angle a with the horizontal by a force P directed along the plane. μ If is the coefficient of friction between the block and the plane, derive an expression for the mechanical efficiency of the system. Show that the mechanical efficiency cannot exceed 1/2 if the block is to remain in place when the force P is removed.arrow_forwardA thin circular rod is supported in a vertical plane by a bracket at A. Attached to the bracket and loosely wound around the rod is a spring of constant k= 3 lb/ft and undeformed length equal to the arc of circle AB. An 8-oz collar C , not attached to the spring, can slide without friction along the rod. Knowing that the collar is released from rest at an angle 0 with the vertical, determine (a) the smallest value of 0 for which the collar will pass through D and reach point A, (b) the velocity of the collar as it reaches point A.arrow_forwardFrom mechanics of materials, it is known that for a simply supported beam of uniform cross section, a static load P applied at the center will cause a deflection of δA=PL3/48 EI, where L is the length of the beam, E is the modulus of elasticity, and I is the moment of inertia of the cross-sectional area of the beam. Knowing that L = 15 ft, E = 30 × 106 psi, and I = 2 × 10 3ft4, determine (a) the equivalent spring constant of the beam, (b) the frequency of vibration of a 1500-lb block attached to the center of the beam. Neglect the mass of the beam and assume that the load remains in contact with the beam.arrow_forward
- A 20-m length of wire having a mass per unit length of 0.2 kg/m is attached to a fixed support at A and to a collar at B . Neglecting the effect of friction, determine (a) the sag h for which L = 15m, (b) the corresponding force P.arrow_forward(a) Determine the maximum allowable horizontal span for a uniform cable with a weight per unit length of w if the tension in the cable is not to exceed a given value Tm. (b) Using the result of part a , determine the maximum span of a steel wire for which w = 0.25 lb/ft and Tm = 8000 lb.arrow_forwardPin B weighs 0.1kg and is free to slide in a horizontal plane along therotating arm OC and along the circular slot DE of radius b=500mm.Neglecting friction and assuming that θ= 15 rad/s andθ=250 rad/s2 for the position θ= 20o , determine for that position(a) the radial and transverse components of the resultant forceexerted on pin B, (b) the forces P and Q exerted on pin B,respectively, by rod OC and the wall of slot DE.arrow_forward
- Three loads are applied as shown to a light beam supported by cables attached at B and D. Neglecting the weight of the beam, determine the range of values of Q for which neither cable becomes slack when P=0.arrow_forwardA counterweight D is attached to a cable that passes over a small pulley at A and is attached to a support at B . Knowing that L = 45 ft and h = 15 ft, determine (a) the length of the cable from A to B, (b) the weight per unit length of the cable. Neglect the weight of the cable from A to D.arrow_forwardShow that the curve assumed by a cable that carries a distributed load w(x) is defined by the differential equation d2y/dx2 = w(x)/t0, ehere T0 is the tension at the lowest point.arrow_forward
- A collar B with a weight of W can move freely along the vertical rod shown. The constant of the spring is k , and the spring is unstretched when 0 = 0. (a) Derive an equation in 0, w, k, and 1 that must be satisfied when the collar is in equilibrium. (b) Knowing that W = 300 N, 1 = 500 mm, and k = 800 N/m, determine the value of 0 corresponding to equilibrium.arrow_forwardA cable is placed around three parallel pipes. Two of the pipes are fixed and do not rotate; the third pipe is slowly rotated. Knowing that the coefficients of friction are μs= 0.25 and μk= 0.20, determine the largest weight W that can be raised (a) if only pipe A is rotated counterclockwise, (b) if only pipe C is rotated clockwise.arrow_forwardA small 250-g collar C can slide on a semicircular rod which is made to rotate about the vertical AB at a constant rate of 7.5 rad/s. Knowing that the coefficients of friction are μs = 0.25 and μk = 0.20, indicate whether the collar will slide on the rod if it is released in the position corresponding to (a) 0= 75°, (b) 0 = 40°. Also, determine the magnitude and direction of the friction force exerted on the collar immediately after release.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





