
Concept explainers
What reagents would you use to achieve each of the following transformations:

Interpretation:
Reagents that can be used to achieve the given transformation has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Amines react with nitrous acid to form diazonium salt. Nitrous acid is prepared in the reaction flask itself by the use of sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid. Nitrous acid is protonated to produce highly reactive intermediate known as nitrosonium ion. Nitrosonium ion when reacted with amine results in the formation of nitrosoamine.
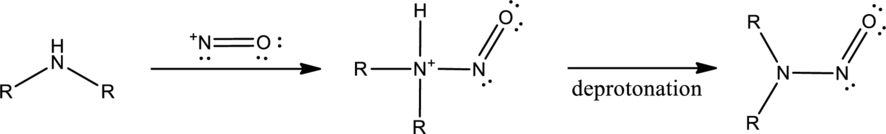
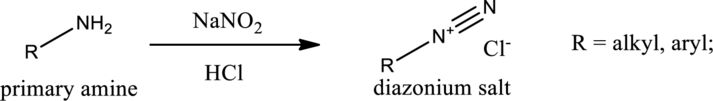
If a primary amine is considered, then tautomerization takes place resulting in formation of diazonium ion. This can be represented as,
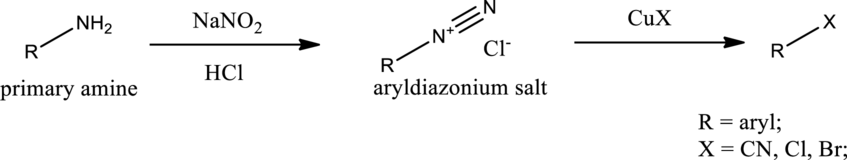
Sandmeyer reaction:
Aryldiazonium salt reacts with copper salts as reagent to obtain the required aryl halides, aryl cyanides etc. General scheme can be given as shown below,
Explanation of Solution
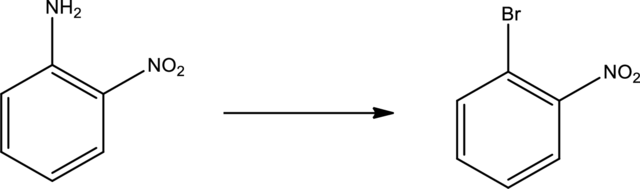
Given transformation is,
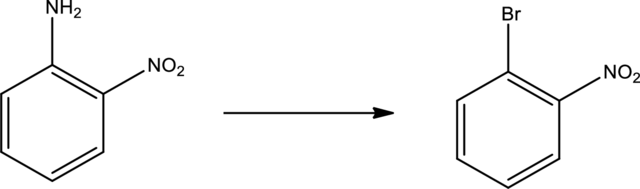
Product is an aryl halide while the starting material is an aryl amine. The route that can be used to accomplish the above reaction is the Sandmeyer reaction. In this the first step is the formation of aryl diazonium salt by the treatment of primary amine with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid. Second step is the treatment of aryldiazonium salt with copper bromide to form the aryl bromide.
The scheme can be given as shown below,
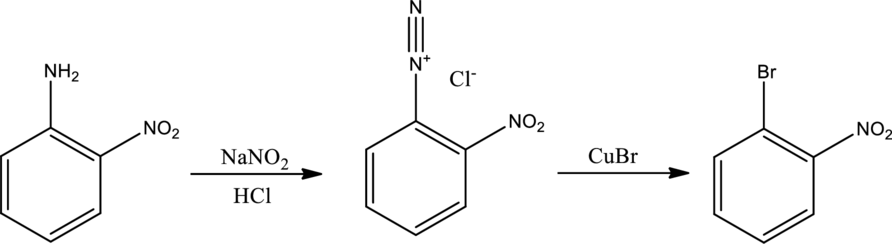
The reagents that are used are sodium nitrite with hydrochloric acid and copper(I) bromide.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry As a Second Language: Second Semester Topics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach
Chemistry: The Central Science (13th Edition)
Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Organic Chemistry (9th Edition)
General Chemistry: Atoms First
- Which reagent would best accomplish the following transformation?arrow_forwardHow would you carry out the following transformation? Tell what reagents you would use in each case.arrow_forwardUsing your reaction roadmap as a guide, show how to convert 3-hexyne into propanal. All of the carbon atoms of the target molecule must be derived from the starting material as efficiently as possible. Show all intermediate molecules synthesized along the way.arrow_forward
- Identify the reagents you would use to accomplish each of the following reactionsarrow_forwardPropose a suitable synthesis to accomplish the following transformations. Please give the reagents and products for every step. Do not just list the reagentsarrow_forwardProvide the reagents needed to accomplish the following transformationsarrow_forward
- What reagent would you use to accomplish the following reactions?arrow_forwardPropose a suitable synthesis to accomplish the following transformation. Please give the reagents and products for each step. Do not just list the reagents.arrow_forwardProvide the reagents necessary for the following synthetic transformations. More than one step may be requiredarrow_forward
- Using your reaction roadmap as a guide, show how to convert 2-methylbutane into racemic 3-bromo-2-methyl-2-butanol. Show all reagents and all molecules synthesized along the way.arrow_forwardUsing your reaction roadmap as a guide, show how to convert cyclohexanol into racemic trans-1,2-cydohexanediol. Show all required reagents and all molecules synthesized along the way.arrow_forwardWrite out the reagents and draw the intermediates necessary to achieve each transformation below. I need expert solutions and step by step answerarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
