
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Java
class Main {
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) {
/*
* Use this code to test your Hexagon class.
* Uncomment the items as you complete parts of the Hexagon class.
*/
Hexagon myHex = new Hexagon();
// Hexagon myOtherHex = new Hexagon(5);
// // print info about myHex
// System.out.println("Information about myHex");
// displayHex(myHex);
// System.out.println();
// // print info about myOtherHex
// System.out.println("Information about myOtherHex");
// displayHex(myOtherHex);
// System.out.println();
// myHex.setSide(3);
// // print info about myHex after changing side length
// System.out.println("Information about myHex with side length 3");
// displayHex(myHex);
}
publicstaticvoid displayHex(Hexagon h) {
// System.out.println("Side length: " + h.getSide());
// System.out.println("Perimeter: " + h.getPerimeter());
// System.out.println("Diagonal length: " + h.getDiagonalLength());
// System.out.println("Surface area: " + h.getArea());
}
}
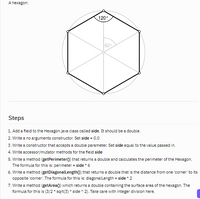
Transcribed Image Text:### A Hexagon
The image shows a hexagon inscribed in a circle. The hexagon's interior angles are 120°, and it is divided into six equilateral triangles. Each triangle has angles of 60°.
### Steps
1. **Add a field to the Hexagon.java class called `side`.**
- It should be a double.
2. **Write a no arguments constructor.**
- Set `side = 0.0`.
3. **Write a constructor that accepts a double parameter.**
- Set `side` equal to the value passed in.
4. **Write accessor/mutator methods for the field `side`.**
5. **Write a method (`getPerimeter()`) that returns a double and calculates the perimeter of the Hexagon.**
- The formula for this is: `perimeter = side * 6`
6. **Write a method (`getDiagonalLength()`) that returns a double that is the distance from one 'corner' to its opposite 'corner'.**
- The formula for this is: `diagonalLength = side * 2`
7. **Write a method (`getArea()`) which returns a double containing the surface area of the hexagon.**
- The formula for this is: `(3/2 * sqrt(3) * side ^ 2)`. Take care with integer division here.
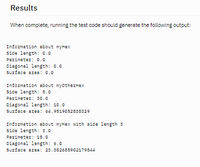
Transcribed Image Text:## Results
When complete, running the test code should generate the following output:
### Information about myHex
- **Side length:** 0.0
- **Perimeter:** 0.0
- **Diagonal length:** 0.0
- **Surface area:** 0.0
### Information about myOtherHex
- **Side length:** 5.0
- **Perimeter:** 30.0
- **Diagonal length:** 10.0
- **Surface area:** 64.9519052838329
### Information about myHex with side length 3
- **Side length:** 3.0
- **Perimeter:** 18.0
- **Diagonal length:** 6.0
- **Surface area:** 23.382685902179844
This text output provides detailed information about hexagonal dimensions, including side length, perimeter, diagonal length, and surface area for different hexagonal shapes.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- ... in javaarrow_forwardLab 9 C balance the same, y, n, why? class CheckingAct { . . . . private int balance; public void processCheck( int amount ) { int charge; if ( balance < 100000 ) charge = 15; else charge = 0; balance = balance - amount - charge ; // change the local copy of the value in "amount" amount = 0 ; } } public class CheckingTester { public static void main ( String[] args ) { CheckingAct act; int check = 5000; act = new CheckingAct( "123-345-99", "Your Name", 100000 ); System.out.println( "check:" + check ); // prints "5000" // call processCheck with a copy of the value 5000 act.processCheck( check ); System.out.println( "check:" + check ); // prints "5000" --- "check" was not changed } }arrow_forwardJavaarrow_forward
- 1 a. is the amount the same, yes or no, why? public class CheckingAct { private String actNum; private String nameOnAct; private int balance; . . . . public void processDeposit( int amount ) { balance = balance + amount ; } // modified toString() method public String toString() { return "Account: " + actNum + "\tName: " + nameOnAct + "\tBalance: " + amount ; } } b. public class CheckingAct { private String actNum; private String nameOnAct; private int balance; . . . . public void processDeposit( int amount ) { // scope of amount starts here balance = balance + amount ; // scope of amount ends here } public void processCheck( int amount ) { // scope of amount starts here int charge; incrementUse(); if ( balance < 100000 ) charge = 15; else charge = 0; balance = balance - amount - charge ; // scope of amount ends here } } c. is the…arrow_forwardStatement that increases numPeople by 5. Ex: If numPeople is initially 10, the output is: There are 15 people.arrow_forwardJavaarrow_forward
- class box { int width; int height; int length; int volume; void volume(int height, int length, int width) { volume = width*height*length; } } class Prameterized_method { public static void main(String args[]) { box obj = new box(); obj.height = 1; obj.length = 5; obj.width = 5; obj.volume(3,2,1); System.out.println(obj.volume); } } Give result for the code Java Try to do ASAParrow_forwardpublic class ItemToPurchase { private String itemName; private int itemPrice; private int itemQuantity; // Default constructor public ItemToPurchase() { itemName = "none"; itemPrice = 0; itemQuantity = 0; } // Mutator for itemName public void setName(String itemName) { this.itemName = itemName; } // Accessor for itemName public String getName() { return itemName; } // Mutator for itemPrice public void setPrice(int itemPrice) { this.itemPrice = itemPrice; } // Accessor for itemPrice public int getPrice() { return itemPrice; } // Mutator for itemQuantity public void setQuantity(int itemQuantity) { this.itemQuantity = itemQuantity; } // Accessor for itemQuantity public int getQuantity() { return itemQuantity; }} import java.util.Scanner; public class ShoppingCartPrinter { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scnr = new…arrow_forwardJava Programming Please do not change anything in Student class or Course class class John_Smith extends Student{ public John_Smith() { setFirstName("John"); setLastName("Smith"); setEmail("jsmith@jaguar.tamu.edu"); setGender("Male"); setPhoneNumber("(200)00-0000"); setJNumber("J0101459"); } class MyCourse extends Course { public MyCourse { class Course { private String courseNumber; private String courseName; private int creditHrs; public Course (String number, String name, int creditHrs){ this.courseNumber = number; this.courseName = name; this.creditHrs = creditHrs; } public String getNumber() { return courseNumber; } public String getName() { return courseName; } public int getCreditHrs() { return creditHrs; } public void setCourseNumber(String courseNumber) { this.courseNumber = courseNumber; } public void setCourseName(String…arrow_forward
- I have the following code: public class Length{private int feet;private int inches;// Your code goes here Length(){feet = inches = 0;} Length(int newFeet, int newInches){feet = newFeet;inches = newInches;} public int getFeet() { return feet; }public void setFeet(int newFeet) { feet = newFeet; } public int getInches() { return inches; }public void setInches(int newInches) { inches = newInches; } public Length add(Length otherLength){int newFeet = feet + otherLength.feet;int newInches = inches + otherLength.inches; if(newInches >= 12){newFeet++;newInches -= 12;} return (new Length(newFeet,newInches));} public Length subtract(Length otherLength){if(this.feet > otherLength.feet){int newFeet = feet - otherLength.feet;int newInches = inches - otherLength.inches;if(newInches < 0){newFeet--;newInches += 12;} return (new Length(newFeet,newInches));}else{int newFeet = otherLength.feet - feet;int newInches = otherLength.inches - inches;if(newInches < 0){newFeet--;newInches += 12;}…arrow_forwardJava prgm basedarrow_forwardFix all the errors and send the code please // Application looks up home price // for different floor plans // allows upper or lowercase data entry import java.util.*; public class DebugEight3 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); String entry; char[] floorPlans = {'A','B','C','a','b','c'} int[] pricesInThousands = {145, 190, 235}; char plan; int x, fp = 99; String prompt = "Please select a floor plan\n" + "Our floorPlanss are:\n" + "A - Augusta, a ranch\n" + "B - Brittany, a split level\n" + "C - Colonial, a two-story\n" + "Enter floorPlans letter"; System.out.println(prompt); entry = input.next(); plan = entry.charAt(1); for(x = 0; x < floorPlans.length; ++x) if(plan == floorPlans[x]) x = fp; if(fp = 99) System.out.println("Invalid floor plan code entered")); else { if(fp…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education