DNA Polymerase Another enzyme, and arguably the most important, is DNA polymerase. This enzyme's function in a cell is to add nucleotides to the growing strand of DNA. DNA polymerase reads the bases on the original (template) strand and adds the complementary bases to the growing strand of DNA. Another type of DNA polymerase proofreads DNA. It corrects any incorrectly matched nucleotides by removing the incorrect one and replacing it with the correct one. 17. is responsible for adding new nucleotides to the DNA strand being created. 18. DNA polymerase knows what nucleotide to add next because it reads the strand. 19. Adenine pairs with DNA Polymerase DNA Primase For DNA polymerase to begin adding new nucleotides, it needs a starting point or a primer. The enzyme responsible for laying down an RNA primer is called DNA primase. This primer tells the DNA polymerase where to begin. Without it, DNA polymerase would be unable to add new nucleotides. The RNA primer is eventually removed and replaced with DNA nucleotides by another type of DNA polymerase. DNA Primase 26. DNA polymerase starts adding new nucleotides at an RNA 27. DNA adds an RNA primer that is complementary to the template RNA Primer RNA strand of DNA. Nucleotide
DNA Polymerase Another enzyme, and arguably the most important, is DNA polymerase. This enzyme's function in a cell is to add nucleotides to the growing strand of DNA. DNA polymerase reads the bases on the original (template) strand and adds the complementary bases to the growing strand of DNA. Another type of DNA polymerase proofreads DNA. It corrects any incorrectly matched nucleotides by removing the incorrect one and replacing it with the correct one. 17. is responsible for adding new nucleotides to the DNA strand being created. 18. DNA polymerase knows what nucleotide to add next because it reads the strand. 19. Adenine pairs with DNA Polymerase DNA Primase For DNA polymerase to begin adding new nucleotides, it needs a starting point or a primer. The enzyme responsible for laying down an RNA primer is called DNA primase. This primer tells the DNA polymerase where to begin. Without it, DNA polymerase would be unable to add new nucleotides. The RNA primer is eventually removed and replaced with DNA nucleotides by another type of DNA polymerase. DNA Primase 26. DNA polymerase starts adding new nucleotides at an RNA 27. DNA adds an RNA primer that is complementary to the template RNA Primer RNA strand of DNA. Nucleotide
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Michael Cummings
Chapter15: Genomes And Genomics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6QP: Which of the following best describes the process of DNA sequencing? a. DNA is separated on a gel,...
Related questions
Question
Please do this fast.
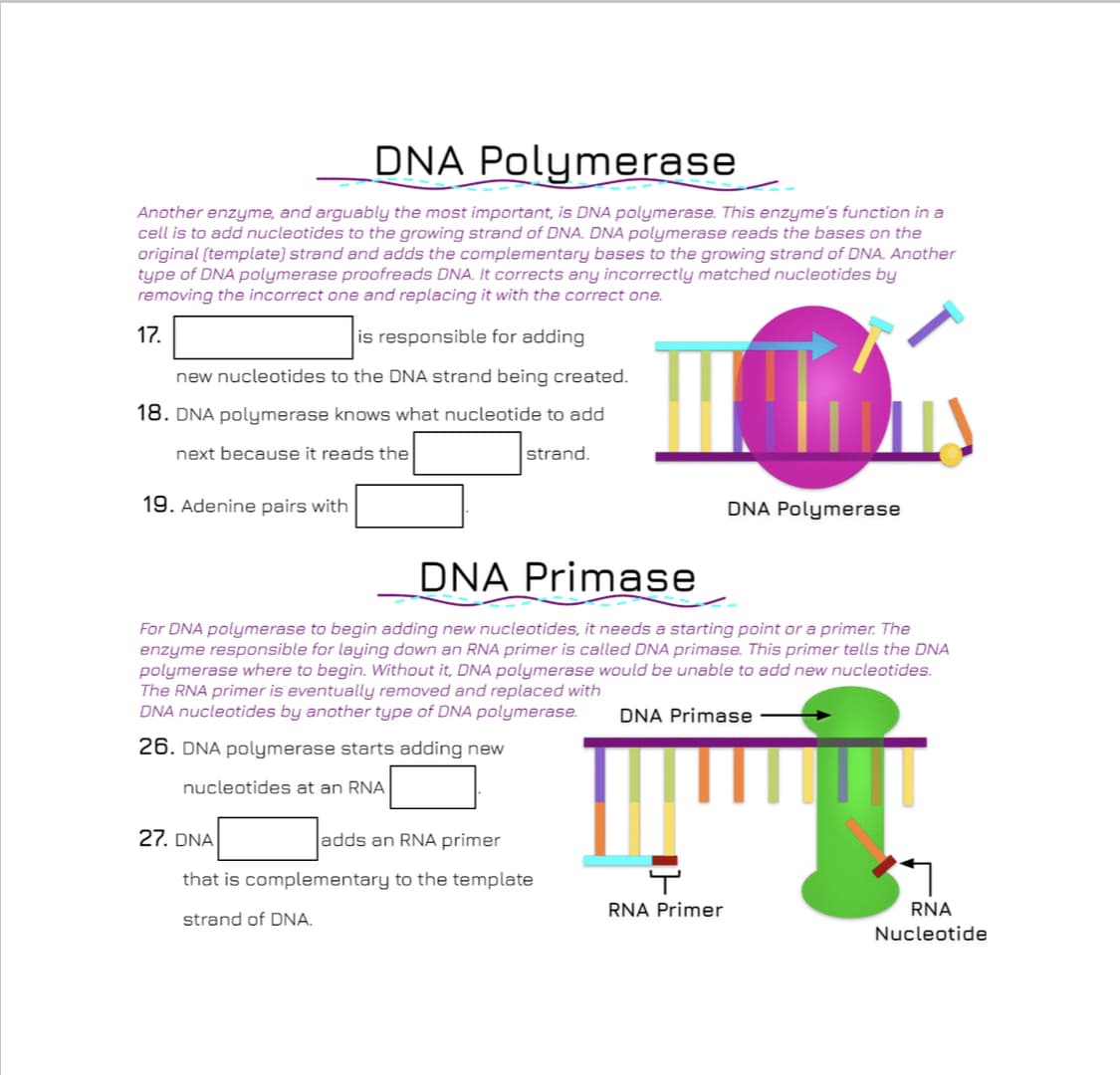
Transcribed Image Text:DNA Polymerase
Another enzyme, and arguably the most important, is DNA polymerase. This enzyme's function in a
cell is to add nucleotides to the growing strand of DNA. DNA polymerase reads the bases on the
original (template) strand and adds the complementary bases to the growing strand of DNA. Another
type of DNA polymerase proofreads DNA. It corrects any incorrectly matched nucleotides by
removing the incorrect one and replacing it with the correct one.
17.
is responsible for adding
new nucleotides to the DNA strand being created.
18. DNA polymerase knows what nucleotide to add
next because it reads the
strand.
19. Adenine pairs with
DNA Polymerase
DNA Primase
For DNA polymerase to begin adding new nucleotides, it needs a starting point or a primer. The
enzyme responsible for laying down an RNA primer is called DNA primase. This primer tells the DNA
polymerase where to begin. Without it, DNA polymerase would be unable to add new nucleotides.
The RNA primer is eventually removed and replaced with
DNA nucleotides by another type of DNA polymerase.
DNA Primase
26. DNA polymerase starts adding new
nucleotides at an RNA
27. DNA
adds an RNA primer
that is complementary to the template
RNA Primer
RNA
strand of DNA.
Nucleotide
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305117396
Author:
Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning