Select the chemical consequences that could contribute to DNA instability at AP sites. fewer hydrogen bonds between the unpaired pyrimidine base and water disruption of the base-stacking interactions increased ability of the deoxyribose ring to open without the attachment of the purine base decreased interaction between the mutated DNA strand and histones
Select the chemical consequences that could contribute to DNA instability at AP sites. fewer hydrogen bonds between the unpaired pyrimidine base and water disruption of the base-stacking interactions increased ability of the deoxyribose ring to open without the attachment of the purine base decreased interaction between the mutated DNA strand and histones
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Michael Cummings
Chapter8: The Structure, Replication, And Chromosomal Organization Of Dna
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 12QP: DNA contains many hydrogen bonds. Are hydrogen bonds stronger or weaker than covalent bonds? What...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Select the chemical consequences that could contribute to DNA instability at AP sites.
fewer hydrogen bonds between the unpaired pyrimidine base and water
disruption of the base-stacking interactions
increased ability of the deoxyribose ring to open without the attachment of the purine base
decreased interaction between the mutated DNA strand and histones
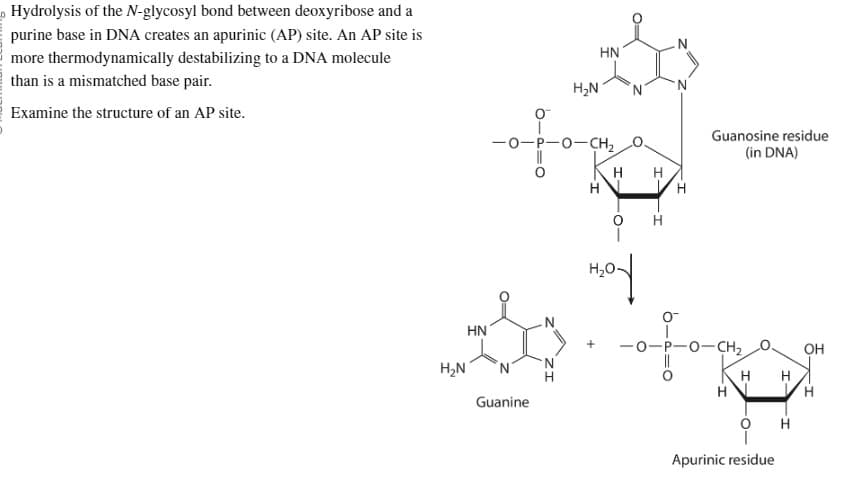
Transcribed Image Text:Hydrolysis of the N-glycosyl bond between deoxyribose and a
purine base in DNA creates an apurinic (AP) site. An AP site is
more thermodynamically destabilizing to a DNA molecule
than is a mismatched base pair.
Examine the structure of an AP site.
HN
H₂N N
0
Guanine
-O-P-O-CH₂O.
H₂N
H
HN
H
H H
Hod
H
ofo
-0-
Guanosine residue
(in DNA)
-0-CH₂
H
H H
Apurinic residue
H
OH
H
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning