
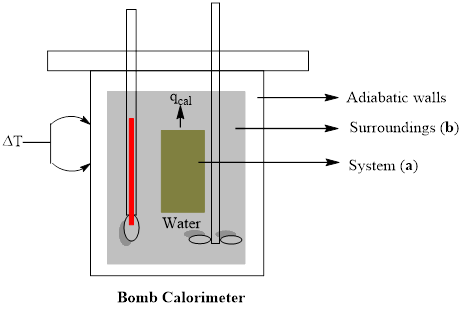
A bomb calorimeter is a study metal vessel in which samples can be ignited and the amount of heat given off can be measured as the heat warms up surrounding water. Draw a rough sketch of such an experimental setup and label (a) the system and (b) the surroundings.
Interpretation:
A rough sketch of experimental setup of bomb calorimeter is to be drawn with labeling of (a) system and (b) surroundings
Concept introduction:
Calorimeter is an instrument which is used to measure the heat of the chemical reactions, physical changes and heat capacity. There are different types of calorimeter such as 1) differential scanning calorimeter 2) isothermal calorimeter 3) titration calorimeter 4) accelerated rate calorimeter. The main components of calorimeter consist of a thermometer attached to a metal container with water suspended above a combustion chamber. This device is used in various fields to study thermodynamics, chemistry and biochemistry.
Answer to Problem 1.1E
Explanation of Solution
A bomb calorimeter is a kind of constant-volume calorimeter, which is used to measure the heat of combustion of a particular reaction. The four important components of bomb calorimeter are as follows; 1) a bomb (vessel) having the combustible material. It must be a strong and thick-walled vessel which is made up of high-quality metal and should have a provision to open for inserting the sample, to remove the products of combustion and to clean the apparatus. 2) a bucket (container) with a measured quantity of water to hold the bomb. Besides, it should be fitted with a probe to read the temperature and a mechanical stirrer to promote rapid thermal equilibrium with no excessive heat in the form of mechanical energy. These buckets are made with a highly polished exterior finish to reduce the absorption and emission of heat as radiation. 3) An insulating jacket to protect the container from transient thermal changes during the combustion process
The enthalpy change per mole of a substance A in a reaction between A and B is measured by adding the substances separately into the calorimeter and calculating the initial and final temperatures of the system. On multiplying the temperature change by the mass and specific heat capacities of the substances, we can get the value of energy which is given off during the reaction. When we divide the energy change by moles of A involved in the reaction, we can obtain the enthalpy change of reaction.
A rough sketch of experimental setup of bomb calorimeter is drawn with labeling of (a) system and (b) surroundings.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Physical Chemistry
- Starting with equation 2.27 andthe original definitionof enthalpy, derive the fact that Cp-=Cv-+Rarrow_forwardDefine the following terms: potential energy, kinetic energy, path-dependent function, state function, system, surroundings.arrow_forwardExplain why absolute enthalpies and energies cannot be measured, and only changes can be determined.arrow_forward
- The statement Energycan beneithercreatednor destroyedis sometimes used as an equivalent statement of the first law of thermodynamics. There areinaccuracies to the statement, however. Restate it tomake it less inaccurate.arrow_forwardWhat is the change in internal energy when a gas contracts from 377mL to 119mLundera pressure of 1550 torr, whileat the same time being cooled by removing 124.0J ofheat energy?arrow_forwardConsider a mixture of air and gasoline vapor in a cylinder with a piston. The original volume is 40. cm3. If the combustion of this mixture releases 950. J of energy, to what volume will the gases expand against a constant pressure of 650. torr if all the energy of combustion is converted into work to push back the piston?arrow_forward
- Suppose that you are studying kinetic energy of helium molecules: A helium weather balloon rises to an altitude of 40,000 ft; the temperature of the gas drops to 70 F. (a) Make an appropriate choice of system and surroundings and describe it unambiguously. (b) Explain why you chose the system and surroundings you did. (c) Identify transfers of energy and material into and out of the system that would be important for you to monitor in your study.arrow_forward9.102 A runner generates 418 kJ of energy per kilometer from the cellular oxidation of food. The runner's body must dissipate this heat or the body will overheat. Suppose that sweat evaporation is the only important cooling mechanism. If you estimate the enthalpy of evaporation of water as 44 kJ/mol and assume that sweat can he treated as water, describe how you would estimate the volume of sweat that would have to be evaporated if the runner runs a 10-km race.arrow_forwardOn complete combustion at constant pressure, a 1.00-L sample of a gaseous mixture at 0C and 1.00 atm (STP) evolves 75.65 kJ of heat. If the gas is a mixture of ethane (C2H6) and propane (C3H8), what is the mole fraction of ethane in the mixture?arrow_forward
- Explain why the high-temperature reservoir of a heat engine must, indeed, be higher in temperature than the low-temperature reservoir. Can it ever be the other way around?arrow_forwardWould the amount of heat absorbed by the dissolution in Example 5.6 appear greater, lesser, or remain the same if the heat capacity of the calorimeter were taken into account? Explain your answer.arrow_forwardThe distance between downtown San Francisco and downtown Oakland is 9 miles. However, a car driving between the two points travels 12.3miles. Of these distances, which one is analogous to a state function? Why?arrow_forward
 Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning, Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





