
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The radicals, in order of theirs decreasing stability, are to be listed.
Concept introduction:
A molecule that contains at least one unpaired electron is known as a radical.
The relative stability of radicals is the same as that of carbocations.
The stability of radicals is as follows:
Answer to Problem 1PP
Solution:
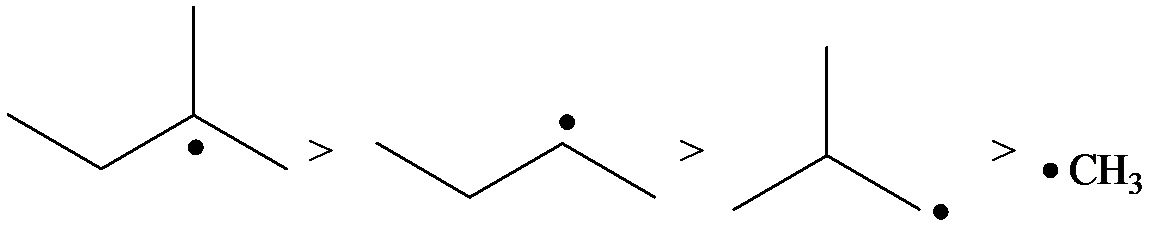
Explanation of Solution

The radical is a methyl radical. So, it is the least stable.
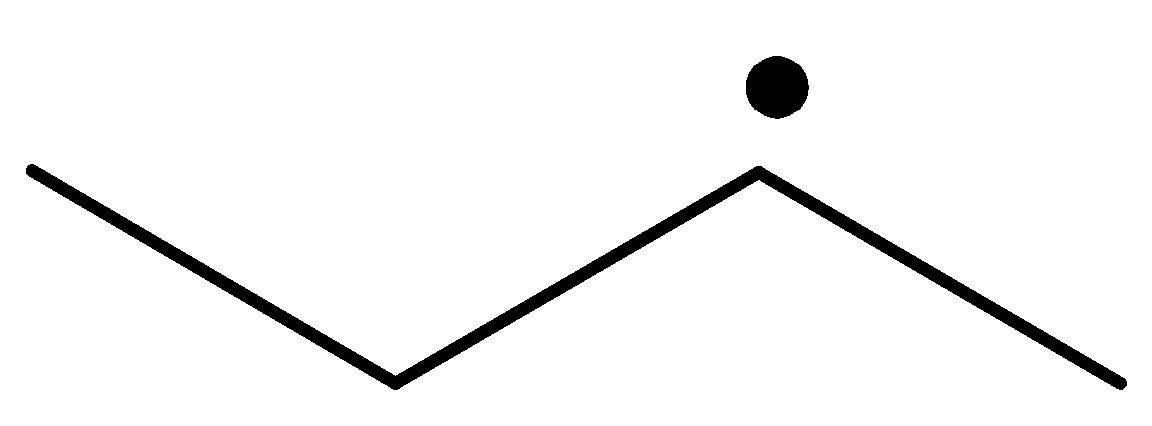
The radical is given as follows:
The carbon containing the unpaired electron is primary. Thus, the radical is a primary radical.
The radical is given as follows:
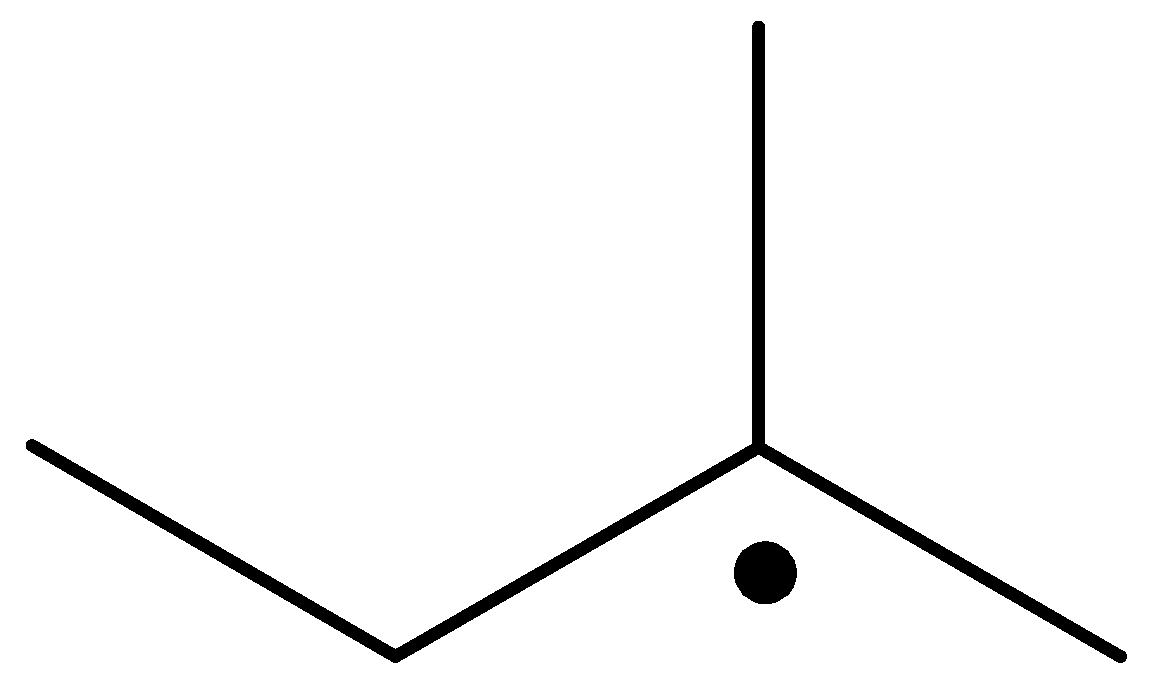
The carbon containing the unpaired electron is tertiary. Thus, the radical is a tertiary radical.
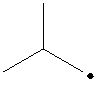
The radical is given as follows:
The carbon containing the unpaired electron is secondary. Thus, the radical is a secondary radical.
Therefore, the tertiary radical is the most stable and the methyl radical is the least stable.
Hence, the decreasing order of the stability of the radical is as follows:
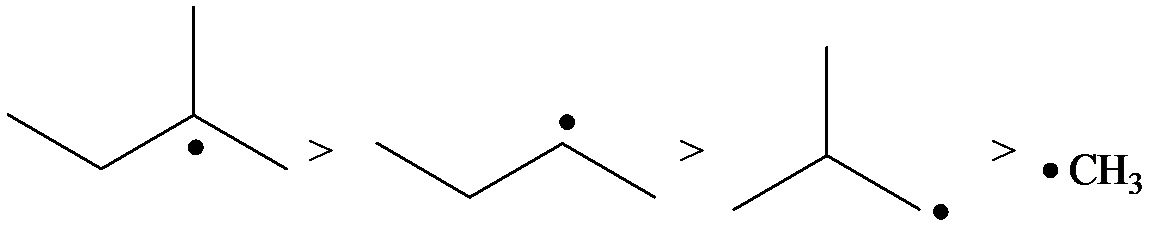
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Give a detailed reaction mechanism for the reaction expected to occur when 2-bromo-2-methylpentane is heated with sodium methoxide. Draw clear structural formulas of all relevant species and use curved arrows to represent electron flow. Discuss the stability of the final compoundarrow_forwardProvide a reasonable synthetic strategy for the synthesis of a racemic mixture of (1R,2R) and (1S,2S)-2-bromo-1-methylcyclopentanol from the compound shown below... Provide the bond line structure for the major organic products obtained in each step of the proposed strategyarrow_forwardIdentify the structure of the compound a with a formula of C3H6O2 having the following IR, and 1H NMR spectra (integrals and multiplicity shown in the boxes: s-singlet, d-doublet, t-triplet, q-quartet, etc.). Label the spectra with proper information you deduced (functional groups, number of protons, fragments, etc.). Compound formula. C3H6O2 Questions to help you decide What is the element of unsaturation of the molecular formula? Show the equation you use: What are the functional groups present in this molecule? Show all of them belowDraw at least two possible structures that have the . required element of unsaturation as well as the observed functional groups: Based on the 1H NMR above, what molecular fragmentations do you see: Draw your final decision of the structure below. Is this one of the structures in your answer 5C?arrow_forward
- Give evidence and prove that E2 reactions are predominantly anti-elimination, and there is a relation between conformation and reactivity.arrow_forwardA difficult problem in the synthesis of PGF2α is the introduction of the OH group at C15 in the desired configuration. a. Label this stereogenic center as R or S. b. A well known synthesis of PGF2α involves reaction of A with Zn(BH4)2, a metal hydride reagent similar in reactivity to NaBH4, to form two isomeric products, B and C. Draw their structures and indicate their stereochemical relationship. c. Suggest a reagent to convert A to the single stereoisomer X.arrow_forwardHow to approach this problem?arrow_forward
- A student was given from the list of the compounds below A, B and D blindly and asked to identify them all. He treated each of them with Brady's reagent (2,4-ditrophenylhydrazine) and isolated a bright yellow compound for one of them, but the other two gave false negatives. The student reasoned that the false negatives may be due to sterics and, on further thinking, it dawned on him that he might be able to rule out one of the false negatives with the haloform test. What compound did he find compatible with the haloform test? That compound did indeed give a false negative in the Brady test. Which of the other two was positive in the Brady test? A = haloform B = Brady A = haloform D = Brady B = haloform A = Brady B = haloform D = Brady D = haloform A = Brady D = haloform B = Bradyarrow_forwardPerhaps it is unsurprising that cyclohexane and ethanol are reasonable UV solvents, whereas toluene is not. Explain why that isarrow_forwardGive the series of reactions below, identify and give the iupac name for the following compounds, in short identify and name A,B,Carrow_forward
- Provide a mechanism which explains the following conversions. Include all intermediates (where appropriate) and watch your arrows and chargesarrow_forward3) Outline an acceptable step by step mechanism for the Nucleophilic aromatic substitution of ortho-fluoronitrobenzene with methylamine. Do not forget to include the formal charges of all non-hydrogen atoms that do not have a neutral charge.arrow_forwardProvide a mechanism which explains the following conversions. Include all intermediate structures where appropriate and watch your arrows and chargesarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

