
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism for the given reaction is to be drawn, and the major product of the reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
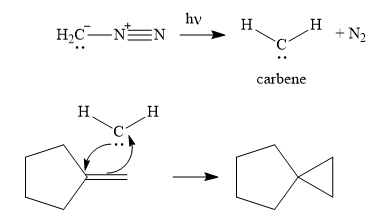
A carbene is a highly reactive species containing a carbon atom that has two bonds and a lone pair of electrons. Carbenes are electron-poor due to the lack of an octet and are
Answer to Problem 12.1P
The complete, detailed mechanism and the major product of the reaction are shown below:
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
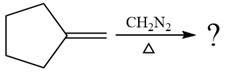
In the first step of the reaction mechanism, the

Next, the reactive carbene adds to the double bond, simultaneously forming bonds with the two carbons of the initial double bond. The lone pair from the carbine forms a bond with one carbon, while the
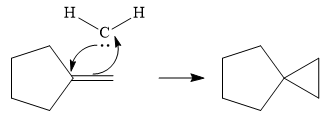
Thus the complete mechanism can be drawn as follows:

Carbenes add to alkenes to form a cyclopropyl ring in place of the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
ORG.CHEM W/TEXT+SOLU.MANUAL
- Predict the major product of each of the reactions shown here and provide the complete, detailed mechanism.arrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following reactions. Draw the complete, detailed mechanism that leads to the formation of each of those products.arrow_forward(SYN) Show how to synthesize the following molecule from any compounds containing two carbons. Draw the complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction.arrow_forward
- Draw a complete, detailed mechanism for the following reaction. A key intermediate is provided.arrow_forwardPredict the major product of each of the following reactions and provide the complete, detailed mechanismarrow_forwardPlease draw the complete, detailed mechanism of the reaction step by step.arrow_forward
- Propose a mechanism for the reaction shown here, which takes place under conditions that favor anarrow_forwardDraw the complete mechanism and the major organic product for each of the following reactions.arrow_forward(a) Predict the product of the set of reactions shown here. (b) Draw the complete, detailed mechanism for the formation of the synthetic intermediate that is not shown.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





