
Concept explainers
Mechanical/Aerospace Engineering
Consider the three mass-four spring system in Fig. P12.37. Determining the equations of motion from
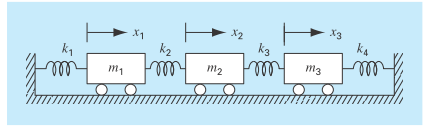
FIGURE P12.37
Where
At a specific time when x 1 5 0.05 m, x 2 5 0.04 m, and x 3 5 0.03 m, this forms a tridiagonal matrix. Solve for the acceleration of each mass.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
EBK NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ENGINEERS
- A block of mass m = 1.2Kg is on a plane %3D inclined at 30 degrees for which uc = 0.11. The block is connected to a spring of constant K = 3.2 N / m, by a rope passing, without slipping, by a pulley. The pulley is a disc of 0.8Kg and 0.14m radius. If the system is initially at rest and the spring has zero elongation, what is the block velocity modulus when the block has slid 0.25m down the inclined plane? k=3,2 N/m 130° A Figure 11.75arrow_forwardOne end of a uniform 2.60m rod with a mass of 38.0kg is supported by a cable connecting one end to the wall so that the cable makes an angle of 42.0° with respect to the rod. The other end rests against the vertical wall, where it is held in place by friction so that the rod is perfectly horizontal. A sign with an unknown mass is hung from the rod 1.90m from the wall so that wall exerts a normal force of 1790N on the rod in the positive x-direction. What is the mass of the sign in kilograms?arrow_forwardPart (A)- In a Hartnell governor, the mass of each ball is 6 kg. The lengths of ball arm and sleeve arm of each bell crank lever are 120 mm and 100 mm respectively. The minimum radius of rotation of governor ball is 90 mm. If the controlling forces are 1200 N and 600 N corresponding to 175 mm and 100 mm radius of rotation of governor balls respectively, find the initial compression of spring required.arrow_forward
- A 0.23 kg block is pressed up against a spring on a frictionless incline of angle 0 = 20.0° to the horizontal. The spring is initially compressed by x = 0.30 m from its equilibrium position (first arrow shown). When released from rest, the block travels along the incline a total distance (d + x) = 1.30 m until coming to rest again (where d = 1.00 m). What is the spring constant k? {Consider gravitational and spring potential energies; conservation of energy 'system'} O 11.5 N/m O 22.3 N/m O 80.9 N/m O 13.7 N/m O 30.2 N/m 8 LE R T K command command optionarrow_forwardM₁ a M₂ Fig. 1.11. 1.63. The following parameters of the arrangement of Fig. 1.11 are available: the angle a which the inclined plane forms with the horizontal, and the coefficient of friction k between the body m₁ and the inclined plane. The masses of the pulley and the threads, as well as the friction in the pulley, are negligible. Assuming both bodies to be motionless at the initial moment, find the mass ratio m₂/m, at which the body m₂ (a) starts coming down; (b) starts going up; (c) is at rest.arrow_forwardProblem 22.77 The 20-kg block is subjected to the action of the harmonic force F = (90 cos 6t) N, where t is in seconds. (Figure 1) Figure k = 400 N/m WWW k = 400 N/m O 0 20 kg O O O O F90 cos 6tr C c = 125 N.s/m 1 of 1 Part A Write the equation which describes the steady-state motion. Express your answer in terms of t. Express your answer using three significant figures. Express the phase in radians and the final result in meters. x = Submit 15. ΑΣΦΑ Provide Feedback Request Answer vec ? marrow_forward
- Consider four springs with the spring constants: k1 =20 lb/in., k2 = 50 lb/in., k3 = 100 lb/in., k4= 200 lb/in. 1 k1, k2, k3, and k4 are in series a. 18.9189 Ib/in. b. 370.0 lb/in. c. 11.7647 Ib/in. d. 300.0 lb/in.arrow_forwardA box with a mass of 3m is on frictionless ground, attached to a wall (on the left-side of the box) by a spring with constant k. Inside the box (on the frictionless floor of the box), is a block of mass m. The block is also attached to the left-side of the box (but inside it), by a second spring, with a spring constant 2k/5.1) What are the F = ma equations for the box and the block? (Remember how the motion of each, affects each other)2) What are the matrices K and M for the system?3) What are the normal frequencies of the system?4) Describe the motion of the masses. In phase? Out of phase? Does one mass oscillate with a higher amplitude than the other?arrow_forwardThe force-deflection relation of a steel helical spring used in an engine is found experimentally as F( x) = 200 x + 50 x2 + 10 x3, where the force (F) and deflection (x) are measured in pounds and inches, respectively. If the spring undergoes a steady deflection of 0.5 in. during the operation of the engine, determine the equivalent linear spring constant of the spring at its steady deflection.arrow_forward
- A load of bricks with mass m1= 14.2 kg hangs from one end of a rope that passes over a small, frictionless pulley. A counterweight of mass m2 = 27.0 kg is suspended from the other end of the rope, as shown in the figure. The system is released from rest. Use g = 9.80 m/s^2 for the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity. 1)What is the magnitude of the upward acceleration of the load of bricks? 2)What is the tension in the rope while the load is moving?arrow_forwardGears B and D are attached to a shaft which is supported by bearings at A and C if the diameters of the gears are 12 and 6 cm respectively, radial and tangential forces act on them as shown, neglecting the weight of the gears. gears as well as the friction of the bearings, if we know that the system is rotating with a constant angular velocity. Calculate the static equilibrium of the system X Z A 175 N 12 CM 110 N B C 40 cm 6 CM D 200 N 450 N 30 cm 20 cmarrow_forwardA sheep with a mass (m) 50 kg is hung on an animal scale system which consist of a helical spring of negligible mass. The stiffness (k) of the spring is 60 kN/m. During the hanging operation, the spring and the sheep are displaced vertically by 20 mm below the equilibrium position. 1.1. Draw a free body diagram and proof that a total length (L) of the scale system 2mg can be expressed as: L = k + Lo, where as Lo is the unstretched length of the spring. 1.2. Calculate the frequency of natural vibration of the system. 1.3. Calculate the velocity and acceleration of the sheep when it is 10 mm below the rest position.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





