
(a)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-superimposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-superimposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer
(b)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halide which will be obtained in greater yield from the given reaction has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
(c)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halide which will be obtained in greater yield from the given reaction has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-super imposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-super imposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Bromination of
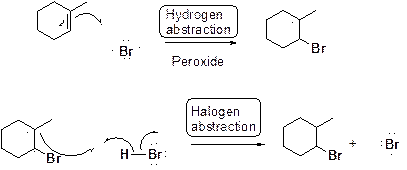
(d)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halide which will be obtained in greater yield from the given reaction has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-super imposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-super imposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Bromination of alkene in presence of peroxide:
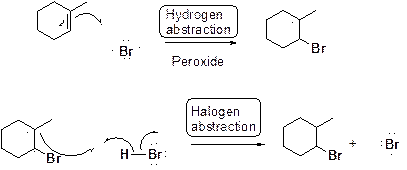
(e)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halide which will be obtained in greater yield from the given reaction has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-super imposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-super imposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Bromination of alkene in presence of peroxide:
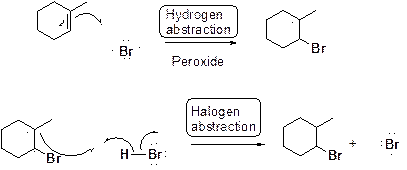
(f)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halide which will be obtained in greater yield from the given reaction has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-super imposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-super imposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Bromination of alkene in presence of peroxide:
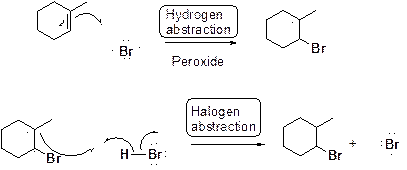
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
- What are the products of the following ether cleavage reactions? What is the mechanism that follows?arrow_forwardAlkyl halides undergo substitution reactions with nucleophiles. Explain this ?arrow_forwardWhich of the following alkenes produces the highest yield of 2,3-dimethylpentan-3-ol at the fastest rate?arrow_forward
- Two products are formed when methylenecyclohexane reacts with NBS? Show how each is formed. Disregard stereoisomers.arrow_forward(1R,2R)-1-Bromo-2-methylcyclopentane is reacted with sodium methoxide. Given the product(s) and show the reaction mechanism, including the depiction of the transition state. Draw an energy diagram for this conversion.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





