
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The equations for the preparation of each of the given compounds from benzene or toluene and any necessary organic or inorganic reagents are to be written.
Concept Introduction:
In electrophilic
When aromatic ring having two comparably activated positions then the substitution usually takes place at the less hindered position.
The reagent zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid is use to convert a carbonyl group into methylene unit. This reaction is known as Clemmenson’s reduction.
In Friedel-Crafts acylation, acyl halides are used to yield aryl
In Friedel-Crafts
A mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid produces a nitronium ion which behaves as an electrophile in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions.
Reagent bromine in acetic acid indicates bromination reaction.
Reagent sulfur trioxide in sulfuric acid indicates sulfonation reaction.
Oxidation of benzylic carbon atom is done using the
Answer to Problem 49P
Solution:
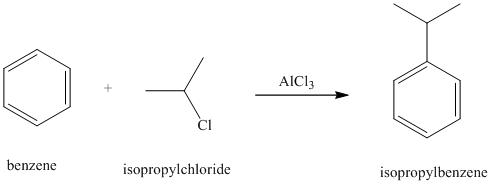
a) Reaction equations for the synthesis of isopropyl benzene from benzene is shown below:
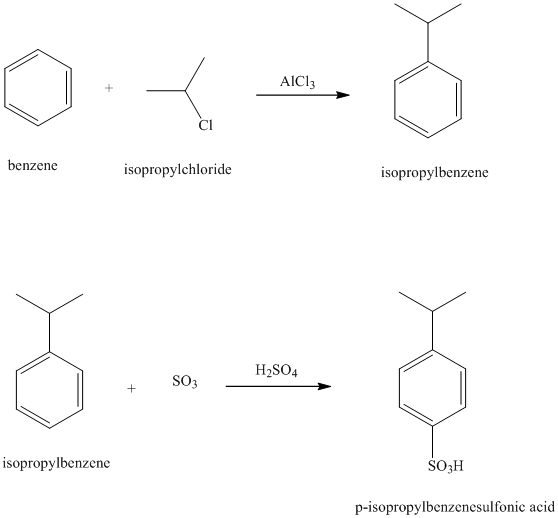
b) Reaction equations for the synthesis of
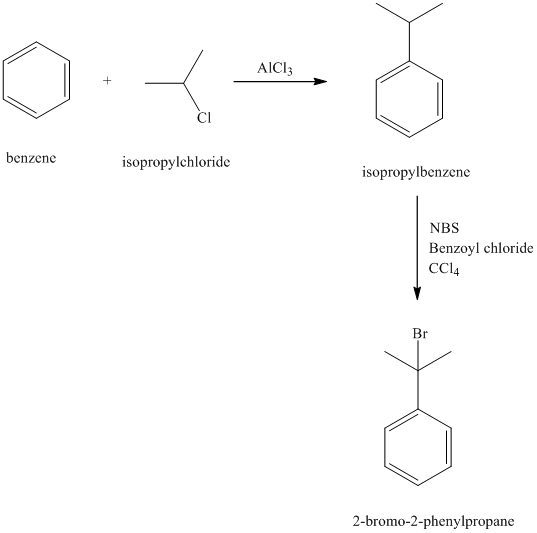
c) Reaction equations for the synthesis of
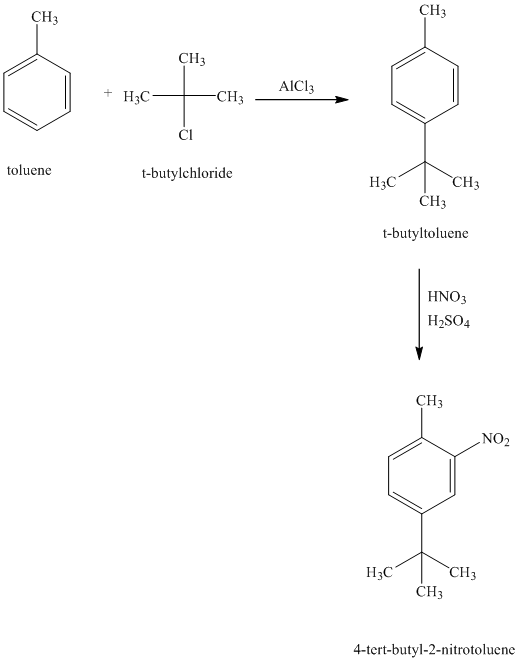
d) Reaction equations for the synthesis of
e) Reaction equations for the synthesis of
f) Reaction equations for the synthesis of
 g) Reaction equations for the synthesis of
g) Reaction equations for the synthesis of
h) Reaction equations for the synthesis of
i) Reaction equations for the synthesis of
j) Reaction equations for the synthesis of
 k) Reaction equations for the synthesis of
k) Reaction equations for the synthesis of
l) Reaction equations for the synthesis of
m) Reaction equations for the synthesis of
 n) Reaction equations for the synthesis of
n) Reaction equations for the synthesis of
Explanation of Solution
a) The structure for isopropyl benzene is:
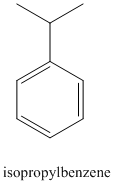
Benzene undergoes Friedel-Crafts alkylation with isopropyl chloride with aluminum chloride to yield isopropyl benzene as shown below:

b) The structure of
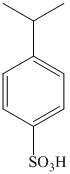
In the above structure, the isopropyl substituents, isopropyl and sulfonic acid are para to each other.
Benzene undergoes Friedel-Crafts alkylation with isopropyl chloride with aluminum chloride to yield isopropyl benzene. In the second step, isopropyl benzene is treated with the solution of sulfur trioxide in sulfuric acid yields
Reaction equations for the synthesis of
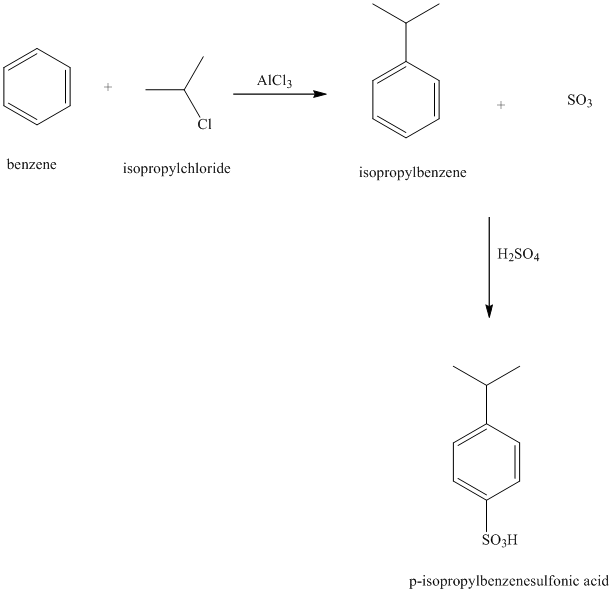
c) The structure of
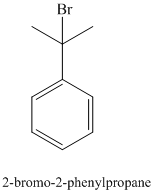
In the structure for the final product, the phenyl group and a bromine atom is attached to

d) The structure of
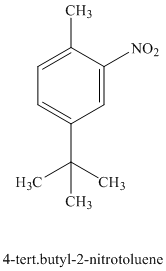
To get this product, toluene should be the starting compound that must be used. In the first step, toluene undergoes Friedel-Crafts alkylation with tertiary butyl chloride with aluminum chloride to yield tert-butyl toluene. In the second step, the tert-butyl toluene undergoes a nitration reaction to yield the product in which the nitro substituent is attached to the ortho position of the methyl group and meta position of the tertiary butyl group. Due to steric hindrance, the product in which the nitro group is attached at the ortho position of the tertiary butyl group is less favorable.
Reaction equations for the synthesis of

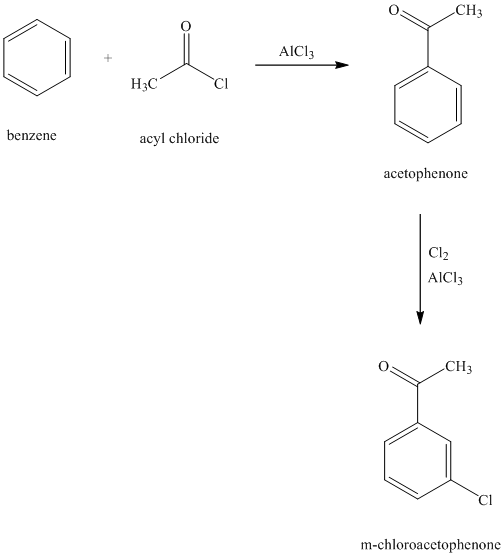
e) The structure for
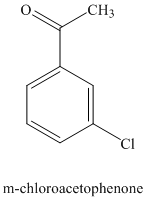
To get this product, benzene should be the starting compound that must be used. In the first step, benzene undergoes Friedel-Crafts acylation with acyl chloride with aluminum chloride to yield
Reaction equations for the synthesis of

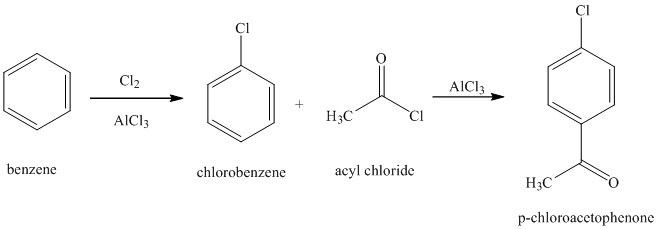
f) The structure of
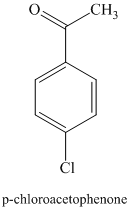
In order to get this product, benzene should be the starting compound that must be used. In the first step, benzene undergoes chlorination reaction in presence of a Lewis acid such as aluminum chloride to yield chlorobenzene. In the second step, chlorobenzene undergoes Friedel-Crafts acylation with acyl chloride with aluminum chloride to yield
Reaction equations for the synthesis of

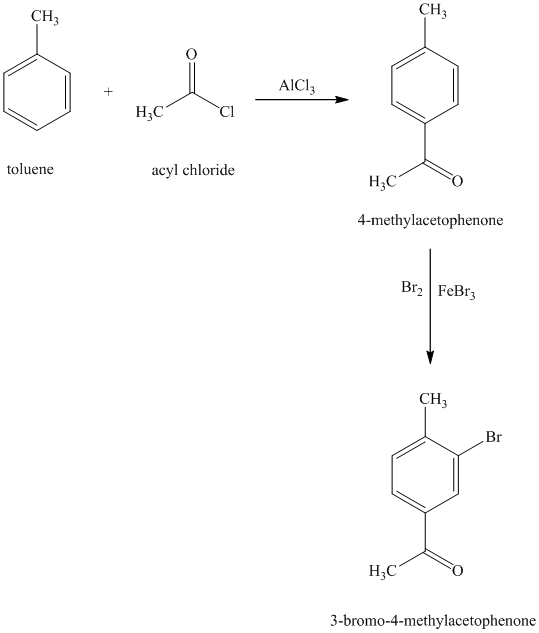
g) The structure for
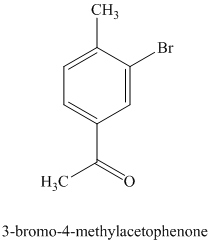
On order to get this product, toluene should be the starting compound that must be used. In the first step, toluene undergoes Friedel-Crafts acylation with acyl chloride with aluminum chloride to yield
Reaction equations for the synthesis of

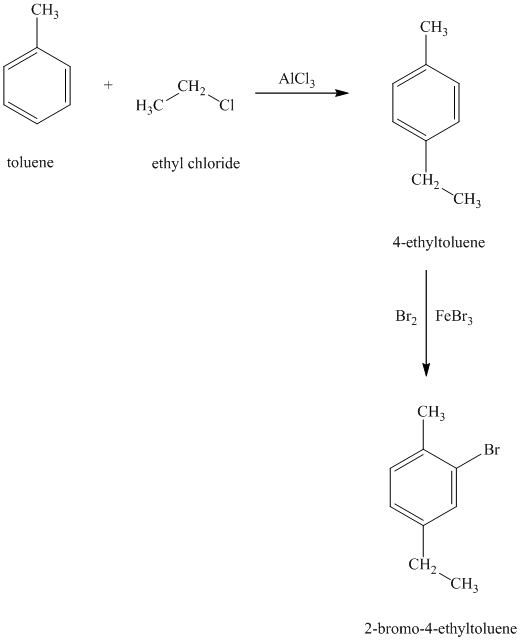
h) The structure for
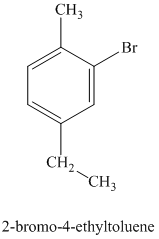
To get this product, toluene should be the starting compound that must be used. In the first step, toluene undergoes Friedel-Crafts alkylation with ethyl chloride with aluminum chloride to yield
Reaction equations for the synthesis of

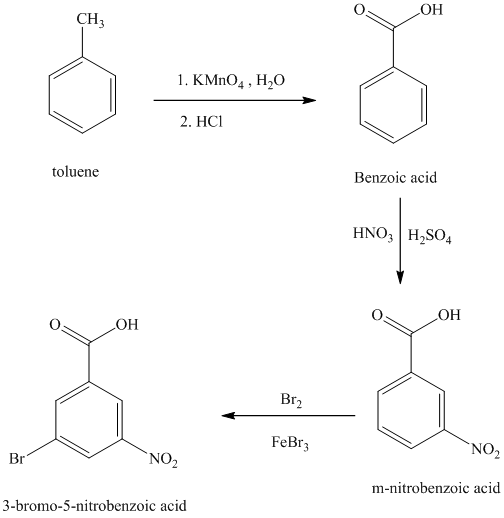
i) The structure for
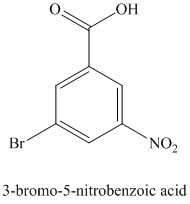
To get this product, toluene should be the starting compound that must be used.
In the first step, toluene undergoes oxidation of benzylic carbon atom in toluene with
In the second step, benzoic acid undergoes a nitration reaction with a mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid giving
In the third step,
Reaction equations for the synthesis of
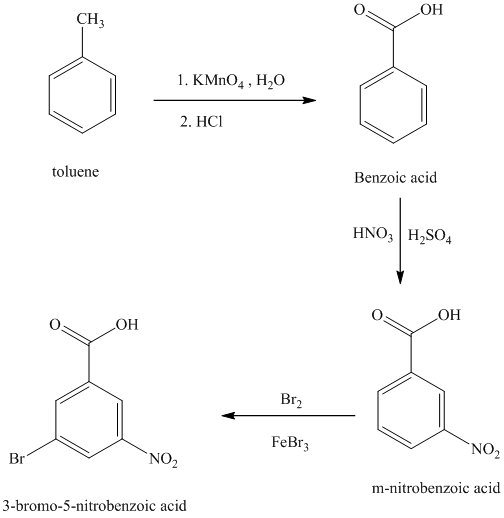
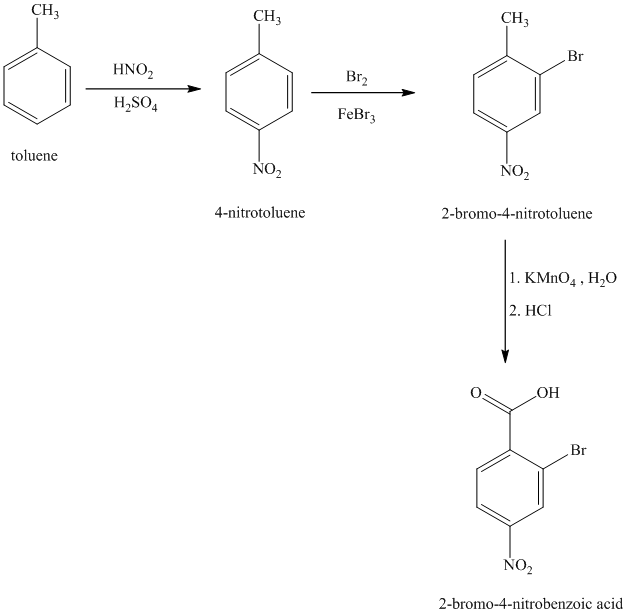
j) The structure for
To get the desired product, toluene should be the starting compound that must be used.
In the first step, toluene with nitric acid and sulfuric acid undergoes a nitration reaction giving
In the second step, benzoic acid undergoes bromination reaction in presence of a Lewis acid such as Iron (III) bromide to yield
In the third step,
Reaction equations for the synthesis of
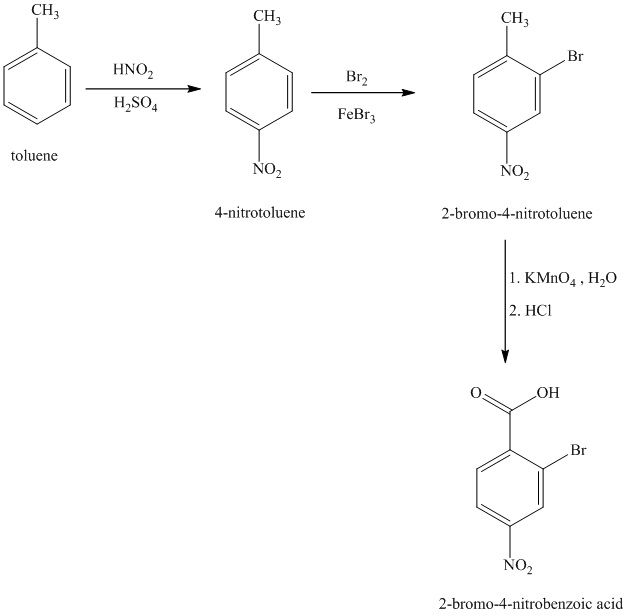
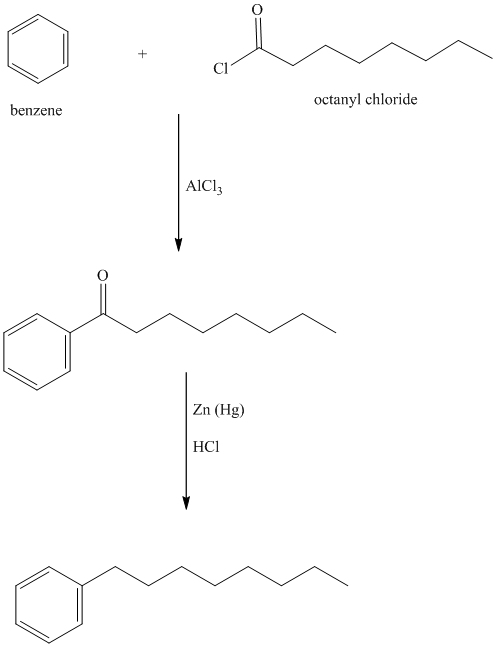
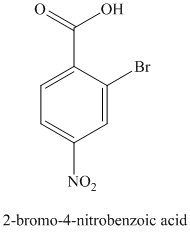
k) The structure for
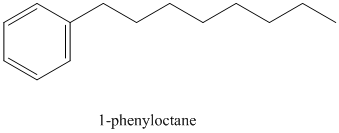
To get this product, benzene should be the starting compound that must be used.
In the first step, benzene undergoes Friedel-Crafts acylation with octanyl chloride with aluminum chloride.
In the second step, the carbonyl group is reduced in the presence of
Reaction equations for the synthesis of
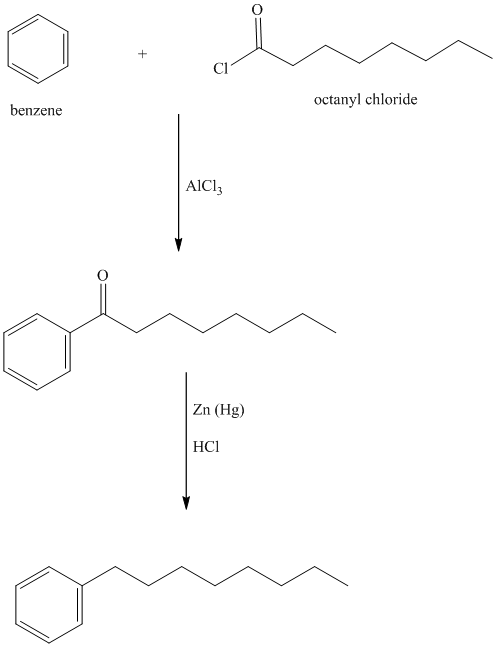
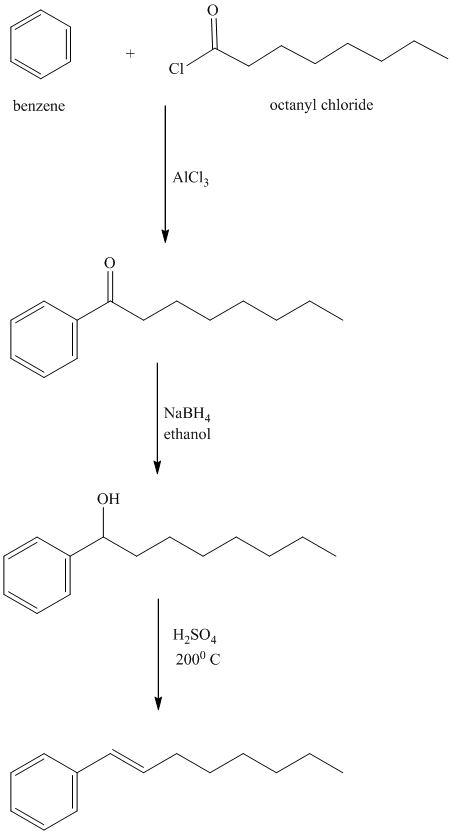
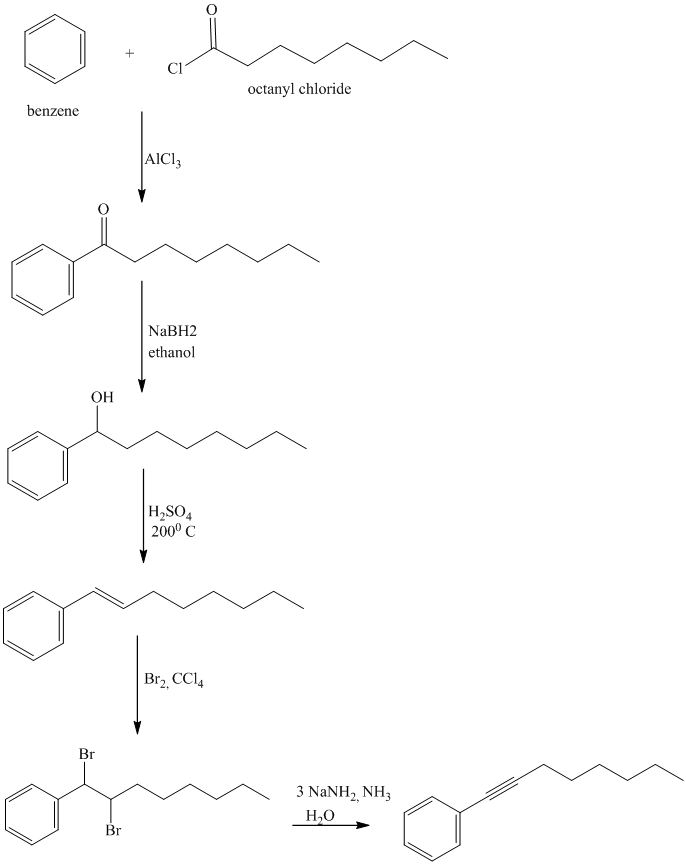
l) The structure of
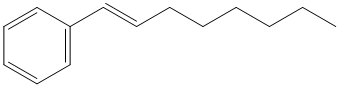
In order to get this product, benzene should be the starting compound that must be used.
In the first step, benzene undergoes Friedel-Crafts acylation with octenyl chloride with aluminum chloride.
In the second step, the carbonyl group is reduced to the hydroxyl group in the presence of
In the third step, the resulting alcohol is heated with sulfuric acid at high temperatures to yield
Reaction equations for the synthesis of
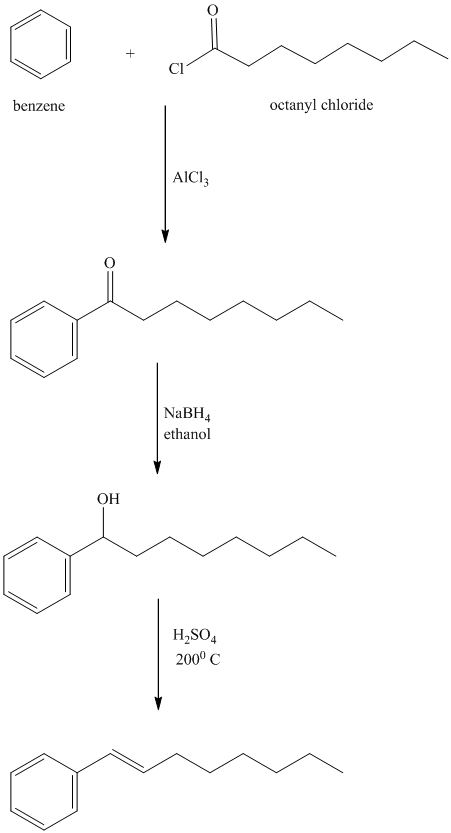
m) The structure of
To get this product, benzene should be the starting compound that must be used.
In the first step, benzene undergoes Friedel-Crafts acylation with octanyl chloride with aluminum chloride.
In the second step, the carbonyl group is reduced to the hydroxyl group in the presence of
In the third step, the resulting alcohol is heated with sulfuric acid at high temperatures to yield
In the fourth step,
Reaction equations for the synthesis of
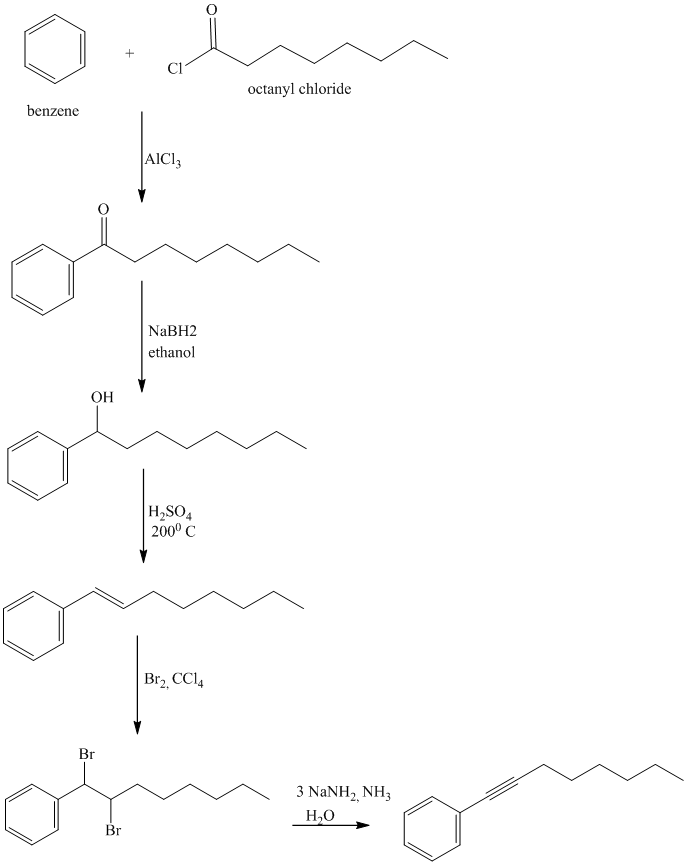
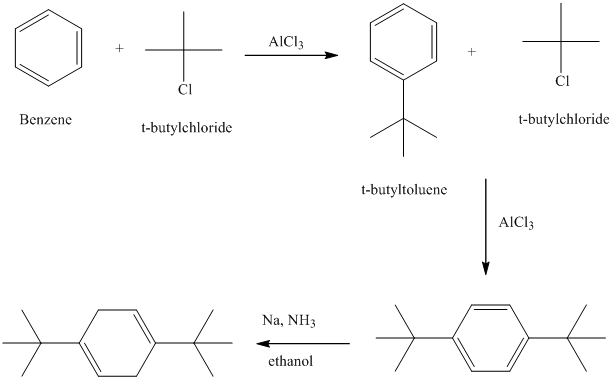
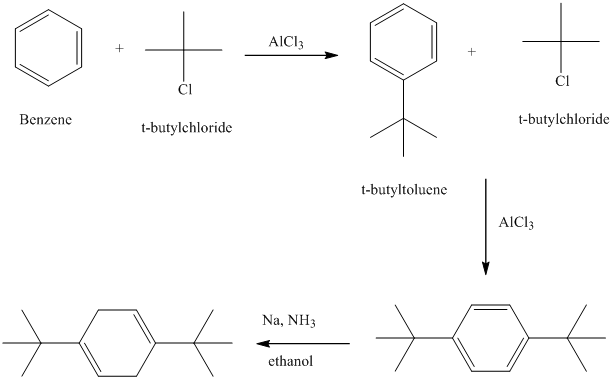
n) The structure of
To get the required product, benzene should be the starting compound that must be used.
In the first step, benzene undergoes Friedel-Crafts acylation with tertiary butyl chloride with aluminum chloride giving tert-butyl toluene.
In the second step again, the tert-butyl toluene undergoes Friedel-Crafts acylation with tertiary butyl chloride with aluminum chloride giving
In the third step,
Reaction equations for the synthesis of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
- Compound A was oxidized with periodic acid to give B, which after acid hydrolysis gave C. Bromine oxidation of C gave D. Suggest structural formulas, including stereochemistry, for compounds B, C, and D.arrow_forwardEach of the following reactions has been described in the chemical literature and involves an organic reactant somewhat more complex than those we have encountered so far. Nevertheless, on the basis of the topics covered in this chapter, you should be able to write the structure of the principal organic product of each reaction.arrow_forwardStarting with the following compounds, outline a practical synthesis of 1-butanolarrow_forward
- Outline the steps invloved in the synthesis of 3-chloro-4-fluroacetophenone from 4-aminoacetophenone. provide the bond line structure for the major organic product obtained in each step of the proposed synthesis.arrow_forwardIn the preparation of p-Nitroaniline, there are three synthetic steps in this reaction, the first is acetylation of the amine, second is nitrates and the third is hydrolysis of the amide. Why must acetylation be done first if at all? Use chemical structures to illustrate your point.arrow_forward(a) Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :(i) Benzoic acid and Phenol (ii) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone(b) An organic compound with molecular formula C5H10O does not reduce Tollen’s reagent but forms an addition compound with sodium hydrogen sulphite and gives a positive iodoform test. On vigorous oxidation, it gives ethanoic acid and propanoic acid. Identify the compound and write all chemical equations for the reactions.arrow_forward
- Compound A is a branched-chain alcohol that undergoes oxidation to produce compound B. Compound B is a ketone that gives positive triiodomethane reaction. Compound B is then reacted with phenyl magnesium bromide, C6H5MgBr in the presence of aqueous acid to form compound C. Compound C has the molecular formula of C11H16O (i) Deduce the structure for compound A, B and C. (ii) State the observation when compound C is added with acidified potassium dichromate(VI).arrow_forwardFor the following reaction scheme, identify by drawing the reagents b and d and the intermediate c that are formed in the synthesis of benzoic acid.arrow_forward(a) Write the structures of main products when benzene diazonium chloride reacts with the following reagents :(i) H3PO2 + H2O (ii) CuCN/KCN (iii) H2O(b) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their basic character in an aqueous solution :C2H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH, (C3H5)3N(c) Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between the following pair of compounds :C6H5—NH2 and C6H5—NH—CH3arrow_forward
- An organic compound A of unknown structure was found to have a molecular formula C8H16. When A was poured in water and heated, compound B having a molecular formula C8H18O was formed. B upon heating with sulfuric acid was converted to C as the major product which is identical to A. Ozonolysis of C gave one molecule each of two different products D and E, both having a molecular formula C4H8O. Write the reactions involved and determine the structure of A,B,C,D and E.arrow_forwardStarting with toluene, outline a synthesis of each of the following: (a) o-nitrobenzoic acid (b) m-nitrobenzoic acid (c) 3-chlorobenzoic acid (d) p-bromobenzoic acidarrow_forwardOutline a synthesis of the following compounds (A-C) from acetoacetic ester OR malonic ester. Show the starting material and reagents. If the synthesis is not possible, indicate why. A) hept-6-en-2-one B) 2-benzylheptanoic acid C) 3-isobutyl-2-heptanonearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





