
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The difference in meaning that is associated with the given pair of notations has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Ether is an organic compound. In ether, an oxygen atom is bonded to two carbon atoms by a single bond. The groups that are attached to the carbon atom by a single bond may be alkyl, aryl, or cycloalkyl groups. The
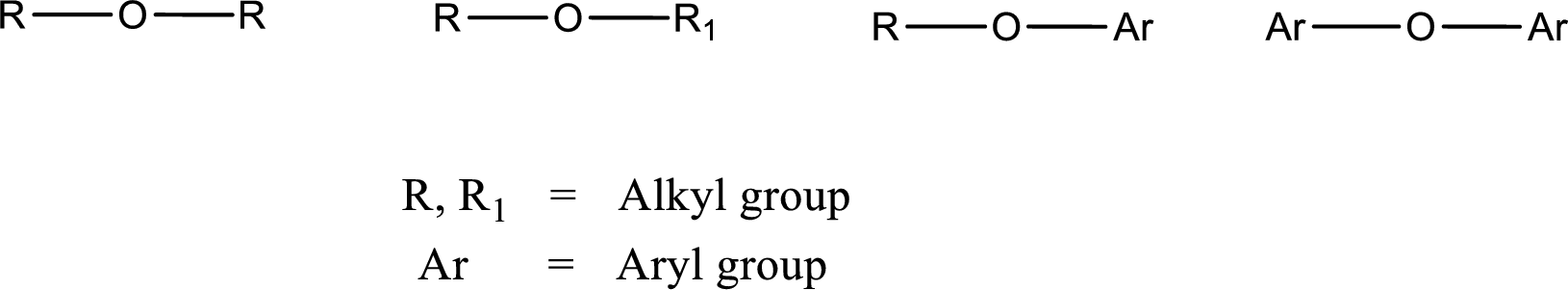
Alcohol is a compound in which a hydrocarbon group is bonded to a hydroxyl group. The generalized formula for alcohol can be given as,
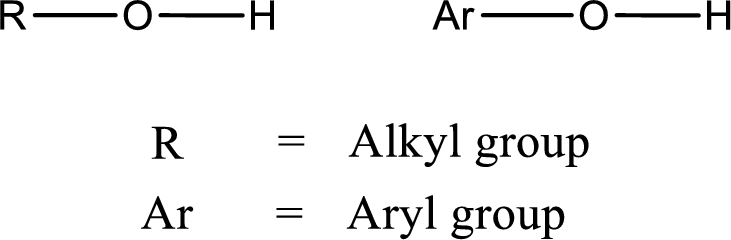
(b)
Interpretation:
The difference in meaning that is associated with the given pair of notations has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Ether is an organic compound. In ether, an oxygen atom is bonded to two carbon atoms by a single bond. The groups that are attached to the carbon atom by a single bond may be alkyl, aryl, or cycloalkyl groups. The functional group of ether is
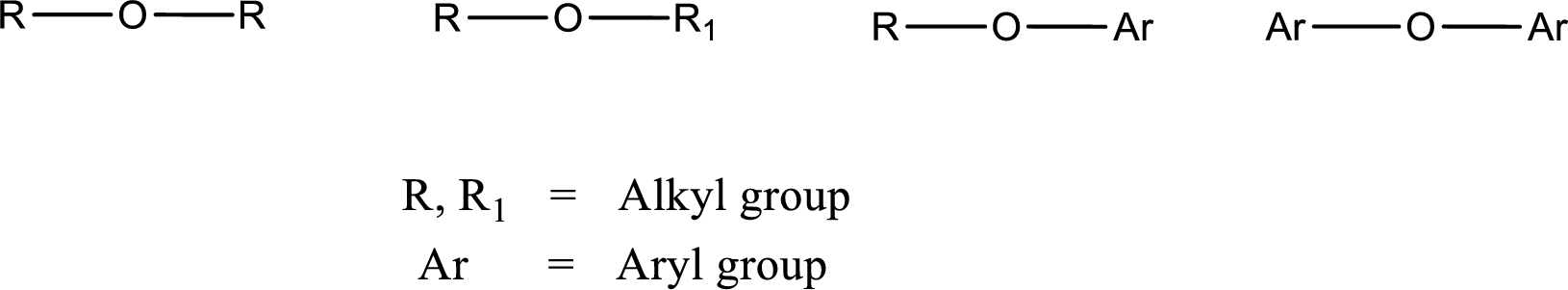
Alcohol is a compound in which a hydrocarbon group is bonded to a hydroxyl group. The generalized formula for alcohol can be given as,
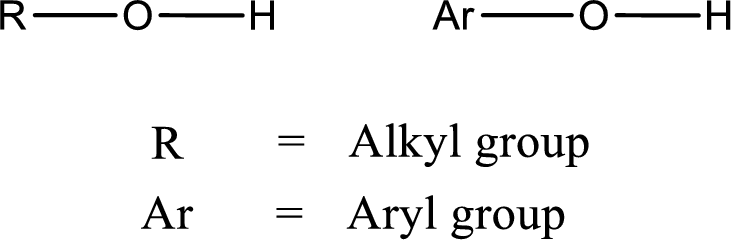
(c)
Interpretation:
The difference in meaning that is associated with the given pair of notations has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Ether is an organic compound. In ether, an oxygen atom is bonded to two carbon atoms by a single bond. The groups that are attached to the carbon atom by a single bond may be alkyl, aryl, or cycloalkyl groups. The functional group of ether is
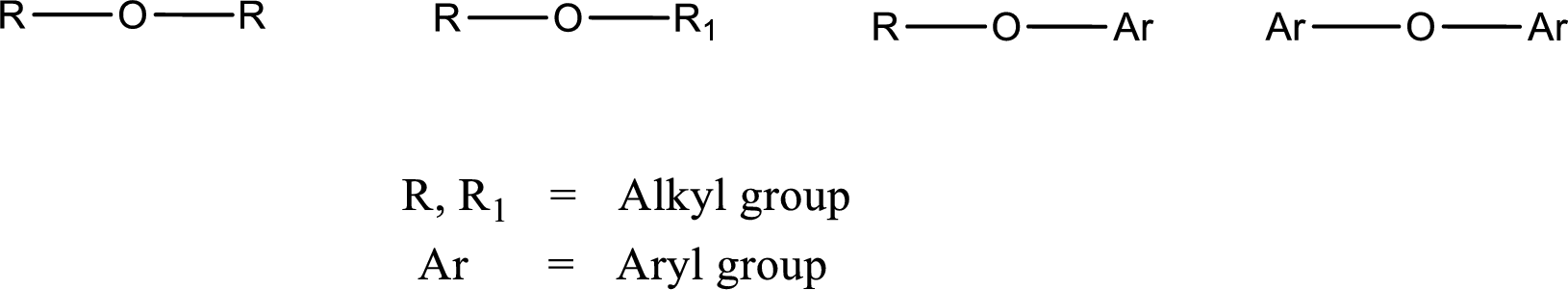
Alcohol is a compound in which a hydrocarbon group is bonded to a hydroxyl group. The generalized formula for alcohol can be given as,
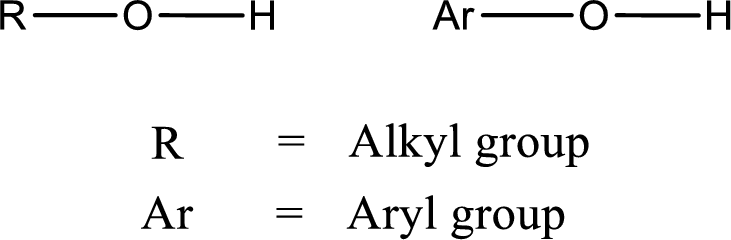
(d)
Interpretation:
The difference in meaning that is associated with the given pair of notations has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Ether is an organic compound. In ether, an oxygen atom is bonded to two carbon atoms by a single bond. The groups that are attached to the carbon atom by a single bond may be alkyl, aryl, or cycloalkyl groups. The functional group of ether is
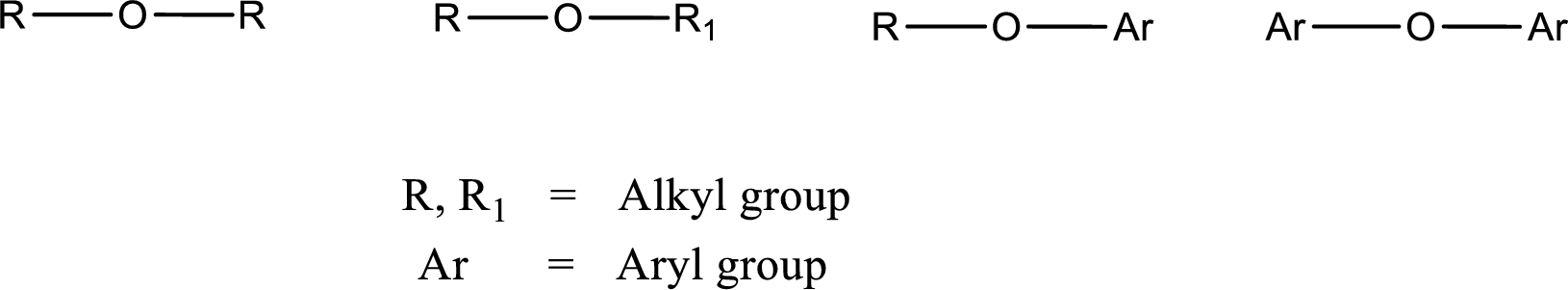
Alcohol is a compound in which a hydrocarbon group is bonded to a hydroxyl group. The generalized formula for alcohol can be given as,
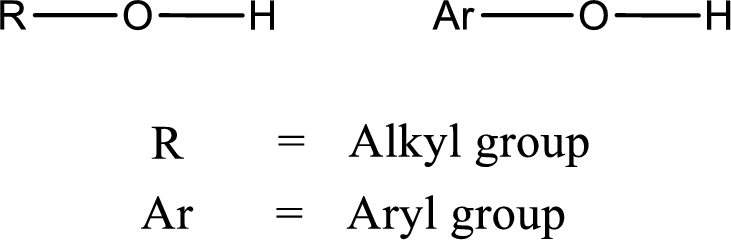
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Bundle: General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th + OWLv2 Quick Prep for General Chemistry, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- Change the bond between the two carbon atoms in each molecule to a double or triple bond as needed to complete the structure. If the bond should remain a single bond, then you do not need to do anything to the bond. Do not change any other bonds in the molecules. Molecule A Molecule B Select Draw Rings More Erase Select Draw Rings More Erase // H. H. H. H. H. H. 1. H - H. H. H. H. H.arrow_forwardThe functional group is the center of reactivity in an organic molecule. Identify the functional groups in the ff. structures. If a functional group is found more than once, it need be to be circled once.arrow_forwardF3 Use the following Lewis diagram for propene to answer the questions: HI 11 2 3 Remember that geometry refers to the geometry defined by the atoms, not the electron pairs. The geometry about atom 1 is The geometry about atom 2 is The geometry about atom 3 is Submit Answer $ 4 R F F4 % H 5 Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. Retry Entire Group F5 T G Cengage Learning Cengage Technical Support ^ 6 MacBook Air F6 9 more group attempts remaining Y H & 7 U * 00 8 FB ( 9 K F9 0 P Previous Email Instructor F11arrow_forward
- What is the correct set of names for molecules, N, P, R? N. CH3 - CH2 - OH Р. CНз-СH-сH-CH2 CI-CH2-CH2 R. CH3 - CH2 -C = CH-CH3 CH3-CH2-CH2-CH-CH3arrow_forwarddd. H3C-CH2-CH2-CEN Type of functional group H3C-CH,-CH2-CEN IUPAC H3C-CH2-CH2-CEN Common Name 1 H3C-CH,-CH2-CEN Common Name 2 (Derived Name) NH H2C-CH2-CH3 Type of functional group ее. NH H2C-CH2-CH3 Common Namearrow_forwardH₂C. C H₂ www CI CI Name using I.U.P.A.C nomenclature.arrow_forward
- Use the molecular structures below to answer the next 4 items. OH OH HO. A B с 22. Which among the illustrated molecules has a parent name of propenol? A. Molecule A B. Molecule B C. Molecule C D. Molecule D 23. Which molecule has an IUPAC name that possibly ends in -dienol? A. Molecule A B. Molecule B C. Molecule C D. MoleculeD 24. Which molecule is expected to have a parent name of methylethylethylene? A. Molecule A B. Molecule B C. Molecule C D. Molecule D D OH E OHarrow_forwardIf a drop of oleic acid is added to a dish of water, the oleic acid will spread out and form a layer that is one molecule thick on top of the water. (a) Draw the Lewis structure for oleic acid. (b) Label the region of the oleic acid molecule that is polar and the region that is nonpolar. (c) In the layer of oleic acid that forms, which part of the oleic acid molecule points down into the water and which part points out of the water?arrow_forward32. С-С-С Which of the following is another correct representation of the compound above? Oa. CH2-CH2-CH2 Ob. CH3-CH3-CH3 Oc. CH3-CH2-CH3 Od. CH4-CH3-CH4arrow_forward
- a. Br Mg+ C. Br + ether -780 ? Br d. Br Mgarrow_forward4. Identify which of the structures below correspond to a. b. C. d. CH,CH,CH,CH(CH3)2 f. (CH3)2(CH2)2CH(CH3)2 (CH3)2CH₂CH₂CH(CH3)2 CH3(CH2)2CH(CH3)2 e. g. h. H H H H—C—C—C—C | H H H с H H H I C-H CIHarrow_forwardREPRESENTATIONS OF ORGANIC MOLECULES Identifying isomers and resonance structures Determine the relationship between Structure A and Structure B in each row of the table. Structure A Structure B Relationship H. o isomers H. H H -H H-C- C-O -H- O resonance structures H H. H H Н—С—Н o neither H o isomers H :0: :0-H H. H H- C-C C-H H-C=C C=C-H O resonance structures H. H. H o neither o isomers :o: H H. H- O resonance structures H H H. H o neither 72°F DELL :ö: IIarrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





