
Concept explainers
To review:
The structures ofproducts of the reaction between nitrogenase complex and substrates hydrogen cyanide, dinitroge, nnd acetylene.
Introduction:
Nitrogenase complex is present in all the species that can fix nitrogen. It is produced by bacteria such as cyanobacteria. This reduces nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3). This is the only enzyme that can catalyze the reaction for nitrogen fixation.
Explanation of Solution
The nitrogenase complex consists of two proteins called dinitrogenase as well asdinitrogenase reductase. The dinitrogenase is heterotetramer of MoFe protein. The dinitrogenase reductase is called Fe(ferrous) protein. It contains Mg-ATP (magnesium-adenosine triphosphate)-binding sites. In the reaction catalyzed by this complex, there is a transfer of electrons from (4Fe-4S) cluster in Fe protein. The Fe transfers the electrons to Mo-Fe protein. The transfer of electrons leads to a reduction of H+. The incoming N2 exchanges withH+ within the active site to form stable intermediates. So, the reaction of nitrogenasecomplex with the given substrates is as follows:
When nitrogenase complex reacts with cyanide, it gives two product, sethylamine and methan, elong with ammonia:
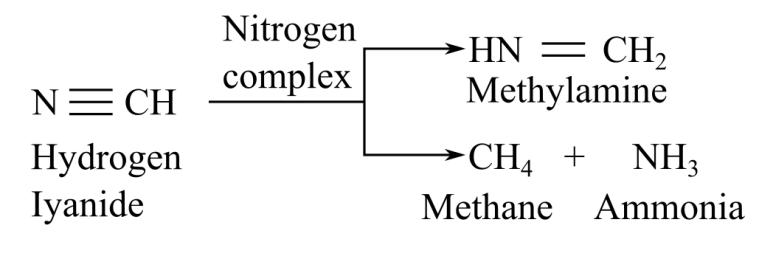
When nitrogenase complex reacts with acetylene, it gives ethylene as a product:
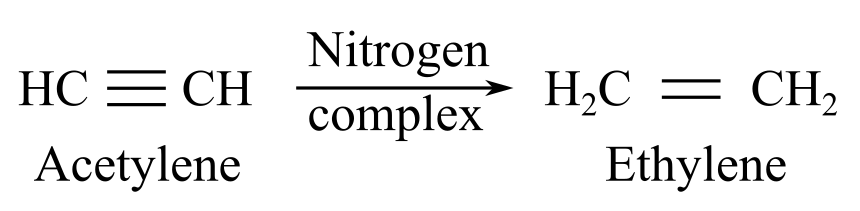
When nitrogenase complex reacts with dinitrogen, it gives hydrazine or ammonia as a product:
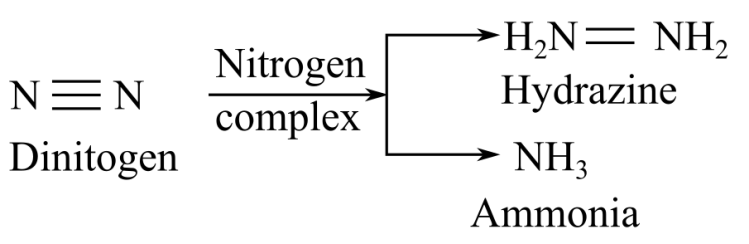
Thus, it can be concluded that the products of substrates hydrogen cyanide, acetylen, endnitrogen are methylamine, ethylene, and hydrazine, respectively.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Biochemistry: The Molecular Basis of Life
- Inhibition of Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism by Pharmacological Agents Indicate which reactions of purine or pyrimidine metabolism are affected by the inhibitors (a) azaserine, (b) methotrexate, (c) sulfonamides, (d) allopurinol, and (e) 5-fluorouracil.arrow_forwardUnderstanding the Mechanism of the -Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase Reaction tshe first step of the -Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase reaction involves decarboxylation of the substrate and leaves a covalent TPP intermediate. Write a reasonable mechanism for this reaction.arrow_forwardExtending the Mechanism of Methylmalonyl-CoA Mutase to Similar Reactions Based on the mechanism for the methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (see problem 14), write reasonable mechanisms for the following reactions shown.arrow_forward
- Understanding the Mechanism of the 3-ketosphinganine Synthase Reaction Write a reasonable mechanism for the 3-ketosphinganine synthase reaction, remembering that it is a pyridoxal phosphate-dependent reaction.arrow_forwardMake an electron-flow-mechanism for this synthetic scheme. This involves predicting major and by-products using electronic and structural effects. The arrow push mechanism must be shown.(from the reaction of α-ketoacids and oxaprolines to proteins that contain native serine residues ) with labelarrow_forwardThe substitution of His 64 of carbonic anhydrase II with Ala results in a sharp decrease in the activity of the enzyme in HEPES buffer (molecular weight of HEPES = 238.3 g/mol). However, increasing concentrations of imidazole (molecular weight = 68.1 g/mol) restores the reaction rate close to that of the wild-type enzyme. Propose an explanation for these results.arrow_forward
- How many tritium atoms (3H) are incorporated into palmitate when fattyacid synthesis is carried out in vitro with the following labeled substrate?arrow_forwardCarboxylic acids, such as the one shown below, can be difficult to reduce Provide the name of a reductant A. Explain why this reductant is able to react with the carboxylic acid whereas others cannot (Hint: Draw and discuss the potential reactive intermediates/transition states).arrow_forward. Separating Glycated Hb From Normal Hb (Integrates with Chapters 5and 6.) Human hemoglobin can react with sugars in the blood(usually glucose) to form covalent adducts. The a-amino groups ofN-terminal valine in the Hb b-subunits react with the C-1 (aldehyde)carbons of monosaccharides to form aldimine adducts, whichrearrange to form very stable ketoamine products. Quantitation ofthis “glycated hemoglobin” is important clinically, especially fordiabetic individuals. Suggest at least three methods by which glycatedHb (also referred to as HbA1c) could be separated from normal Hband quantitatedarrow_forward
- Ethyl alcohol is sometimes used in hospital emergency rooms to treat patients who have ingested radiator or gas-line antifreeze. A major chemical component of these products is methanol. The methanol itself is not especially harmful; however, it is transformed by enzymes called dehydrogenases to the very toxic substances, formaldehyde, and formic acid. Can you explain the biochemical principles behind this medical treatment?arrow_forwardRuBP carboxylaseis by no means an idesl enzyme. Describe some of the problems with its active site and its substrate specificity. If we compare the amino acid sequences of this enzyme from many different species, they are almost identical. What is the significance of this uniformity?arrow_forwardThe isoelectric point (pI) of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase is 6.0. Explain why the buffer used in DEAE cellulose chromatography must have a pH greater than 6 but less than 9 in order for the enzyme to bind to the DEAE resin.arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
