
Concept explainers
Consider the following bromination:
a. Calculate
b. Draw out a stepwise mechanism for the reaction, including the initiation, propagation, and termination steps.
c. Calculate
d. Draw an energy diagram for the propagation steps.
e. Draw the structure of the transition state of each propagation step.
(a)
Interpretation: The value of
Concept introduction: The value of
Answer to Problem 15.53P
The value of
Explanation of Solution
The given bromination reaction is,
In the given reaction,
The value of
Where,
•
•
The bond dissociation energy of
The bond dissociation energy of
The bond dissociation energy of
The bond dissociation energy of
Substitute the bond dissociation energy of
Therefore, the value of
The value of
(b)
Interpretation: The stepwise mechanism for the given reaction which includes initiation, propagation and termination steps is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The general steps followed by free-radical reaction are stated below:
1. First step is initiation that involves formation of radical.
2. Second step is propagation.
3. Third step is the termination that involves the formation of stable bond.
Answer to Problem 15.53P
The stepwise mechanism for the given reaction which includes initiation, propagation and termination steps is,
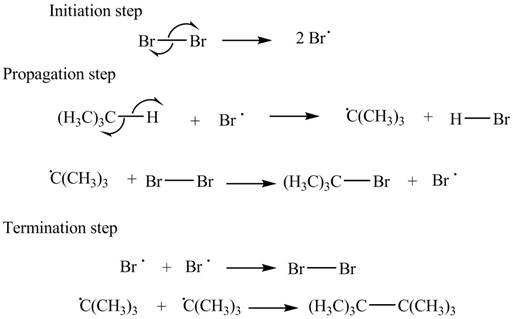
Figure 1
Explanation of Solution
The initiation step involves the generation of bromine radical by hemolytic cleavage of
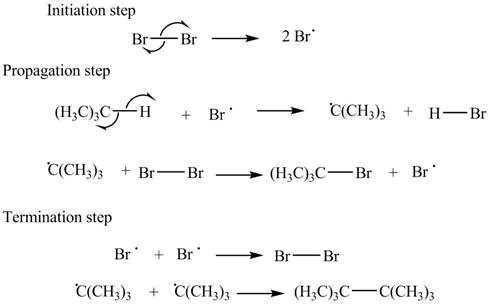
Figure 1
The stepwise mechanism for the given reaction which includes initiation, propagation and termination steps is shown in Figure 1.
(c)
Interpretation: The value of
Concept introduction: The general steps followed by free-radical reaction are stated below:
1. First step is initiation that involves formation of radical.
2. Second step is propagation.
3. Third step is the termination that involves the formation of stable bond.
Answer to Problem 15.53P
The value of
Explanation of Solution
The propagation step of given reaction involves two steps. In the first step
The value of
Where,
•
•
The bond dissociation energy of
The bond dissociation energy of
The bond dissociation energy of
The bond dissociation energy of
The value of
The value of
The value of
(d)
Interpretation: The energy level diagram for the propagation steps is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The graphical representation of chemical reaction in which x-axis represents energy of the reaction and y-axis represents the reaction coordinate is called energy profile diagram.
Answer to Problem 15.53P
The energy level diagram for the propagation steps is,
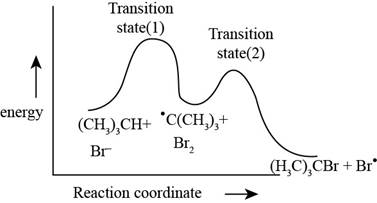
Figure 2
Explanation of Solution
The energy level diagram for the propagation steps is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2
The energy level diagram for the propagation steps is shown in Figure 2.
(e)
Interpretation: The structure of transition state of each propagation step is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The general steps followed by free-radical reaction are stated below:
1. First step is initiation that involves formation of radical.
2. Second step is propagation.
3. Third step is the termination that involves the formation of stable bond.
Answer to Problem 15.53P
The structure of transition state of first and second propagation step is,
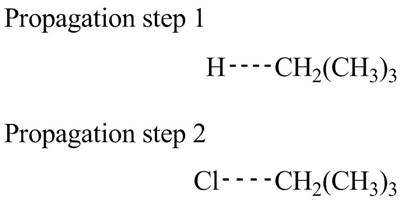
Figure 3
Explanation of Solution
The propagation step of given reaction involves two steps. In the first step
The transition state of the first propagation step is,
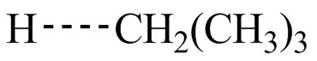
Figure 4
The transition state of the first propagation step is,
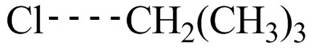
Figure 5
The structure of transition state of first and second propagation step is shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5, respectively.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Following is a balanced equation for the allylic bromination of propene. CH2==CHCH3 + Br2 h CH2==CHCH2Br + HBr (a) Calculate the heat of reaction, H 0, for this conversion. (b) Propose a pair of chain propagation steps and show that they add up to the observed stoichiometry. (c) Calculate the H 0 for each chain propagation step and show that they add up to the observed H 0 for the overall reaction.arrow_forwardReaction of (CH3)3CH with Cl2 forms two products: (CH3)2CHCH2Cl (63%) and (CH3)3CCl (37%). Why is the major product formed by cleavage of the stronger 1° C–H bond?arrow_forwardWhy is this reaction considered "green" chemistry and how is it different from a "non-green" bromination? Based on this is this reaction completely "green" chemistryarrow_forward
- A haloalkane reacts with a strong base to yield only one alkene product. Select the possible structures that can give this result from Figure 9. * A B C Darrow_forwardWhy does bromine's color disappear when Br2 is added to an alkene sample?arrow_forwardFinish ONE of the indicated reactions by filling in any starting materials, reagents, or products as needed.arrow_forward
- Organic Chemistry 1. EA27. Please explain why B. letter is the answer, and not A, C, or D letters ? Thanksarrow_forwardNeed help with Step 2arrow_forwardIn the reaction from compound 10 to compound 11, why the C=C bond is retained and is not hydrogenated? f) LiAlH4, Et2O, 08C; g) Ac2O, py, DMAP, CH2Cl2, RT, 77% over 2 steps;arrow_forward
- 1. b) Show the MECHANISM for the POLAR addition of molecular chlorine to cyclopentane. c) The reaction of toluene and ethylbenzene was through the alkyl groups, -CH 3 and -CH 2 CH 3, respectively. Why didn’t xylene, which has TWO methyl groups, react with bromine in the time allotted?arrow_forwardFree radical halogenation is used to replace one or more hydrogens on an alkane with one or more halogens (either chlorine or bromine). It is a substitution reaction. A student performs a free radical bromination on 3-methyl-pentane (5.88 g) to create the desired product of 3-bromo-3-methyl-pentane. The product mix, which hopefully contains almost all 3-bromo-3-methyl-pentane, is cleaned up by passing it through a gas chromoatograph, which separates out the 3-bromo-3-methyl-pentane from any undesired products made during the reaction (undesired products are created frequently in free radical halogenation). The initial product mix weighed 9.45 g; the purified 3-bromo-3-methyl-pentane weighed 7.21 g. What is the student's percent recovery?arrow_forwardIn the reaction observed in part III, where is the slow step? do you expect the reaction in part III to be faster for tert-butyl chloride or 2-chloropropane and why? Part III Silver Nitrate Test for Tertiary Alkyl Halides Set up the reaction. Obtain three 13 100 test tubes and label 13. Pipet 10 drops of distilled water into Test Tube 1. Pipet 10 drops of tert-butyl chloride into Test Tube 2 Pipet 10 drops of your product into Test Tube 3. Add approximately 1 mL of the 1% ethanolic silver nitrate solution to each test tube. Swirl each test tube to mix the contents. The appearance of a white precipitate indicates the presence of a 3° halide. Record your observations in the data table. Note: Avoid getting the AgNO3 solution on your skin. At the end of the experiment, discard the solutions as directed by your instructor. IMAGES PROVIDEDarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


