
Concept explainers
A gene expressed in long muscle of the mouse is identified, and the regulatory region upstream of the gene is isolated. Various segments of the upstream sequence are fused to the lacZgene, and each fusion is assayed to determine howefficiently it transcribes the gene. In the accompanyingdiagram, the dark bars indicate the upstream segments that are present in each of six different fusion genes. The transcriptional efficiency of each fusion is measured against thecontrol fusion, that is, the full-length upstream segmentfused to the lacZgene.
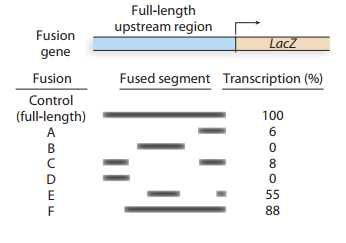
Identify the upstream region that contains theenhancer.
Identify the upstream region containing thepromoter.
Speculate about the reason for the different transcription rates detected in fusions E and F
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
GENETIC ANALYSIS: AN INTEG. APP. W/MAS
- An electrophoretic mobility shift assay can be used to study the binding of proteins to a segment of DNA. In the results shown here, an EMSA was used to examine the requirements for the binding of RNA polymerase |l (from eukaryotic cells) to the promoter of a protein-encoding gene. The assembly of general transcription factors and RNA polymerase Il at the core promoter is described in Week 4. In this experiment, the segment of DNA containing a promoter sequence was 1100 bp in length. The fragment was mixed with various combinations of proteins and then subjected to an EMSA. Lane 1: No proteins added Lane 2: TFIID Lane 3: TFIIB Lane 4: RNA polymerase IIl Lane 5: TFIID + TFIIB Lane 6: TFIID + RNA 1 2 3 4 5 6. 7 polymerase II Lane 7: TFIID + TFIIB + RNA polymerase Il 1100 bp Explain the results.arrow_forwardGal4 is a transcription factor that activates transcription of galactose metabolism genes in yeast. These genes are ‘turned on’ when yeast cells need to metabolize galactose. To identify promoter sequences necessary for regulation of transcription of GAL1, reporter gene fusions were made and introduced into yeast cells. Deletions of GAL1 promoter were cloned upstream of LacZ gene. β-Galactosidase activity was measured in presence of galactose. Shown below is a representation of the results obtained. In the diagrams below (not to scale!): • Construct 1 contains ~ 130bp of the promoter, which is predicted to have all the predicted/putative proximal promoter elements (indicated by the solid boxes) needed to regulate transcription of GAL1.• The stippled box is the core promoter.• The arrow represents the transcriptional start site for the reporter gene Lac Z• Number of + signs represents level of transcription• Star represents a mutation in DNA sequence at that location (few nucleotides…arrow_forwardGR and PPAR are transcription factors that bind to GRE and PPARE sequences respectively and activate transcription of genes. A reporter cell line is created in which the the green fluoresecent protein (GFP) is controlled by a GRE sequence and the pink fluorescent protein mCherry is under control of a PPARE sequence. If the gene for GR is introduced into the reporter cell line, the cells produce a green color. Chimeric proteins are created in which the DNA Binding Domains (DBD) and Activation Domains (AD) of the transcription factors are introduced into various cell lines. Match the following cell-types with the fluorescent color(s) you would expect the cells to produce.arrow_forward
- In the galactose operon of E. coli, a repressor, encoded by the galR gene, binds to an operator site,galo, to regulate the expression of three structuralgenes, galE, galT, and galK. Expression is inducedby the presence of galactose in the media. For eachof the strains listed, would the cell show constitutive, inducible, or no expression of each of the structural genes? (Assume that galR− is a loss-of-functionmutation.)a. galR−galo+galE+galT+galK+b. galR+galocgalE+galT+galK+ c. galR−galo+galE+galT+galK−/galR+galo+galE−galT+galK+d. galR−galocgalE+galT+galK−/galR+galo+galE−galT+galK+arrow_forwardFor each of the E. coli strains that follow, indicate theeffect of the genotype on the expression of the trpEand trpC genes in the presence or absence of tryptophan. [In the wild type (R+ P+ o+ att+ trpE+ trpC+),trpC and trpE are fully repressed in the presence oftryptophan and are fully expressed in the absence oftryptophan.]R = repressor gene; Rnproduct cannot bind tryptophan; R− product cannot bind operatoro = operator for the trp operon; o− cannot bind repressoratt = attenuator; att− is a deletion of the attenuatorP = promoter; P− is a deletion of the trp operonpromotertrpE− and trpC− are null (loss-of-function) mutationsa. R+ P− o+ att+ trpE+ trpC+b. R− P+ o+ att+ trpE+ trpC+c. RnP+ o+ att+ trpE+ trpC+d. R− P+ o+ att− trpE+ trpC+e. R+ P+ o− att+ trpE+ trpC−/R− P+ o+ att+trpE− trpC+f. R+ P− o+ att+ trpE+ trpC−/R− P+ o+ att+trpE− trpC+g. R+ P+ o− att− trpE+ trpC−/R− P+ o− att+trpE− trpC+arrow_forwardThe genes that encode the enzymes for arginine biosynthesis are located at several positions around the genome of E. coli, and they are regulated coordinately by a transcription regulator encoded by the ArgR gene. The activity of the Argr protein is modulated by arginine. upon binding arginine, Argr alters its conformation, dramatically changing its affinity for the DNA sequences in the promoters of the genes for the arginine biosynthetic enzymes. given that ArgR is a repressor protein, would you expect that ArgR would bind more tightly or less tightly to the DNA sequences when arginine is abundant? if ArgR functioned instead as an activator protein, would you expect the binding of arginine to increase or to decrease its affinity for its regulatory DNA sequences? explain your answers.arrow_forward
- Enhancer RPA Gene A Use the diagram above, which depicts a chromosomal region less than 500,000 bp, to determine the expression of each gene under the scenarios specified in the table. Regulatory promoters are indicated by "RP". Genes A, B, and C have intermediate expression when no regulatory proteins are bound. Complete the table by choosing high, intermediate, or low to describe the expression level of each gene under each specified scenario (i and ii). No regulatory proteins bound (i) A repressor binds to RPA and an activator binds to RPC (ii) A regulatory protein binds at each of the activator, insulator, and silencer. Expression of A? Intermediate 1. [Select] 4. [Select] Insulator RPB Expression of B? 2. Gene B Intermediate 5. [Select] [Select] Silencer RPC Expression of C? 3. Gene C Intermediate 6. [Select] [Select]arrow_forwardPlease describe the regulatory role of enhancers that binds to responsible regulators to activate the target gene at a given time and place through comparing different organisms according to the presence of regulatory sequences. regulatory promoter sequence bacteria FIGURE 19-1 The regulatory ele- ments of bacterial, yeast, and human genes. Illustrated is the increasing complex- ity of regulatory sequences from a simple bacterial gene controlled by a repressor to a human gene controlled by multiple activa- tors and repressors. In each case, a promoter is shown at the site where transcription is initiated. Although this is accurate for the bacterial case, in the eukaryotic examples, transcription initiates somewhat down- stream from where the transcription ma- chine binds (see Chapter 13). Some groups of regulatory binding sites in the human reg- ulatory sequences represent enhancers, as shown in one case. yeast human enhancerarrow_forwardIn the galactose operon of Escherichia coli, a repressor, encoded by the galR gene, binds to an operator site, galo, to regulate the expression of three structural genes, galE, galT, and galK. Expression is induced by the presence of galactose in the media. For each of the strains listed, would the cell show constitutive, inducible, or no expression of each of the structural genes? (Assume that galR−is a loss-of-function mutation.) galR− galo+ galE+ galT+ galK+ galR+ galoc galE+ galT+ galK+ galR− galo+ galE+ galT+ galK−/ galR+ galo+ galE− galT+ galK+ galR− galoc galE+ galT+ galK−/ galR+ galo+ galE− galT+ galK+arrow_forward
- In addition to Tc1, the C. elegans genome contains otherfamilies of DNA transposons such as Tc2, Tc3, Tc4, andTc5. Like Tc1, their transposition is repressed in thegerm line but not in somatic cells. Predict the behaviorof these elements in the mutant strains where Tc1 is nolonger repressed due to mutations in the RNAi pathway.Justify your answer.arrow_forwardMutations in bacterial promoters may increase or decrease therate of gene transcription. Promoter mutations that increasetranscription are termed up-promoter mutations, and those thatdecrease transcription are termed down-promoter mutations.The sequence of the −10 site of the promoter for the lac operonis TATGTT (see Figure 14.5). Would you expect each of thefollowing mutations to be an up-promoter or down-promotermutation?A. TATGTT to TATATTB. TATGTT to TTTGTTC. TATGTT to TATGATarrow_forwardThe PIC is highly conserved among species, from yeast to humans. Why is the positioning of the first TFII protein so important for proper transcription of the gene?arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





