
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The mole concept map is to be drawn. The volume of hydrogen sulfide
Concept introduction:
A mole of a substance is defined as the same number of particles of the substance as present in
Answer to Problem 21E
The mole concept map is shown below.
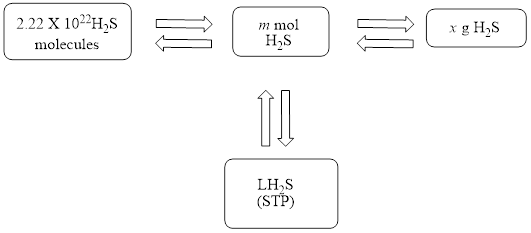
The volume of
Explanation of Solution
It is given that the number of molecules of
The mole concept map is shown below.

Figure 1
The Figure 1 shows that the number of moles should be calculated first, to calculate other parameters.
The number of moles is calculated from the relation shown below.
Therefore, the number of moles for
The volume of
The number of moles of
The volume for
Therefore, the volume of
The mole concept map is shown in Figure 1. The volume of
(b)
Interpretation:
The mole concept map is to be drawn. The mass of
Concept introduction:
A mole of a substance is defined as the same number of particles of the substance as present in
Answer to Problem 21E
The grams of
Explanation of Solution
It is given that the number of molecules of
The mole concept map is shown below.

Figure 1
The Figure 1 shows that the number of moles should be calculated first, to calculate other parameters.
The number of moles is calculated from the relation shown below.
Therefore, the number of moles for
The molar mass of hydrogen is
The molar mass of sulfur is
The mass of
The number of moles of
The mass for
Therefore, the mass of
The mass of
(c)
Interpretation:
The mole concept map is to be drawn and the molar concentration of
Concept introduction:
A mole of a substance is defined as the same number of particles of the substance as present in
Answer to Problem 21E
The molar concentration of
Explanation of Solution
It is given that the number of molecules of
The mole concept map is shown below.

Figure 1
The Figure 1 shows that the number of moles should be calculated first, to calculate other parameters.
The number of moles is calculated from the relation shown below.
Therefore, the number of moles for
The number of moles of
The formula to determine molarity is shown below.
Where
•
•
•
The relation between
The probable unit factors are given below.
The unit factor to determine
Therefore, the volume in
Substitute the value of number of moles as
Therefore, the molar concentration of
The molar concentration of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Pearson Etext Introductory Chemistry: Concepts And Critical Thinking -- Access Card (8th Edition)
- Grease fires can be extinguished by applying baking soda (sodium hydrogen carbonate), which decomposes due to the heat to produce sodium oxide, carbon dioxide and water. The carbon diocide produced helps to smother the flames. How many grams of baking soda would need to be thrown on to a fire to produce 0.500 moles (approximately 11 L) of carbon dioxide gas?arrow_forwardHow many moles of gas would be produced if 0.0595mol of sodium bicarbonate reacted completely with acetic acid,arrow_forwardt snowed, it melted and now the temperature is going to dip below freezing, to -2.00 °C overnight. You notice a puddle of water in the driveway of your house. You don’t want to start your morning by slipping on the ice, so you decide to put some salt down before the temperature dips. You guess the puddle contains about 10 L of water. How much salt (NaCl) would you have to throw into the water to prevent it from freezing? Molar mass of NaCl is 58.44 g/mol.arrow_forward
- 4. Phosphorus pentachloride reacts with water to give phosphoric acid and hydrogen chloride. In oneexperiment, 0.360 mol of phosphorus pentachloride was slowly added to 2.88 mole of water. Howmany grams of hydrogen chloride were formed in the reaction?arrow_forwardHow many particles are present in 936 milliliters of hydrogen gas at standard temperature and pressure? to the nearest thousandthsarrow_forwardwhat is the total volume if 20 cm² of oxygen react with 20cm² of hydrogenarrow_forward
- How many moles of aluminum oxide can form if 26.2 moles of Al metal react with an unlimited amount of oxygen?arrow_forwardHow many equivalents of O²⁻ are there in 2 moles of Al₂O₃?arrow_forwardNa2S2O3 (aq) + 4 Cl2 (g) + 5 H2O (aq) ---> 2 NaHSO4 (aq) + 8 HCl (aq) 168 grams of HCl were generated from the reaction shown by the equation, below. How much chlorine gas (Cl2) was destroyed during this process? Molar masses of solid chemical (given or desired) must be calculated if it is not provided in the context of the problem. First, calculate molar mass. An example of how to is attached. Next, set up and solve the problem exactly like the example attached.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





