
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
To identify the reagents used to convert methyl propanoate to the following compounds.
Concept introduction:
A reagent is a substance used to convert one chemical compound into another.
The structural formula for methyl propanoate is:
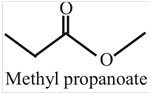
This compound can be converted into different compounds by undergoing a
(b)
Interpretation:
To identify the reagents used to convert methyl propanoate to the following compounds.
Concept introduction:
A reagent is a substance used to convert one chemical compound into another.
The structural formula for methyl propanoate is:

This compound can be converted into different compounds by undergoing a chemical reaction with reagents like water,
(c)
Interpretation:
To identify the reagents used to convert methyl propanoate to the following compounds.
Concept introduction:
A reagent is a substance used to convert one chemical compound into another.
The structural formula for methyl propanoate is:

This compound can be converted into different compounds by undergoing a chemical reaction with reagents like water,
(d)
Interpretation:
To identify the reagents used to convert methyl propanoate to the following compounds.
Concept introduction:
A reagent is a substance used to convert one chemical compound into another.
The structural formula for methyl propanoate is:

This compound can be converted into different compounds by undergoing a chemical reaction with reagents like water,
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Find two practical methods to prepare phenyl benzoatearrow_forwardWhat reagents would I use to produce 1-phenylethanol from 2-phenylethanol?arrow_forwardFor Fehling's Test not all aldehydes reacts to this test, what are the limitations and does the samples given below reacts to Fehling's Test? Explain a. formaldehyde b. glucose c. benzaldehyde d. acetonearrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

