
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
The number of unshared valence electrons on the metal is the number
Answer to Problem 18.9P
The
Explanation of Solution
The formula for calculation of
The formula for the calculation of oxidation state is given below
• n is the number of ligands.
•
•
•
Therefore, the oxidation state of
Now, valence electronic configuration of
L-type ligands have no effect on the
Value of
Therefore, the given complex is a
The value of
(b)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
The number of unshared valence electrons on the metal is the number
Answer to Problem 18.9P
The
Explanation of Solution
The formula for calculation of
The oxidation state of the metal is calculated by the formula given below.
Since phosphine is a neutral ligand and there is no overall charge on the complex.
The formula for the calculation of oxidation state is given below
• n is the number of ligands
•
•
•
So, the oxidation state of Pd in the complex is calculated as shown below.
Now, valence electronic configuration of
Value of
Therefore, the given complex is a
The value of
(c)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
The number of unshared valence electrons on the metal is the number
Answer to Problem 18.9P
The
Explanation of Solution
The given complex is shown below.
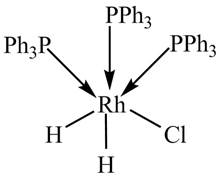
Figure 1
The formula for calculation of
The oxidation state of metal is calculated by the formula given below.
Since, phosphine is a neutral ligand.and there is no overall charge on the complex. The charge assosciated with chlorine and hydride ligands is
The formula for the calculation of oxidation state is given below.
• n is the number of ligands.
•
•
•
So, the oxidation state of Rh in the complex is calculated below.
The valence electronic configuration of Rh is
Value of
Therefore, the given complex is a
The value of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY SAPLING ACCESS + ETEX
- Four different octahedral chromium coordination compounds exist that all have the same oxidation state for chromium and have H2O and Cl as the ligands and counterions. When 1 mole of each of the four compounds is dissolved in water, how many moles of silver chloride will precipitate upon addition of excess AgNO3?arrow_forwardPredict whether the carbonate ligand CO32- will coordinate to a metal center as a monodentate, bidentate, or tridentate ligand.arrow_forwardGive the number of unpaired electrons in octahedral complexes with strong-field ligands for (a) Rh3+ (b) Mn3+ (c) Ag+ (d) Pt4+ (e) Au3+arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





