
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
Answer to Problem 21.1P
The structure of
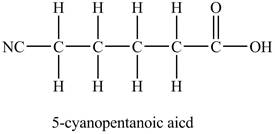
Explanation of Solution
In
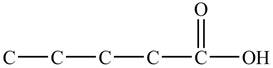
Figure 1
At the fifth carbon, there is a cyano group
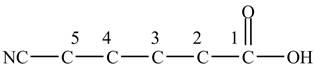
Figure 2
The above skeleton is completed by adding hydrogens as per the tetravalency of carbon as shown below.
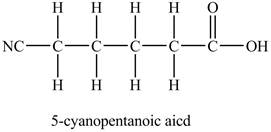
Figure 3
The structure of
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of isopropyl valerate is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
Answer to Problem 21.1P
The structure of isopropyl valerate is shown below.
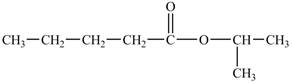
Explanation of Solution
The structure of isopropyl valerate consists of eight carbons, sixteen hydrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms. Isopropyl valerate is a common name of isopropyl pentanoate. It is a five carbon carboxylic acid. The structure of pentanoic acid is shown below.
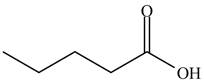
Figure 4
The hydrogen of carboxylic group is replaced by an isopropyl group to form an ester. The structure of isopropyl valerate is shown below.
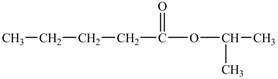
Figure 5
The structure of isopropyl valerate is shown in Figure 5.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of ethyl methyl malonate is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
Answer to Problem 21.1P
The structure of ethyl methyl malonate is shown below.
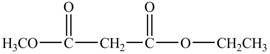
Explanation of Solution
The structure of ethyl methyl malonate consists of a eight carbons, fourteen hydrogen and four oxygen. Ethyl methyl malonate consists of propane dioic acid as parent chain.
The structure of propane dioic acid is shown below.
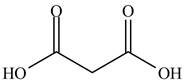
Figure 6
In the above structure, at first position hydrogen is substituted by a methyl group and at the last carboxyl group an ethyl group replaces the hydrogen of the carboxyl group. The structure of ethyl methyl malonate is shown below.
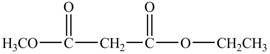
Figure 7
The structure of ethyl methyl malonate is shown in Figure 6.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of cyclohexyl acetate is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
Answer to Problem 21.1P
The structure of cyclohexyl acetate is shown below.
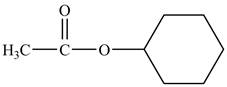
Explanation of Solution
Cyclohexyl acetate consists of a cyclohexane ring and an acetate group. The acetate group is given by the formula
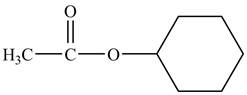
Figure 8
The structure of cyclohexyl acetate is shown in Figure 8
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure of
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
Answer to Problem 21.1P
The structure of
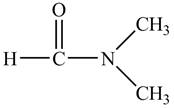
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
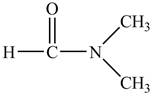
Figure 9
The structure of
(f)
Interpretation:
The structure of
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
Answer to Problem 21.1P
The structure of
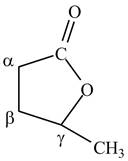
Explanation of Solution
Lactones are cyclic esters. The structure of
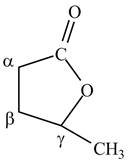
Figure 10
The structure of
(g)
Interpretation:
The structure of glutarimide is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
Answer to Problem 21.1P
The structure of glutarimide is shown below.
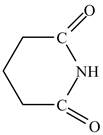
Explanation of Solution
The structure of glutarimide consists of a piperidine ring. There are two carbonyl group present adjacent to the nitrogen group. The structure of a piperidine ring is shown below.
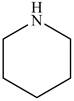
Figure 11
Therefore, the structure of glutarimide is shown below.
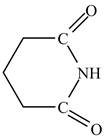
Figure 12
The structure of glutarimide is shown in Figure 12.
(h)
Interpretation:
The structure of
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
Answer to Problem 21.1P
The structure of
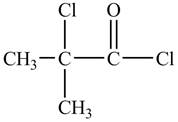
Explanation of Solution
There is carboxyl group present in
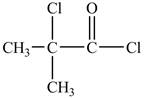
Figure 13
The structure of
(i)
Interpretation:
The structure of
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
Answer to Problem 21.1P
The structure of
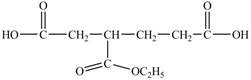
Explanation of Solution
In
Figure 14
In the above structure there is a ethoxy carbonyl group at the third position. Therefore, the structure of
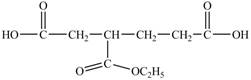
Figure 15
The structure of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY SAPLING ACCESS + ETEX
- Explain why we speak of acidic hydrolysis of an ester as acid-catalyzed, but of basichydrolysis as base-promotedarrow_forwardThe hydrolysis of the ester shown here is catalyzed by morpholine. Explain how morpholine catalyzes the reaction. (Hint: The pKa of the conjugateacid of morpholine is 9.3, so morpholine is too weak a base to function as a base catalyst.)arrow_forwardA synthesis of the pain reliever phenacetin is outlined in the following equation. What is the structure of phenacetin?arrow_forward
- For the following reaction scheme, identify by drawing the reagents b and d and the intermediate c that are formed in the synthesis of benzoic acid.arrow_forwardPropose the structure of a starting material that would allow you to use the procedures given to synthesize acetaminophenarrow_forwardGive the clear handwritten answer and complete the reactionarrow_forward
- Which among the following statements best explains the purpose that sulfuric acid serve in the nitration test for aromaticity? A. a protecting group to prevent over-nitration B. a source of electrophiles to activate the aromatic ring for nitration C. a catalyst to convert nitrate to nitrite ion D. a temporary electrophile followed by its replacement with nitronium ion E. a catalyst to convert nitrate to nitronium ion Kindly explain your answer.arrow_forwardGive steucture of organic and inorganic products of the following sn2 reaction, and identify the nucleophile, substrate, and leaving group.arrow_forwardStarting with the following compounds, outline a practical synthesis of 1-butanolarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





