
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The structures of the two different
Concept introduction:
舧 A carbohydrate is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen-oxygen atom ratio of 2:1
舧
舧 Carbohydrates are oxidized by
舧 Aldaric acids are carbohydrates having two
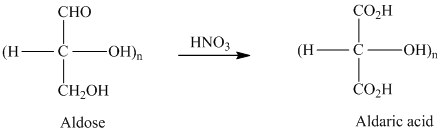
舧
舧 Aldaric acids (obtained from oxidation of aldohexoses) produces lactones of the same order that is as:
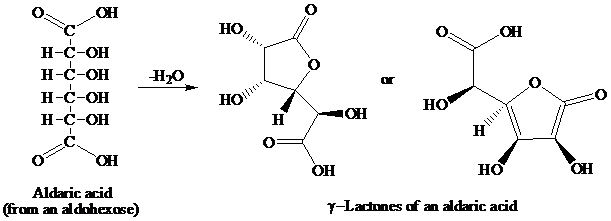
舧 The reaction in which there is removal of water molecule is called dehydration reaction.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- (ii) Describe the key molecular structure features of the pharmacologically active 2- oxazolidinone group of antibacterial agents.arrow_forwardGive the expected organic product when phenylacetic acid, PhCH2COOH, is treated with reagent Q.)NaHCO3, H2Oarrow_forward1. Draw structures corresponding to the following IUPAC names: (a) 4-Methylpentanoic acid (b) o-Hydroxybenzoic acid (c) 2,2-Dimethylpropanoyl chloride (d) trans-2-Methylcyclohexanecarboxamide (e) p-Methylbenzoic anhydride (f) p-Bromobenzonitrilearrow_forward
- Give the chemical tests to distinguish between following pair of compounds : (i) Propanol and propanone (ii) Ethyl acetate and methyl acetate (iii) Benzaldehyde and benzoic acid (iv) Benzaldehyde and acetaldehyde (v) Formic acid and acetic acid (vi) Propanal and propanol (vii) Ethanoic acid and ethylethanoatearrow_forwardGive reasons: (i) Bond length of C = O in carboxylic acids is slightly larger than C = O bond length in carbonyl compounds. (ii) There are two –NH2 groups in semicarbazide. However, only one –NH2 group is involved in the formation of semicarbazones. (iii) Benzoic acid is less soluble in water than acetic acid. (iv) Formic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid.arrow_forwardWhich Compound Is Oxidized To Benzoic Acid With K2Cr2O7 In Acidic Medium?arrow_forward
- Please draw the skeletal formula of the following compounds: (A) Isobutyraldehyde (B) α-Ethyl-γ-methoxycaproaldehyde (C) 6-Hydroxyhexanal (D) 2,4-Pentanedione (E)3-Cyano-7-oxoheptanoic acidarrow_forwardGive one chemical test to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds : (i) Methylamine and dimethylamine (ii) Secondary and tertiary amines (iii) Ethylamine and aniline (iv) Aniline and benzylamine (v) Methylamine and methanol (vi) Methylamine and N, N-Dimethylamine (vii) Ethanol and ethanaminearrow_forward19.62 Naltrexone is used to help recovering narcotic addicts stay drug free. HO O OH naltrexone LO1,6,7 (a) Label and name all the functional groups. Where relevant, indicate whether the group is primary, secondary or tertiary. (b) Upon addition of dilute hydrochloric acid solution, naltrexone forms a water-soluble salt. Draw the structure of this salt.arrow_forward
- Consider the following compounds: Compound E: benzoic acid Compound F: benzoyl chloride Compound G: benzamide Compound H: benzaldehyde a) Identify the compound can be oxidised into compound E. b) Select one compound that can undergo alcoholysis to yield an ester. c) Select two compounds which áre known as carboxylic acid derivatives.arrow_forwardPredict the products formed when limonene reacts with the followingreagents.(a) excess HBr (b) excess HBr, peroxides (c) excess Br2 in CCl4(d) ozone, followed by dimethyl sulfidearrow_forward(a) Draw the structure of the following :(i) p-Methylbenzaldehyde (ii) 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one(b) Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :(i) Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate, (ii) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone.(iii) Phenol and Benzoic acid.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
