(a)
Interpretation:
The compound that neutralizes
Concept introduction:
The neutralization reaction is defined as the reaction between acid and base in order to produce salt and water.
(b)
Interpretation:
The compound that neutralizes
Concept introduction:
The neutralization reaction is defined as the reaction between acid and base in order to produce salt and water.
Nucleophilic substitution reaction
(c)
Interpretation:
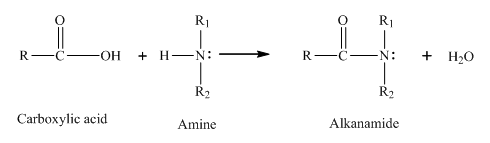
The compound that forms amide with ethanoic acid should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Amine reacts with a carboxylic acid to form an amide. The general reaction between a carboxylic acid and an amine is as follows:
(d)
Interpretation:
The compound reacts with ammonia should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction
Nucleophilic substitution reaction
(e)
Interpretation:
The compound that reacts with
Concept introduction:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction
Nucleophilic substitution reaction
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 27 Solutions
Generl Chem Looself&mod Mst/et&stdy Crd Pkg, 11/e
- 1. What type of reaction explains solubility of phenol in sodium hydroxide? Explain the organic product formed. 2. How do the reactions of phenol samples with FeCl3 compare? Which structural component of the phenols account for the observationarrow_forwardTiO2 is one of the most useful materials to decompose organic substances using photocatalytic oxidation. What final products of photocatalytic oxidation over TiO2 do you expect for the following two substances: phenyl isothiocyanate and trinitrotoluene, assuming complete mineralization of these compounds in photocatalytic processes? Write a chemical formula for a whole reaction for each compound and explain the reactions.arrow_forwardWhy do you wash the dichloromethane solution of your reductive amination product with sodium bicarbonate, rather than dilute aqueous HCl? a) Sodium bicarbonate is a good method of removing aldehydes from organic solvent.b) The amine product will be protonated by acid and remain in the aqueous layer as a salt.c) Sodium bicarbonate transfers the amine starting material into the aqueous layer.d) Sodium bicarbonate reacts with leftover NaBH(OAc)3 and removes it from the mixture.arrow_forward
- a) Write down the products that will occur when you extract HBr from 2-bromo-3-methyl butane in a basic medium, State the reaction conditions. Show which product is the main product. b) Does the main product show the geometric isomer, so please write together. If it shows write the isomers. c) Write the product that will be formed when the main product reacts with KMnO4 in a basic environment in coldarrow_forwardIn which of the statements given below, the event is not an oxidation reaction? A. Reaction of an alkyl halide with ammonia B. Formation of the product as a result of the reaction of 2-propene at KMnO4 / Basic ambient temperature C. Formation of the product as a result of the reaction of 2-propene in KMnO4 / Basic medium cold D. Formation of the product as a result of the reaction of benzoine with nitric acid E. CH3CH2OH + KMnO4 ® CH3COOHarrow_forwardGive only typing answer with explanation and conclusion Which of the following statements is/are incorrect? (6,25 p) I- In order for an organic compound to be a dyestuff, it must be chromor and auxochrochrome. II- Hydroxyl or amino groups can be given as examples of chromophore groups III- Decrease of chromophore groups in a molecule causes color deepening. A. b) II, III B. a) I only C. d) II only D. c) III onlyarrow_forward
- Define Reaction of ROH with PBr3arrow_forwardShow how to convert carboxylic acids to other functional groups, and devisemultistep syntheses using carboxylic acids as starting materials and intermediates.Explain how acid chlorides are used as activated derivatives of carboxylic acidsarrow_forwardDescribe the following giving the relevant chemical equation in each case: (i) Carbylamine reaction (ii) Hoffmann’s bromamide reaction.arrow_forward
- Given the chemical equation in the synthesis of benzoic acid from toluene and potassium permanganate: C7H8(I) + 2KMnO4(aq) → KC7H5O2 + 2MnO2 (s) + KOH (aq) + H2O (I) KC2H5O2 (aq) + HCl (aq) → C7H8O2 (s) + KCl (aq) MW: C7H8 = 92.14 KMnO4 = 158.03 MnO2 = 86.94 KC7H5O2 = 160.21 C7H8O2 = 122 Density: C7H8 = 0.87 g/mL KMnO4 = 2.7 g/mL KC7H5O2 = 1.5 g/mL C7H8O2 = 1.27 g/mL If 1 mL of toluene and 4 mL of 50% w/v potassium permanganate solution are used to synthesize the benzoic acid in a reflux set-up, calculate the theoretical yield of benzoic acid. Show your complete solution and underline your final answer.arrow_forwardExplain why iodine (I2) does not react with ethane, even though I2 is more easily cleaved homolytically than the other halogens.arrow_forwarda) Write down the products that will occur when you withdraw HBr from 2-bromine-3-methyl butane in a basic medium, State the reaction conditions. Show which product is the main product. b) Does the main product show the geometric isomer, so please write together. If it shows write the isomers. c) Write the product that will be formed when the main product reacts with KMnO4 in a basic environment in cold.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
