
Interpretation:
The correct product should be identified for the given [1, 3] sigmatropic rearrangement reaction.
Concept introduction:
In a sigmatropic reaction “ one new sigma-bond is formed as another breaks.”
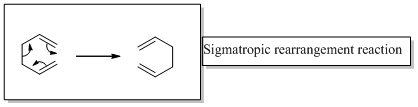
Sigmatropic rearrangement reactions are designated with digits. For example a [1, 3] sigmatropic rearrangement describe a reaction in which the residue migrates from position 1 to position 3.
[3,3] sigmatropic rearrangement of a 1,3-diene known as Cope rearrangement reaction.
Woodward –Hoffmann rules are the set of rules used to vindicate or predict certain aspects of the stereo chemical outcome and activation energy of pericyclic reactions.
Woodward – Hoffmann rules for sigmatropic rearrangement reactions are listed below


Carbon migrating with one lobe of its p orbital interacting
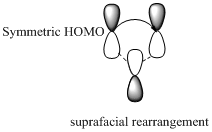

Carbon migrating with both lobe of its p orbital interacting

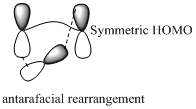
of configuration is the inversion of a chiral center in a molecule in a
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 28 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY W/ST.GDE W/ACCESS
- What happens to the rate of an SN1 reaction under the following conditions? [RX] is tripled, and [:Nu−] stays the same.arrow_forward1. Which among these would be the most stable carbocation?a. Allylicb. Vinylicc. Primaryd. Secondary2. What is the primary reason for the stability of tertiary carbocations?a. Free rotationb. Resonancec. Hyperconjugationarrow_forwardWhich reaction below gives a single enantiomer of a chiral product?arrow_forward
- Draw the product of the [3,3] sigmatropic rearrangement of each compound.arrow_forwardWith reference to diene A:a. What product is formed when A undergoes a [2 + 2] cycloaddition?b. What product is formed when A undergoes a [3,3] sigmatropic rearrangement?arrow_forwardA8 Is there anyone who can provide this pericyclic rxn mechanism?arrow_forward
- Considering both 5-methylcyclopenta-1,3-diene (A) and 7methylcyclohepta-1,3,5-triene (B), which labeled H atom is most acidic? Which labeled H atom is least acidic? Explain your choices.arrow_forwardWhich alkyl halide from the following pair is (i) Chiral and (ii) undergoes SN1 reaction faster?(a) (CH3)2CBr(b) CH3CH2CHBrCH3arrow_forwardWhat happens to the rate of an SN1 reaction under the following conditions? [Both [RX] and [:Nu−] are tripled.arrow_forward
- Which of the following are correct? Correct any false statements. a. A conjugated diene with an even number of double bonds undergoes conrotatory ring closure under thermal conditions. b. A conjugated diene with an antisymmetric HOMO undergoes conrotatory ring closure under thermal conditions. c. A conjugated diene with an odd number of double bonds has a symmetric HOMO.arrow_forwardWhat product is formed by the [3,3] sigmatropic rearrangement of each compound?arrow_forwardConsidering both 5-methylcyclopenta-1,3-diene (A) and 7-methylcyclohepta-1,3,5-triene (B), which labeled H atom is most acidic?Which labeled H atom is least acidic? Explain your choices.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
