
Concept explainers
The following ordinary
where
The spring is cubic spring and is also nonlinear with
The initial conditions are
Initial velocity
Initial displacement
Solve this equation using a numerical method over the time period
(a) A similar linear equation;
(b) The nonlinear equation with only a nonlinear spring term
(c) The nonlinear equation with only a nonlinear damping term
(d) The full nonlinear equation where both the damping and spring terms are nonlinear
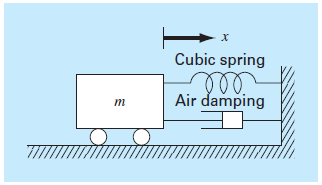
FIGURE P28.46
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 28 Solutions
EBK NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ENGINEERS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Basic Technical Mathematics
Fundamentals of Differential Equations (9th Edition)
Statistical Reasoning for Everyday Life (5th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry: Graphs and Models (6th Edition)
- 2. Consider a car suspension, modeled as a mass/spring/damper system (mass m, stiffness k, damping b). Suppose the height of the chassis is lo at rest, the height of the terrain below the driver varies as h(t), and the height of the chassis is denoted lo + y(t). (i.e., spring deflection away from rest is y(t) – h(t)). 2 (a) Give the transfer function G(s) = H(s) · = (b) Suppose the ground follows an oscillatory profile h(t) A cos(wx (t)) with magnitude A (in meters) and frequency w (measured in radians per meter). Suppose the car is traveling at a constant forward speed v. Using a frequency response analysis strategy, give the amplitude of oscillations experienced by the driver at steady state as a function of m, k, b, A, w, and v. Hint: You can't simply consider |G(iw)| to get the amplification in this case. (c) Suppose the ground varies by A = 5cm, w = 2 rad/m, and you are driving at v = 15 m/s. Using your answer to part (b), what amplitude of oscillation is felt by the driver when m…arrow_forward1. Verify Eqs. 1 through 5. Figure 1: mass spring damper In class, we have studied mechanical systems of this type. Here, the main results of our in-class analysis are reviewed. The dynamic behavior of this system is deter- mined from the linear second-order ordinary differential equation: where (1) where r(t) is the displacement of the mass, m is the mass, b is the damping coefficient, and k is the spring stiffness. Equations like Eq. 1 are often written in the "standard form" ď²x dt2 r(t) = = tan-1 d²r dt2 m. M +25wn +wn²x = 0 (2) The variable wn is the natural frequency of the system and is the damping ratio. If the system is underdamped, i.e. < < 1, and it has initial conditions (0) = zot-o = 0, then the solution to Eq. 2 is given by: IO √1 x(1) T₁ = +b+kr = 0 dt 2π dr. dt ل لها -(wat sin (wat +) and is the damped natural frequency. In Figure 2, the normalized plot of the response of this system reveals some useful information. Note that the amount of time Ta between peaks is…arrow_forwardASAParrow_forward
- 1. A spring mass system serving as a shock absorber under a car's suspension, supports the M 1000 kg mass of the car. For this shock absorber, k = 1 × 10°N /m and c = 2 × 10° N s/m. The car drives over a corrugated road with force %3| F = 2× 10° sin(@t) N . Use your notes to model the second order differential equation suited to this application. Simplify the equation with the coefficient of x'" as one. Solve x (the general solution) in terms of w using the complimentary and particular solution method. In determining the coefficients of your particular solution, it will be required that you assume w – 1z w or 1 – o z -w. Do not use Matlab as its solution will not be identifiable in the solution entry. Do not determine the value of w. You must indicate in your solution: 1. The simplified differential equation in terms of the displacement x you will be solving 2. The m equation and complimentary solution xe 3. The choice for the particular solution and the actual particular solution x,…arrow_forward6. A 1kg mass is attached to a spring (with spring constant k = 4 N/m), and the spring itself is attached to the ceiling. If you pull the mass down to stretch the spring past its equilibrium position, when you release the mass and observe its (vertical) position, it's said to undergo simple harmonic motion. AT REST MASS PULLED DOWN wwww Under certain initial conditions, the mass's vertical position (in metres) relative to its equilibrium position at time t, y(t), can be modelled by the equation y(t) = cos(2t) – sin(2t), (Note that y measures how much the spring has been stretched, so y = 1 indicates the mass is Im below its equilibrium position, whereas y = -1 indicates it is 1m above its equilibrium position.) (a) Find expressions for the mass's (vertical) velocity v(t) (relative to its equilibrium position) and the mass's (vertical) acceleration a(t) (relative to its equilibrium position). (b) Is the mass moving toward the ceiling or toward the floor at t= T? Justify your answer with…arrow_forwardA spring with mass 1 kg is attached to one side of a spring with spring constant k = 12 kg/sec2. The other end of the spring is connected to the side of a steel beam so that the spring may oscillate in the horizontal direction. Suppose that friction is proportional to velocity with constant of proportionality f = 7 kg/sec. Write a differential equation for y(t), the position of the mass at time t, with the initial conditions y(0) = 0 and y(0) =1 m/sec. Solve your resulting IVP.arrow_forward
- 3. Consider a mass - spring - damper system with mass of 3, damping constant 6, and spring constant 12, and an external force of r(t) = 3 cos(wt). (a) Find the value of w that will result in the largest amplitudes in the steady state of the system. (b) Using your value of w from part a), find a function to describe the displacement of the system as a function of time, if the initial displacement is 1, and the initial velocity is 0. (c) Suppose the external force of r(t) = 3 cos(wt) is then stopped, the system is returned to its equilibrium position (so it has 0 displacement and 0 velocity), and an instantaneous force is applied, given by r(t) = 36(t - 2). Find a function that describes the displacement of the system as a function of time with this new input.arrow_forwardProblem 2.151: Energy Dissipated in Viscous Damping Find the energy dissipated during a cycle of simple harmonic motion given by x(t)=0.2sinwot (m) by a viscously damped single-degree-of-freedom system with the following parameters. (a) m=10 kg, c=50 (b) m = 10 kg, c=150 N• sec m N sec m k = 1,000 k = 1,000 N m N marrow_forward1. Suppose you are riding your bicycle on a bumpy road having a surface profile that varies harmonically with +/- 6 cm undulations. The distance between consecutive peaks of these undulations is 2 m. When you sit on the seat of your bike for your casual ride, the springs deflect 5 cm. When you are seated, the damper under the seat provides an equivalent linear viscous damping of 10% of the critical damping. A simple representation of your ride on the "never-ending" rough road is shown below. (a) If you are riding your bicycle at a horizontal speed of 2.5 m/sec, how much bumping up and down will you experience? (b) Next day, you are carrying a backpack which increases your on-seat weight by 20%. Assuming that you are still able to ride with same speed, will this "loaded" ride be more or less comfortable than your previous, "no backpack" ride? M k/23 k/2 6 cm 2 marrow_forward
- Consider the spring mass damper system shown below. k m x(t) The forces of the spring and damper are represented by Fspring = -kx and Fdamper = -bx' respectively, where k is the spring constant and b is the damping coefficient. The mass has an initial displacement +1 m and velocity 0 m/s. 1. Use Newton's 2nd Law of Motion to derive an ODE to describe the mass's motion. 2. Find x (t) for m = 2 kg, b = 1 N s/m and k = {0.1,0.3,0.5} N. m. What happens when the stiffness of the spring is being increased?arrow_forwardThe equivalent spring stiffness of an inclined spring whose k = 5 N/m and angle of inclination θ = 35° 3.355 N/m 4.095 N/m 5.867 N/m 4.511 N/marrow_forwardThe relative displacement u(t) of a single-storey shear building subjected to an earthquake ground motion is represented by the following second-order linear ordinary differential equation: d?u dt2 du + c + ku = a, (t) m dt where m, c, and k are the mass (kg), damping constant (Ns/m), and stiffness of the structure (N/m), respectively. Meanwhile, a,(t) is the function of earthquake ground acceleration. Suppose the building with a mass of 2000 kg and supported by columns of combined stiffness of 32 x 103 N/m is subjected to earthquake with ground acceleration given by the following function: ag(t) = 36000 cos 2t Find the equation of the displacement, u(t), given the damping is not installed to the building. Then, find how much the building is displaced from t =30 seconds to t =60 seconds of earthquake.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





