
Concept explainers
The following unadjusted
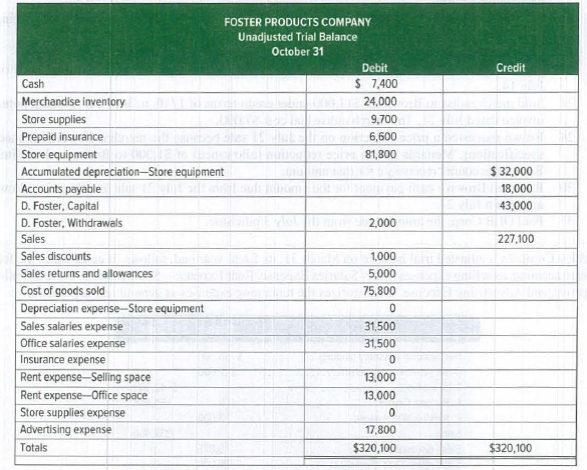
Required
- 1. Prepare
adjusting journal entries to reflect each of the following:- a. Store supplies still available at fiscal year-end amount to $3,700.
- b. Expired insurance, an administrative expense, for the fiscal year is $2,800.
- c. Depreciation expense on store equipment, a selling expense, is $3,000 for the fiscal year.
- d. To estimate shrinkage, a physical count of ending merchandise inventory is taken. It shows $21,300 of inventory is still available at fiscal year-end.
- 2. Prepare a multiple-step income statement for the year ended October 31 that begins with gross sales and includes separate categories for net sales, cost of goods sold, selling expenses, and general and administrative expenses.
- 3. Prepare a single-step income statement for the year ended October 31.
- 4. Compute the
current ratio , acid-test ratio, and gross margin ratio as of October 31. (Round ratios to two decimals.)
1.
Journalize adjusting entries of Company FP.
Explanation of Solution
Journal entry: Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Adjusting entries: Adjusting entries are those entries which are recorded at the end of the year, to update the income statement accounts (revenue and expenses) and balance sheet accounts (assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity) to maintain the records according to accrual basis principle.
Record the adjusting entries of Company FP.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| a. | Store supplies expense (1) | 6,000 | ||
| Store supplies | 6,000 | |||
| (To record store supplies expense) | ||||
| b. | Insurance expenses | 2,800 | ||
| Prepaid expenses | 2,800 | |||
| (To record prepaid selling expenses) | ||||
| c. | Depreciation expense - Store equipment | 3,000 | ||
| Accumulated Depreciation - Store equipment | 3,000 | |||
| (To record depreciation expenses) | ||||
| d. | Cost of goods sold | 2,700 | ||
| Merchandise inventory (2) | 2,700 | |||
| (To record the inventory shrinkage) |
Table (1)
a. To record store supplies expense:
- Store supplies expense is an expense account and it is increased. Therefore, debit office supplies expense with $6,000.
- Store supplies are an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit office supplies with $6,000.
b. To record prepaid insurance expenses:
- Insurance expense is an expense account and it is increased. Therefore, it is debited with $2,800.
- Prepaid expense is an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit prepaid selling expense with $2,800.
c. To record depreciation expenses:
- Depreciation expense is an expense account and it is increased. Therefore, it is debited with $3,000.
- Prepaid expense is an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit prepaid selling expense with $3,000.
d. To record the shrinkage of inventory:
- Cost of goods sold is an expense and they are increased. Thus, it is debited with $2,700.
- Inventory is an asset account, and they are increased. Hence, debit the inventory returns estimated account by $2,700.
Working Note:
Compute the Store supplies expense.
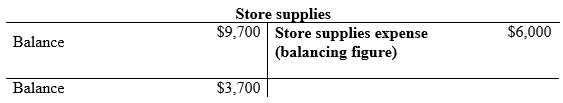
…… (1)
Compute the shrinkage of inventory.
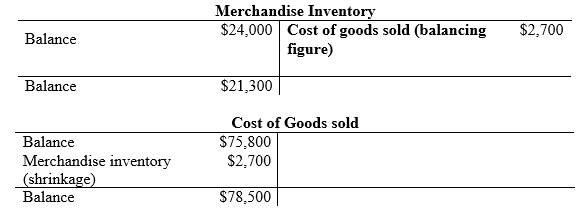
…… (2)
2.
Prepare the multi- step income statement of Company FP for the year ended October 31.
Explanation of Solution
Multi-step income statement: The income statement represented in multi-steps with several subtotals, to report the income from principal operations, and separate the other expenses and revenues which affect net income, is referred to as multi-step income statement.
Prepare the income statement of Company FP for the year ended October 31.
| Company FP | ||
| Statement of Income | ||
| For the year ended October 31 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Sales | $227,100 | |
| Less: Sales discounts | $1,000 | |
| Sales returns and allowances | $5,000 | ($6,000) |
| Net sales | $221,100 | |
| Less: Cost of goods sold (2) | ($78,500) | |
| Gross profit | $142,600 | |
| Expenses | ||
| Selling expenses | ||
| Depreciation expense—Store equipment | $3,000 | |
| Sales salaries expense | $31,500 | |
| Rent expense—Selling space | $13,000 | |
| Store supplies expense (1) | $6,000 | |
| Advertising expense | $17,800 | |
| Total selling expenses | $71,300 | |
| General and administrative expenses | ||
| Insurance expense | $2,800 | |
| Office salaries expense | $31,500 | |
| Rent expense—Office space | $13,000 | |
| Total general and administrative expenses | $47,300 | |
| Total expenses | ($118,600) | |
| Net income | $24,000 | |
Table (2)
Thus, the net income of Company FP for the year ended October 31 is $24,000.
3.
Prepare the single-step income statement of Company FP for the year ended October 31.
Explanation of Solution
Single-step income statement: This statement displays the total revenues as one line item from which the total expenses including cost of goods sold is subtracted to arrive at the net profit /net loss for the period.
Prepare the income statement of Company FP for the year ended October 31.
| Company FP | ||
| Statement of Income | ||
| For the year ended October 31 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Net sales | $221,100 | |
| Less: Expenses | ||
| Cost of goods sold (2) | $78,500 | |
| Selling expenses (Refer Table (2)) | $71,300 | |
| General and administrative expense (Refer Table (2)) | $47,300 | |
| Total expenses | ($197,100) | |
| Net income | $24,000 | |
Table (3)
Thus, the net income of Company FP for the year ended October 31 is $24,000.
4.
Compute current ratio, acid-test ratio and gross margin ratio.
Explanation of Solution
Current ratio: Current ratio is one of the liquidity ratios, which measures the capacity of the company to meet its short-term obligations using its current assets. Current ratio is calculated by using the formula:
Acid test ratio: It is a ratio used to determine a company’s ability to pay back its current liabilities by liquid assets that are current assets except inventory and prepaid expenses.
Gross margin ratio: The percentage of gross profit generated by every dollar of net sales is referred to as gross margin ratio. This ratio measures the profitability of a company by quantifying the amount of income earned from sales revenue generated after cost of goods sold are paid. The higher the ratio, the more ability to cover operating expenses. It is calculated by using the formula:
Compute current ratio, acid test ratio and gross margin ratio of Company FP.
| Computation of ratios | |
| Particulars | Amount |
| Cash | $7,400 |
| Merchandise inventory (2) | $21,300 |
| Store supplies (1) | $3,700 |
| Prepaid insurance | $3,800 |
| Total current assets (A) | $36,200 |
| Current liabilities (B) | $18,000 |
| Current ratio | 2.01 |
| Quick assets (Cash) (C) | $7,400 |
| Current liabilities (D) | $18,000 |
| Acid-test ratio | 0.41 |
| Net Sales (E) | $221,100 |
| Less: Cost of Goods Sold (2) | ($78,500) |
| Gross margin (F) | $142,600 |
| Gross margin ratio | 0.64 or 64% |
Table (4)
The current ratio, acid- test ratio and gross margin ratio of Company FP is 2.01, 0.41 and 0.64 or 64% respectively.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Principles of Financial Accounting.
- The accounts and their balances in the ledger of Markeys Mountain Shop as of December 31, the end of its fiscal year, are as follows: Data for the adjustments are as follows. Assume that Markeys Mountain Shop uses the perpetual inventory system. a. Merchandise Inventory at December 31, 140,357. b. Store supplies inventory (on hand) at December 31, 540. c. Depreciation of building, 3,400. d. Depreciation of store equipment, 3,800. e. Salaries accrued at December 31, 1,250. f. Insurance expired during the year, 1,480. Required 1. Complete the work sheet after entering the account names and balances onto the work sheet. Ignore this step if using CLGL. 2. Journalize the adjusting entries. If using manual working papers, record adjusting entries on journal page 63.arrow_forwardHere are the accounts in the ledger of Mishas Jewel Box, with the balances as of December 31, the end of its fiscal year. Here are the data for the adjustments. Assume that Mishas Jewel Box uses the perpetual inventory system. a. Merchandise Inventory at December 31, 124,630. b. Insurance expired during the year, 1,294. c. Depreciation of building, 3,300. d. Depreciation of store equipment, 6,470. e. Salaries accrued at December 31, 2,470. f. Store supplies inventory (on hand) at December 31, 1,959. Required 1. Complete the work sheet after entering the account names and balances onto the work sheet. Ignore this step if using CLGL. 2. Journalize the adjusting entries. If using manual working papers, record adjusting entries on journal page 63.arrow_forwardThe trial balance of Jillson Company as of December 31, the end of its current fiscal year, is as follows: Here are the data for the adjustments. ab. Merchandise Inventory at December 31, 54,845.00. c. Store supplies inventory (on hand), 488.50. d. Insurance expired, 680. e. Salaries accrued, 692. f. Depreciation of store equipment, 3,760. Required Complete the work sheet after entering the account names and balances onto the work sheet.arrow_forward
- The following accounts appear in the ledger of Celso and Company as of June 30, the end of this fiscal year. The data needed for the adjustments on June 30 are as follows: ab.Merchandise inventory, June 30, 54,600. c.Insurance expired for the year, 475. d.Depreciation for the year, 4,380. e.Accrued wages on June 30, 1,492. f.Supplies on hand at the end of the year, 100. Required 1. Prepare a work sheet for the fiscal year ended June 30. Ignore this step if using CLGL. 2. Prepare an income statement. 3. Prepare a statement of owners equity. No additional investments were made during the year. 4. Prepare a balance sheet. 5. Journalize the adjusting entries. 6. Journalize the closing entries. 7. Journalize the reversing entry as of July 1, for the wages that were accrued in the June adjusting entry. Check Figure Net income, 14,066arrow_forwardWhich of the following describes features of a perpetual inventory system? A. Technology is normally used to record inventory changes. B. Merchandise bought is recorded as purchases. C. An adjusting journal entry is required at year end, to match physical counts to the asset account. D. Inventory is updated at the end of the period.arrow_forwardA firm is preparing to make adjusting entries at the end of the accounting period. The balance of the merchandise inventory account is 200,000. If the firm is using the periodic inventory system, what does this balance represent?arrow_forward
- Palisade Creek Co. is a retail business that uses the perpetual inventory system. The account balances for Palisade Creek as of May 1, 20Y6 (unless otherwise indicated), are as follows: During May, the last month of the fiscal year, the following transactions were completed: Record the following transactions on Page 21 of the journal: Instructions 1. Enter the balances of each of the accounts in the appropriate balance column of a four-column account. Write Balance in the item section, and place a check mark () in the Posting Reference column. Journalize the transactions for May, starting on Page 20 of the journal. 2. Post the journal to the general ledger, extending the month-end balances to the appropriate balance columns after all posting is completed. In this problem, you are not required to update or post to the accounts receivable and accounts payable subsidiary ledgers. 3. Prepare an unadjusted trial balance. 4. At the end of May, the following adjustment data were assembled. Analyze and use these data to complete (5) and (6). 5. (Optional) Enter the unadjusted trial balance on a 10-column end-of-period spreadsheet (work sheet), and complete the spreadsheet. 6. Journalize and post the adjusting entries. Record the adjusting entries on Page 22 of the journal. 7. Prepare an adjusted trial balance. 8. Prepare an income statement, a statement of stockholders equity, and a balance sheet. Assume that additional common stock of 10,000 was issued in January 20Y6. 9. Prepare and post the closing entries. Record the closing entries on Page 23 of the journal. Indicate closed accounts by inserting a line in both the Balance columns opposite the closing entry. Insert the new balance in the retained earnings account. 10. Prepare a post-closing trial balance.arrow_forwardOn December 31, the end of the year, the accountant for Fireside Magazine was called away suddenly because of an emergency. However, before leaving, the accountant jotted down a few notes pertaining to the adjustments. Journalize the necessary adjusting entries. Assume that Fireside Magazine uses the periodic inventory system. ab. A physical count of inventory revealed a balance of 199,830. The Merchandise Inventory account shows a balance of 202,839. c. Subscriptions received in advance amounting to 156,200 were recorded as Unearned Subscriptions. At year-end, 103,120 has been earned. d. Depreciation of equipment for the year is 12,300. e. The amount of expired insurance for the year is 1,612. f. The balance of Prepaid Rent is 2,400, representing four months rent. Three months rent has expired. g. Three days salaries will be unpaid at the end of the year; total weekly (five days) salaries are 4,000. h. As of December 31, the balance of the supplies account is 1,800. A physical inventory of the supplies was taken, with an amount of 920 determined to be on hand.arrow_forwardPalisade Creek Co. is a merchandising business that uses the perpetual inventory system. The account balances for Palisade Creek Co. as of May 1, 2019 (unless otherwise indicated), are as follows: During May, the last month of the fiscal year, the following transactions were completed: Instructions 1. Enter the balances of each of the accounts in the appropriate balance column of a four-column account. Write Balance in the item section and place a check mark () in the Posting Reference column. Journalize the transactions for May, starting on Page 20 of the journal. 2. Post the journal to the general ledger, extending the month-end balances to the appropriate balance columns after all posting is completed. In this problem, you are not required to update or post to the accounts receivable and accounts payable subsidiary ledgers. 3. Prepare an unadjusted trial balance. 4. At the end of May, the following adjustment data were assembled. Analyze and use these data to complete (5) and (6). 5. (Optional) Enter the unadjusted trial balance on a 10-column end-of-period spreadsheet (work sheet), and complete the spreadsheet. 6. Journalize and post the adjusting entries. Record the adjusting entries on Page 22 of the journal. 7. Prepare an adjusted trial balance. 8. Prepare an income statement, a statement of owners equity, and a balance sheet. 9. Prepare and post the closing entries. Record the closing entries on Page 23 of the journal. Indicate closed accounts by inserting a line in both Balance columns opposite the closing entry. Insert the new balance in the owners capital account. 10. Prepare a post-closing trial balance.arrow_forward
- Palisade Creek Co. is a merchandising business that uses the perpetual inventory system. The account balances for Palisade Creek Co. as of May 1, 2016 (unless otherwise indicated), are as follows: During May, the last month of the fiscal year, the following transactions were completed: Instructions 1. Enter the balances of each of the accounts in the appropriate balance column of a four-column account. Write Balance in the item section, and place a check mark () in the Posting Reference column. Journalize the transactions for July, starting on Page 20 of the journal. 2. Post the journal to the general ledger, extending the month-end balances to the appropriate balance columns after all posting is completed. In this problem, you are not required to update or post to the accounts receivable and accounts payable subsidiary ledgers. 3. Prepare an unadjusted trial balance. 4. At the end of May, the following adjustment data were assembled. Analyze and use these data to complete (5) and (6). 5. (Optional) Enter the unadjusted trial balance on a 10-column end-of-period spreadsheet (work sheet), and complete the spreadsheet. 6. Journalize and post the adjusting entries. Record the adjusting entries on Page 22 of the journal. 7. Prepare an adjusted trial balance. 8. Prepare an income statement, a statement of owners equity, and a balance sheet. 9. Prepare and post the closing entries. Record the closing entries on Page 23 of the journal. Indicate closed accounts by inserting a line in both the Balance columns opposite the closing entry. Insert the new balance in the owners capital account. 10. Prepare a post-closing trial balance.arrow_forwardJohn Neff owns and operates Waikiki Surf Shop. A year-end trial balance is provided on page 561. Year-end adjustment data for the Waikiki Surf Shop are shown below. Neff uses the periodic inventory system. Year-end adjustment data are as follows: (a, b)A physical count shows that merchandise inventory costing 51,800 is on hand as of December 31, 20--. (c, d, e)Neff estimates that customers will be granted 2,000 in refunds of this years sales next year and the merchandise expected to be returned will have a cost of 1,200. (f)Supplies remaining at the end of the year, 600. (g)Unexpired insurance on December 31, 2,600. (h)Depreciation expense on the building for 20--, 5,000. (i)Depreciation expense on the store equipment for 20--, 3,000. (j)Wages earned but not paid as of December 31, 1,800. (k)Neff also offers boat rentals which clients pay for in advance. Unearned boat rental revenue as of December 31 is 3,000. Required 1. Prepare a year-end spreadsheet. 2. Journalize the adjusting entries. 3. Compute cost of goods sold using the spreadsheet prepared for part (1).arrow_forwardA firm is preparing to make adjusting entries at the end of the accounting period. The balance of the merchandise inventory account is 100,000. If the firm is using the perpetual inventory system, what does this balance represent?arrow_forward
 College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





