
Concept explainers
Palisade Creek Co. is a retail business that uses the perpetual inventory system. The account balances for Palisade Creek as of May 1, 20Y6 (unless otherwise indicated), are as follows:
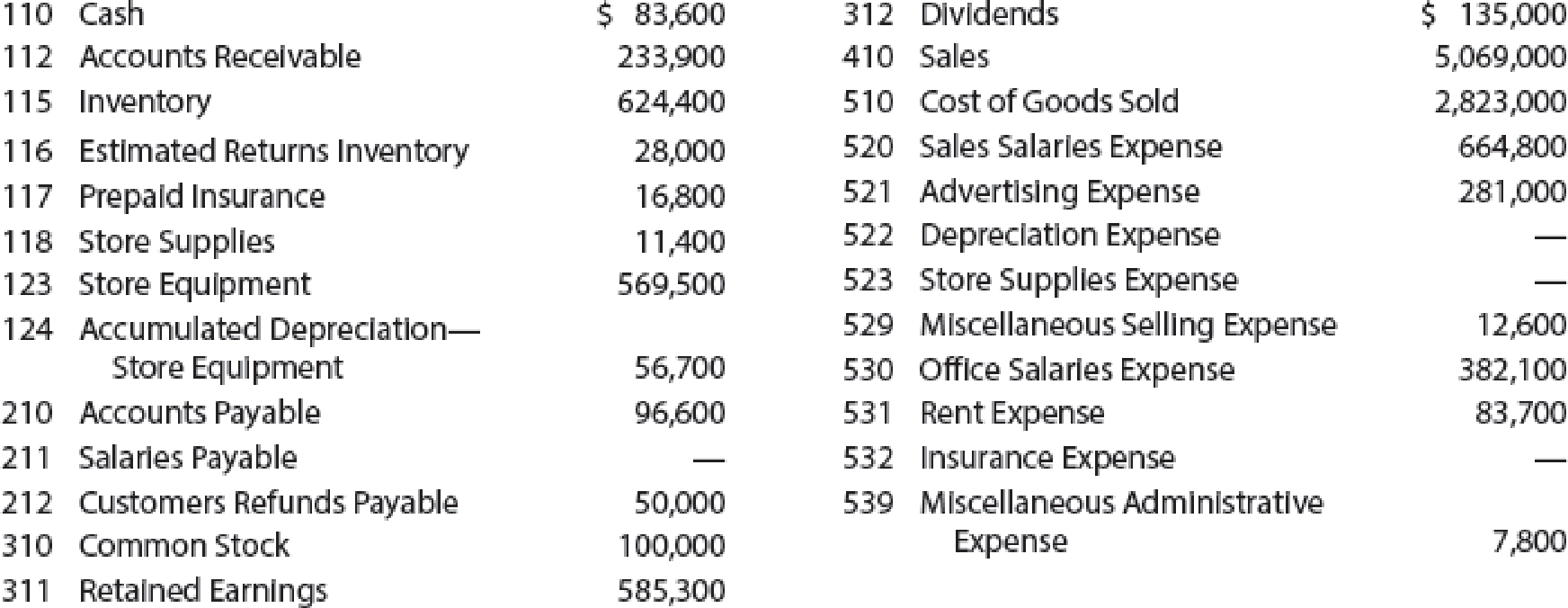
During May, the last month of the fiscal year, the following transactions were completed:


Record the following transactions on Page 21 of the journal:

Instructions
- 1. Enter the balances of each of the accounts in the appropriate balance column of a four-column account. Write Balance in the item section, and place a check mark (✓) in the Posting Reference column. Journalize the transactions for May, starting on Page 20 of the journal.
- 2. Post the journal to the general ledger, extending the month-end balances to the appropriate balance columns after all posting is completed. In this problem, you are not required to update or post to the accounts receivable and accounts payable subsidiary ledgers.
- 3. Prepare an unadjusted
trial balance . - 4. At the end of May, the following adjustment data were assembled. Analyze and use these data to complete (5) and (6).
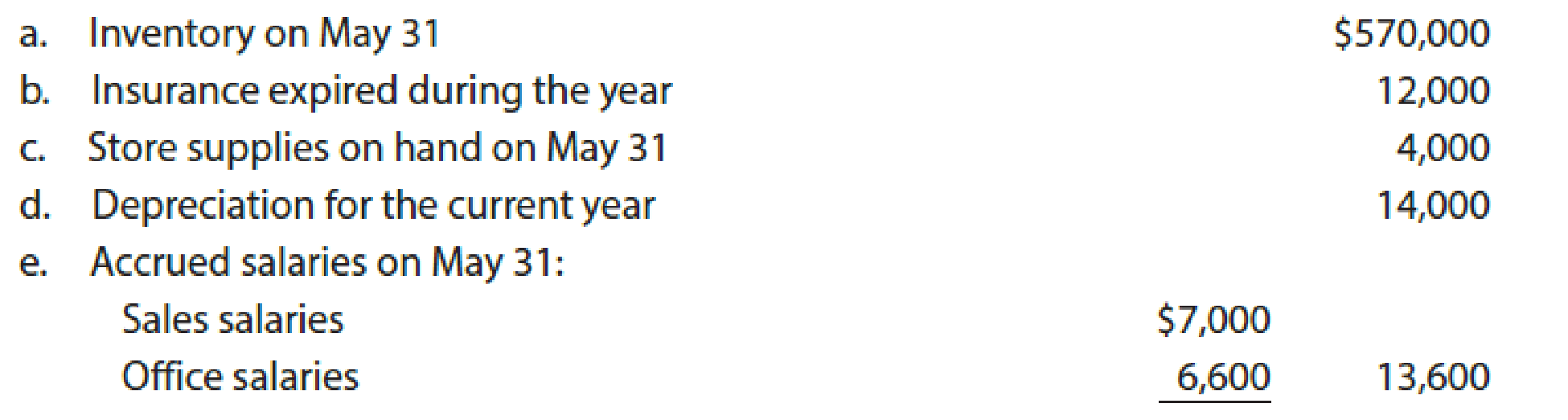
- 5. (Optional) Enter the unadjusted trial balance on a 10-column end-of-period spreadsheet (work sheet), and complete the spreadsheet.
- 6. Journalize and post the
adjusting entries . Record the adjusting entries on Page 22 of the journal. - 7. Prepare an adjusted trial balance.
- 8. Prepare an income statement, a statement of stockholders’ equity, and a balance sheet. Assume that additional common stock of $10,000 was issued in January 20Y6.
- 9. Prepare and post the closing entries. Record the closing entries on Page 23 of the journal. Indicate closed accounts by inserting a line in both the Balance columns opposite the closing entry. Insert the new balance in the
retained earnings account. - 10. Prepare a post-closing trial balance.
1, 2, 6, and 9
Post the balance of each of the accounts.
Explanation of Solution
Enter the balances of each of the accounts.
General ledger: General ledger is a record of all accounts of assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity, necessary to prepare financial statements.
Cash Account:
| Cash Account | Account No. 110 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 83,600 | |||
| 1 | 20 | 5,000 | |||||
| 4 | 20 | 600 | |||||
| 7 | 20 | 22,300 | |||||
| 10 | 20 | 54,000 | |||||
| 13 | 20 | 35,280 | |||||
| 15 | 20 | 11,000 | |||||
| 16 | 20 | 67,130 | |||||
| 19 | 20 | 18,700 | |||||
| 19 | 20 | 33,450 | |||||
| 20 | 20 | 13,230 | |||||
| 21 | 21 | 2,300 | |||||
| 21 | 21 | 42,900 | |||||
| 26 | 21 | 7,500 | |||||
| 28 | 21 | 85,000 | |||||
| 29 | 21 | 2,400 | |||||
| 30 | 21 | 111,200 | |||||
| 31 | 21 | 82,170 | 84,500 | ||||
Table (1)
Accounts Receivable Account:
| Accounts Receivable | Account No. 112 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 233,900 | |||
| 6 | 20 | 67,130 | |||||
| 7 | 20 | 22,300 | |||||
| 16 | 20 | 67,130 | |||||
| 20 | 21 | 108,900 | |||||
| 21 | 21 | 2,300 | |||||
| 21 | 21 | 42,900 | |||||
| 30 | 21 | 77,175 | |||||
| 30 | 21 | 111,200 | 245,875 | ||||
Table (2)
Inventory Account:
| Inventory | Account No. 115 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 624,400 | |||
| 3 | 20 | 35,280 | |||||
| 4 | 20 | 600 | |||||
| 6 | 20 | 41,000 | |||||
| 10 | 20 | 32,000 | |||||
| 19 | 20 | 18,700 | |||||
| 20 | 20 | 8,000 | |||||
| 20 | 21 | 70,000 | |||||
| 21 | 21 | 87,120 | |||||
| 24 | 21 | 4,950 | |||||
| 26 | 21 | 4,800 | |||||
| 30 | 21 | 47,000 | 583,950 | ||||
| 31 | Adjusting | 22 | 13,950 | 570,000 | |||
Table (3)
Estimated Returns Inventory Account:
| Estimated Returns Inventory | Account No. 116 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 28,000 | |||
| 20 | 20 | 8,000 | |||||
| 26 | 21 | 4,800 | 15,200 | ||||
| 31 | Adjusting | 22 | 35,000 | 50,200 | |||
Table (4)
Prepaid Insurance Account:
| Prepaid Insurance | Account No. 117 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 16,800 | |||
| 31 | Adjusting | 22 | 12,000 | 4,800 | |||
Table (5)
Store Supplies Account:
| Store Supplies | Account No. 118 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 11,400 | |||
| 29 | 21 | 2,400 | 13,800 | ||||
| 31 | Adjusting | 22 | 9,800 | 4,000 | |||
Table (6)
Store Equipment Account:
| Store Equipment | Account No. 123 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 569,500 | |||
Table (7)
Accumulated Depreciation – Store Equipment Account:
| Accumulated Depreciation – Store Equipment | Account No. 124 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 56,700 | |||
| 31 | Adjusting | 22 | 14,000 | 70,700 | |||
Table (8)
Accounts Payable Account:
| Accounts Payable | Account No. 210 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 96,600 | |||
| 3 | 20 | 35,280 | |||||
| 13 | 20 | 35,280 | |||||
| 19 | 20 | 33,450 | |||||
| 21 | 21 | 87,120 | |||||
| 24 | 21 | 4,950 | |||||
| 31 | 21 | 82,170 | 63,150 | ||||
Table (9)
Salaries Payable Account:
| Salaries Payable | Account No. 211 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 31 | Adjusting | 22 | 13,600 | 13,600 | ||
Table (10)
Customers Refunds Payable Account:
| Customers Refunds Payable | Account No. 212 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 50,000 | |||
| 20 | 20 | 13,230 | |||||
| 26 | 21 | 7,500 | 29,270 | ||||
| 31 | Adjusting | 22 | 60,000 | 89,270 | |||
Table (11)
Common Stock Account:
| Common Stock | Account No. 310 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 100,000 | |||
Table (12)
Retained Earnings Account:
| Retained Earnings | Account No. 311 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 2017 | |||||||
| June | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 585,300 | |||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 31 | Closing | 23 | 741,855 | |||
| 31 | Closing | 23 | 135,000 | 1,192,155 | |||
Table (13)
Dividends Account:
| Dividends | Account No. 312 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 135,000 | |||
| 31 | Closing | 23 | 135,000 | ||||
Table (14)
Income Summary Account:
| Income Summary | Account No. 313 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 31 | Closing | 23 | 5,316,205 | |||
| 31 | Closing | 23 | 4,574,350 | 741,855 | |||
| 31 | Closing | 23 | 741,855 | ||||
Table (15)
Sales Account:
| Sales | Account No. 410 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 5,069,000 | |||
| 6 | 20 | 67,130 | |||||
| 10 | 20 | 54,000 | |||||
| 20 | 21 | 108,900 | |||||
| 30 | 21 | 77,175 | 5,376,205 | ||||
| 31 | Adjusting | 22 | 60,000 | 5,316,205 | |||
| 31 | Closing | 23 | 5,316,205 | ||||
Table (16)
Cost of Goods Sold Account:
| Cost of Goods Sold | Account No. 510 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 2,823,000 | |||
| 6 | 20 | 41,000 | |||||
| 10 | 20 | 32,000 | |||||
| 20 | 21 | 70,000 | |||||
| 30 | 21 | 47,000 | 3,013,000 | ||||
| 31 | Adjusting | 22 | 13,950 | ||||
| 31 | Adjusting | 22 | 35,000 | 2,991,950 | |||
| 31 | Closing | 23 | 2,991,950 | ||||
Table (17)
Sales Salaries Expense Account:
| Sales Salaries Expense | Account No. 520 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 664,800 | |||
| 28 | 21 | 56,000 | 720,800 | ||||
| 31 | Adjusting | 22 | 7,000 | 727,800 | |||
| 31 | Closing | 23 | 727,800 | ||||
Table (18)
Advertising Expense Account:
| Advertising Expense | Account No. 521 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 281,000 | |||
| 15 | 20 | 11,000 | 292,000 | ||||
| 31 | Closing | 23 | 292,000 | ||||
Table (19)
Depreciation Expense Account:
| Depreciation Expense | Account No. 522 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 31 | Adjusting | 22 | 14,000 | 14,000 | ||
| 31 | Closing | 23 | 14,000 | ||||
Table (20)
Stores Supplies Expense Account:
| Stores Supplies Expense | Account No. 523 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 31 | Adjusting | 22 | 9,800 | 9,800 | ||
| 31 | Closing | 23 | 9,800 | ||||
Table (21)
Miscellaneous Selling Expense Account:
| Miscellaneous Selling Expense | Account No. 529 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 12,600 | |||
| 31 | Closing | 23 | 12,600 | ||||
Table (22)
Office Salaries Expense Account:
| Office Salaries Expense | Account No. 530 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 382,100 | |||
| 28 | 21 | 29,000 | 411,100 | ||||
| 31 | Adjusting | 22 | 6,600 | 417,700 | |||
| 31 | Closing | 23 | 417,700 | ||||
Table (23)
Rent Expense Account:
| Rent Expense | Account No. 531 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 83,700 | |||
| 1 | 20 | 5,000 | 88,700 | ||||
| 31 | Closing | 23 | 88,700 | ||||
Table (24)
Insurance Expense Account:
| Insurance Expense | Account No. 532 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 31 | Adjusting | 22 | 12,000 | 12,000 | ||
| 31 | Closing | 23 | 12,000 | ||||
Table (25)
Miscellaneous Administrative Expense Account:
| Miscellaneous Administrative Expense | Account No. 539 | ||||||
| Date | Item |
Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance ($) | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| 20Y6 | |||||||
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 7,800 | |||
| 31 | Closing | 23 | 7,800 | ||||
Table (26)
1. and 2.
Record the journal entries.
Explanation of Solution
Journal:
Journal is the book of original entry. Journal consists of the day today financial transactions in a chronological order. The journal has two aspects; they are debit aspect and the credit aspect.
Rules of debit and credit:
“An increase in an asset account, an increase in an expense account, a decrease in liability account, and a decrease in a revenue account should be debited.
Similarly, an increase in liability account, an increase in a revenue account and a decrease in an asset account, a decrease in an expenses account should be credited”.
Record the journal entries.
| Date | Particulars | Post. Ref. | Page 20 | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||
| 20Y6 | |||||
| May | 1 | Rent Expense | 531 | 5,000 | |
| Cash | 110 | 5,000 | |||
| 3 | Inventory | 115 | 35,280 | ||
| Accounts Payable | 210 | 35,280 | |||
| 4 | Inventory | 115 | 600 | ||
| Cash | 110 | 600 | |||
| 6 | Accounts Receivable | 112 | 67,130 | ||
| Sales | 410 | 67,130 | |||
| 6 | Cost of Goods Sold | 510 | 41,000 | ||
| Inventory | 115 | 41,000 | |||
| 7 | Cash | 110 | 22,300 | ||
| Accounts Receivable | 112 | 22,300 | |||
| 10 | Cash | 110 | 54,000 | ||
| Sales | 410 | 54,000 | |||
| 10 | Cost of Goods Sold | 510 | 32,000 | ||
| Inventory | 115 | 32,000 | |||
| 13 | Accounts Payable | 210 | 35,280 | ||
| Cash | 110 | 35,280 | |||
| 15 | Advertising Expense | 521 | 11,000 | ||
| Cash | 110 | 11,000 | |||
| 16 | Cash | 110 | 67,130 | ||
| Accounts Receivable | 112 | 67,130 | |||
| 19 | Inventory | 115 | 18,700 | ||
| Cash | 110 | 18,700 | |||
| 19 | Accounts Payable | 210 | 33,450 | ||
| Cash | 110 | 33,450 | |||
| 20 | Customers Refunds Payable | 212 | 13,230 | ||
| Cash | 110 | 13,230 | |||
| 20 | Inventory | 115 | 8,000 | ||
| Estimated Returns Inventory | 116 | 8,000 | |||
| Date | Particulars | Post. Ref. | Page 21 | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||
| 20 | Accounts Receivable | 112 | 108,900 | ||
| Sales | 410 | 108,900 | |||
| 20 | Cost of Goods Sold | 510 | 70,000 | ||
| Inventory | 115 | 70,000 | |||
| 21 | Accounts Receivable | 112 | 2,300 | ||
| Cash | 110 | 2,300 | |||
| 21 | Cash | 110 | 42,900 | ||
| Accounts Receivable | 112 | 42,900 | |||
| 21 | Inventory | 115 | 87,120 | ||
| Accounts Payable | 210 | 87,120 | |||
| 24 | Accounts Payable | 210 | 4,950 | ||
| Inventory | 115 | 4,950 | |||
| 26 | Customers Refunds Payable | 212 | 7,500 | ||
| Cash | 110 | 7,500 | |||
| 26 | Inventory | 115 | 4,800 | ||
| Estimated Returns Inventory | 116 | 4,800 | |||
| 28 | Sales Salaries Expense | 520 | 56,000 | ||
| Office Salaries Expense | 530 | 29,000 | |||
| Cash | 110 | 85,000 | |||
| 29 | Store Supplies | 118 | 2,400 | ||
| Cash | 110 | 2,400 | |||
| 30 | Accounts Receivable | 112 | 77,175 | ||
| Sales | 410 | 77,175 | |||
| 30 | Cost of Goods Sold | 510 | 47,000 | ||
| Inventory | 115 | 47,000 | |||
| 30 | Cash | 110 | 111,200 | ||
| Accounts Receivable | 112 | 111,200 | |||
| 31 | Accounts Payable | 210 | 82,170 | ||
| Cash | 110 | 82,170 | |||
Table (27)
3.
Prepare the unadjusted trial balance of Company P.
Explanation of Solution
Unadjusted trial balance:
The unadjusted trial balance is the summary of all the ledger accounts that appears on the ledger accounts before making adjusting journal entries.
Prepare an unadjusted trial balance.
|
P Company Unadjusted Trial Balance As on May 31, 20Y6 | |||
| Accounts |
Account No. |
Debit Balances ($) |
Credit Balances ($) |
| Cash | 110 | 84,500 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 112 | 245,875 | |
| Inventory | 115 | 583,950 | |
| Estimated Returns Inventory | 116 | 15,200 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 117 | 16,800 | |
| Store Supplies | 118 | 13,800 | |
| Store Equipment | 123 | 569,500 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation—Store Equipment | 124 | 56,700 | |
| Accounts Payable | 210 | 63,150 | |
| Salaries Payable | 211 | — | |
| Customers Refunds Payable | 212 | 29,270 | |
| Common Stock | 310 | 100,000 | |
| Retained Earnings | 311 | 585,300 | |
| Dividends | 312 | 135,000 | |
| Sales | 410 | 5,376,205 | |
| Cost of Goods Sold | 510 | 3,013,000 | |
| Sales Salaries Expense | 520 | 720,800 | |
| Advertising Expense | 521 | 292,000 | |
| Depreciation Expense | 522 | — | |
| Store Supplies Expense | 523 | — | |
| Miscellaneous Selling Expense | 529 | 12,600 | |
| Office Salaries Expense | 530 | 411,100 | |
| Rent Expense | 531 | 88,700 | |
| Insurance Expense | 532 | — | |
| Miscellaneous Administrative Expense | 539 | 7,800 | |
| Total | 6,210,625 | 6,210,625 | |
Table (28)
4. and 6.
Record the adjusting entry.
Explanation of Solution
| Date | Particulars |
Post. Ref. | Page 22 | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||
| 20Y6 | Adjusting Entries | ||||
| May | 31 | Cost of Goods Sold | 510 | 13,950 | |
| Inventory | 115 | 13,950 | |||
| 31 | Insurance Expense | 532 | 12,000 | ||
| Prepaid Insurance | 117 | 12,000 | |||
| 31 | Store Supplies Expense | 523 | 9,800 | ||
| Store Supplies | 118 | 9,800 | |||
| 31 | Depreciation Expense | 522 | 14,000 | ||
|
Accumulated. Depreciation —Store Equipment | 124 | 14,000 | |||
| 31 | Sales Salaries Expense | 520 | 7,000 | ||
| Office Salaries Expense | 530 | 6,600 | |||
| Salaries Payable | 211 | 13,600 | |||
| 31 | Sales | 410 | 60,000 | ||
| Customer Refunds Payable | 212 | 60,000 | |||
| 31 | Estimated Returns Inventory | 116 | 35,000 | ||
| Cost of Goods Sold | 510 | 35,000 | |||
Table (29)
7.
Prepare the adjusted trial balance of Company P.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the adjusted trial balance.
|
P Company Adjusted Trial Balance As on May 31, 20Y6 | |||
| Particulars |
Account No. |
Debit Balances ($) |
Credit Balances ($) |
| Cash | 110 | 84,500 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 112 | 245,875 | |
| Inventory | 115 | 570,000 | |
| Estimated Returns Inventory | 116 | 50,200 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 117 | 4,800 | |
| Store Supplies | 118 | 4,000 | |
| Store Equipment | 123 | 569,500 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation—Store Equipment | 124 | 70,700 | |
| Accounts Payable | 210 | 63,150 | |
| Salaries Payable | 211 | 13,600 | |
| Customers Refunds Payable | 212 | 89,270 | |
| Common Stock | 310 | 100,000 | |
| Retained Earnings | 311 | 585,300 | |
| Dividends | 312 | 135,000 | |
| Sales | 410 | 5,316,205 | |
| Cost of Goods Sold | 510 | 2,991,950 | |
| Sales Salaries Expense | 520 | 727,800 | |
| Advertising Expense | 521 | 292,000 | |
| Depreciation Expense | 522 | 14,000 | |
| Store Supplies Expense | 523 | 9,800 | |
| Miscellaneous Selling Expense | 529 | 12,600 | |
| Office Salaries Expense | 530 | 417,700 | |
| Rent Expense | 531 | 88,700 | |
| Insurance Expense | 532 | 12,000 | |
| Miscellaneous Administrative Expense | 539 | 7,800 | |
| Total | 6,238,225 | 6,238,225 | |
Table (30)
8.
Prepare the income statement, retained earnings, and balance sheet of P Company.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the income statement.
|
P Company Income Statement For the Year Ended May 31, 20Y6 | |||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Sales | 5,316,205 | ||
| Cost of goods sold | (2,991,950) | ||
| Gross profit | 2,324,255 | ||
| Expenses: | |||
| Selling expenses: | |||
| Sales salaries expense | 727,800 | ||
| Advertising expense | 292,000 | ||
| Depreciation expense | 14,000 | ||
| Store supplies expense | 9,800 | ||
| Miscellaneous selling expense | 12,600 | ||
| Total selling expenses | 1,056,200 | ||
| Administrative expenses: | |||
| Office salaries expense | 417,700 | ||
| Rent expense | 88,700 | ||
| Insurance expense | 12,000 | ||
| Miscellaneous administrative expense | 7,800 | ||
| Total administrative expenses | 526,200 | ||
| Total expenses | (1,582,400) | ||
| Net income | 741,855 | ||
Table (31)
Prepare the retained earnings statement.
|
P Company Retained Earnings Statement For the Year Ended May 31, 20Y6 | ||
| Retained earnings, June 1, 2017 | 585,300 | |
| Net income | 741,855 | |
| Dividends | (135,000) | |
| Change in retained earnings | 606,855 | |
| Retained earnings, May 31, 20Y6 | 1,192,155 | |
Table (32)
Prepare the balance sheet of P Company.
|
P Company Balance Sheet As on May 31, 20Y6 | ||
| Assets | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Current assets: | ||
| Cash | $ 84,500 | |
| Accounts receivable | 245,875 | |
| Inventory | 570,000 | |
| Estimated returns inventory | 50,200 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 4,800 | |
| Store supplies | 4,000 | |
| Total current assets | $ 959,375 | |
| Property, plant, and equipment: | ||
| Store equipment | $ 569,500 | |
| Accumulated depreciation—store equipment | (70,700) | |
| Total property, plant, and equipment | 498,800 | |
| Total assets | $1,458,175 | |
| Liabilities | ||
| Current liabilities: | ||
| Accounts payable | $ 63,150 | |
| Salaries payable | 13,600 | |
| Customers refunds payable | 89,270 | |
| Total liabilities | $ 166,020 | |
| Stockholders’ Equity | ||
| Common stock | $ 100,000 | |
| Retained earnings | 1,192,155 | |
| Total stockholders’ equity | 1,292,155 | |
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | $1,458,175 | |
Table (33)
9.
Post the closing entries.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the closing entries.
| Date | Particulars |
Post. Ref. | Page 23 | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||
| 20Y6 | Closing Entries | ||||
| May | 31 | Sales | 410 | 5,316,205 | |
| Income Summary | 313 | 5,316,205 | |||
| 31 | Income Summary | 313 | 4,574,350 | ||
| Cost of Goods Sold | 510 | 2,991,950 | |||
| Sales Salaries Expense | 520 | 727,800 | |||
| Advertising Expense | 521 | 292,000 | |||
| Depreciation Expense | 522 | 14,000 | |||
| Store Supplies Expense | 523 | 9,800 | |||
| Miscellaneous Selling Expense | 529 | 12,600 | |||
| Office Salaries Expense | 530 | 417,700 | |||
| Rent Expense | 531 | 88,700 | |||
| Insurance Expense | 532 | 12,000 | |||
| Miscellaneous Administrative Expenses | 539 | 7,800 | |||
| 31 | Income Summary | 313 | 741,855 | ||
| Retained Earnings | 311 | 741,855 | |||
| 31 | Retained Earnings | 311 | 135,000 | ||
| Dividends | 312 | 135,000 | |||
Table (34)
10.
Prepare the post-closing trial balance.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the post-closing trial balance.
|
P Company Post-Closing Trial Balance May 31, 20Y6 | |||
| Accounts |
Account No. |
Debit Balances ($) |
Credit Balances ($) |
| Cash | 110 | 84,500 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 112 | 245,875 | |
| Inventory | 115 | 570,000 | |
| Estimated Returns Inventory | 116 | 50,200 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 117 | 4,800 | |
| Store Supplies | 118 | 4,000 | |
| Store Equipment | 123 | 569,500 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation—Store Equipment | 124 | 70,700 | |
| Accounts Payable | 210 | 63,150 | |
| Salaries Payable | 211 | 13,600 | |
| Customers Refunds Payable | 212 | 89,270 | |
| Common Stock | 310 | 100,000 | |
| Retained Earnings | 311 | 1,192,155 | |
| Total | 1,528,875 | 1,528,875 | |
Table (35)
5.
Prepare the worksheet for Company P.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the worksheet.
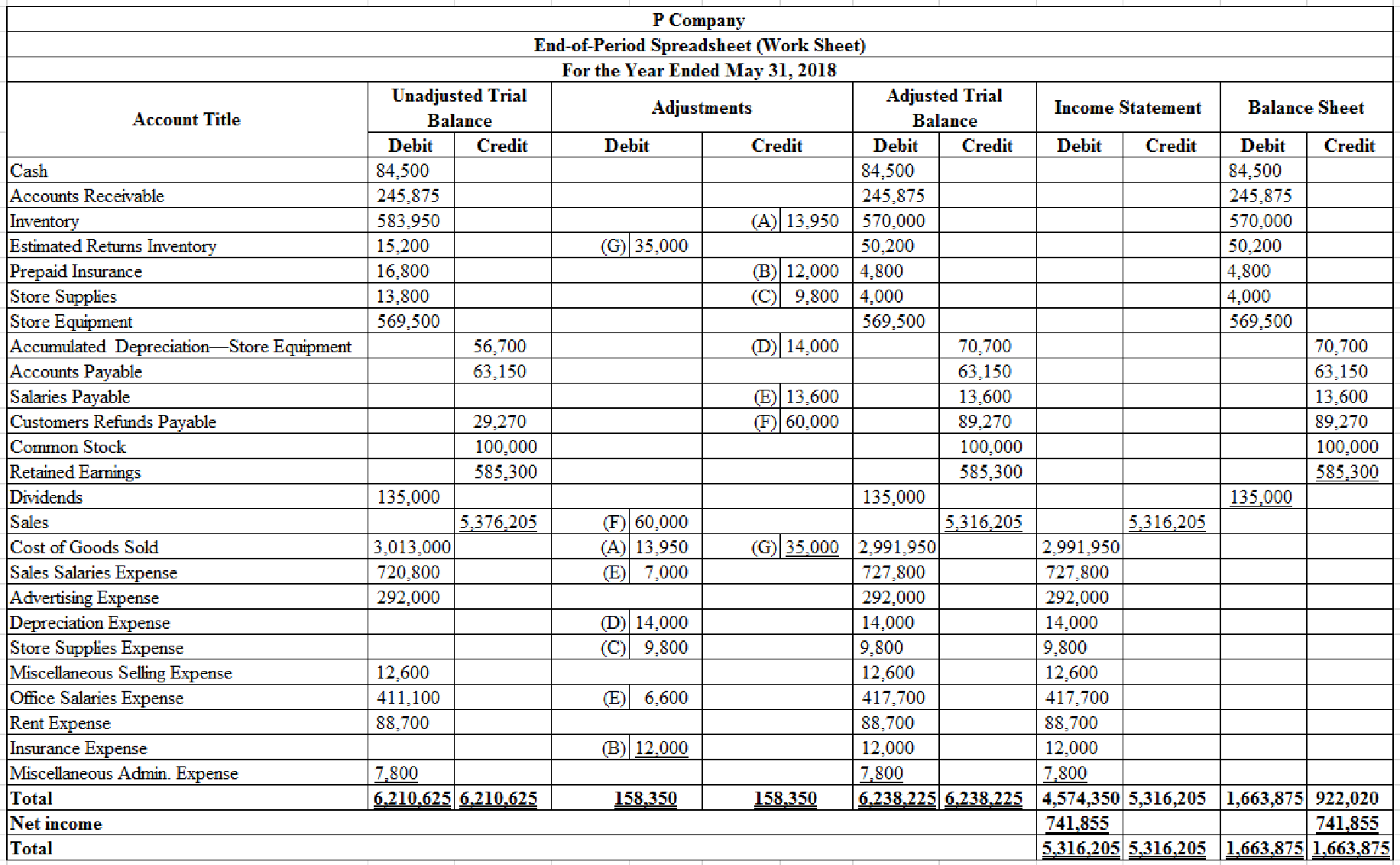
Figure (1)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Financial And Managerial Accounting
- Palisade Creek Co. is a merchandising business that uses the perpetual inventory system. The account balances for Palisade Creek Co. as of May 1, 2016 (unless otherwise indicated), are as follows: During May, the last month of the fiscal year, the following transactions were completed: Instructions 1. Enter the balances of each of the accounts in the appropriate balance column of a four-column account. Write Balance in the item section, and place a check mark () in the Posting Reference column. Journalize the transactions for July, starting on Page 20 of the journal. 2. Post the journal to the general ledger, extending the month-end balances to the appropriate balance columns after all posting is completed. In this problem, you are not required to update or post to the accounts receivable and accounts payable subsidiary ledgers. 3. Prepare an unadjusted trial balance. 4. At the end of May, the following adjustment data were assembled. Analyze and use these data to complete (5) and (6). 5. (Optional) Enter the unadjusted trial balance on a 10-column end-of-period spreadsheet (work sheet), and complete the spreadsheet. 6. Journalize and post the adjusting entries. Record the adjusting entries on Page 22 of the journal. 7. Prepare an adjusted trial balance. 8. Prepare an income statement, a statement of owners equity, and a balance sheet. 9. Prepare and post the closing entries. Record the closing entries on Page 23 of the journal. Indicate closed accounts by inserting a line in both the Balance columns opposite the closing entry. Insert the new balance in the owners capital account. 10. Prepare a post-closing trial balance.arrow_forwardPalisade Creek Co. is a merchandising business that uses the perpetual inventory system. The account balances for Palisade Creek Co. as of May 1, 2019 (unless otherwise indicated), are as follows: During May, the last month of the fiscal year, the following transactions were completed: Instructions 1. Enter the balances of each of the accounts in the appropriate balance column of a four-column account. Write Balance in the item section and place a check mark () in the Posting Reference column. Journalize the transactions for May, starting on Page 20 of the journal. 2. Post the journal to the general ledger, extending the month-end balances to the appropriate balance columns after all posting is completed. In this problem, you are not required to update or post to the accounts receivable and accounts payable subsidiary ledgers. 3. Prepare an unadjusted trial balance. 4. At the end of May, the following adjustment data were assembled. Analyze and use these data to complete (5) and (6). 5. (Optional) Enter the unadjusted trial balance on a 10-column end-of-period spreadsheet (work sheet), and complete the spreadsheet. 6. Journalize and post the adjusting entries. Record the adjusting entries on Page 22 of the journal. 7. Prepare an adjusted trial balance. 8. Prepare an income statement, a statement of owners equity, and a balance sheet. 9. Prepare and post the closing entries. Record the closing entries on Page 23 of the journal. Indicate closed accounts by inserting a line in both Balance columns opposite the closing entry. Insert the new balance in the owners capital account. 10. Prepare a post-closing trial balance.arrow_forwardThe beginning inventory for Dunne Co. and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period are shown in Problem 7-1B. Instructions 1. Determine the inventory on June 30 and the cost of merchandise sold for the three-month period, using the first-in, first-out method and the periodic inventory system. 2. Determine the inventory on June 30 and the cost of merchandise sold for the three-month period, using the last-in, first-out method and the periodic inventory system. 3. Determine the inventory on June 30 and the cost of merchandise sold for the three-month period, using the weighted average cost method and the periodic inventory system. Round the weighted average unit cost to the dollar. 4. Compare the gross profit and June 30 inventories using the following column headings:arrow_forward
- Jessie Stores uses the periodic system of calculating inventory. The following information is available for December of the current year when Jessie sold 500 units of inventory. Using the FIFO method, calculate Jessies inventory on December 31 and its cost of goods sold for December.arrow_forwardOn December 31, 2019, the balances of the accounts appearing in the ledger of Wyman Company are as follows: Instructions 1. Does Wyman Company use a periodic or perpetual inventory system? Explain. 2. Prepare a multiple-step income statement for Wyman Company for the year ended December 31, 2019. The merchandise inventory as of December 31, 2019, was 305,000. The adjustment for estimated returns inventory for sales for the year ending December 31, 2019, was 30,000. 3. Prepare the closing entries for Wyman Company as of December 31, 2019. 4. What would the net income have been if the perpetual inventory system had been used?arrow_forwardDymac Appliances uses the periodic inventory system. Details regarding the inventory of appliances at January 1, purchases invoices during the next 12 months, and the inventory count at December 31 are summarized as follows: Instructions 1. Determine the cost of the inventory on December 31 by the first-in, first-out method. Present data in columnar form, using the following headings: If the inventory of a particular model comprises one entire purchase plus a portion of another purchase acquired at a different unit cost, use a separate line for each purchase. 2. Determine the cost of the inventory on December 31 by the last-in, first-out method, following the procedures indicated in (1). 3. Determine the cost of the inventory on December 31 by the weighted average cost method, using the columnar headings indicated in (1). 4. Discuss which method (FIFO or LIFO) would be preferred for income tax purposes in periods of (a) rising prices and (b) declining prices.arrow_forward
- Pappas Appliances uses the periodic inventory system. Details regarding the inventory of appliances at January 1, purchases invoices during the year, and the inventory count at December 31 are summarized as follows: Instructions 1. Determine the cost of the inventory on December 31 by the first-in, first-out method. Present data in columnar form, using the following headings: If the inventory of a particular model comprises one entire purchase plus a portion of another purchase acquired at a different unit cost, use a separate line for each purchase. 2. Determine the cost of the inventory on December 31 by the last-in, first-out method, following the procedures indicated in (1). 3. Determine the cost of the inventory on December 31 by the weighted average cost method, using the columnar headings indicated in (1). 4. Discuss which method (FIFO or LIFO) would be preferred for income tax purposes in periods of (a) rising prices and (b) declining prices.arrow_forwardMacDonald Bookshop had the following transactions that occurred during February of this year: Required 1. Journalize the transactions for February in the cash payments journal. Assume the periodic inventory method is used. 2. If you are using Working Papers, total and rule the journal. Prove the equality of the debit and credit totals.arrow_forwardOn June 30, 2019, the balances of the accounts appearing in the ledger of Simkins Company are as follows: Instructions 1. Does Simkins Company use a periodic or perpetual inventory system? Explain. 2. Prepare a multiple-step income statement for Simkins Company for the year ended June 30, 2019. The merchandise inventory as of June 30, 2019, was 508,000. The adjustment for estimated returns inventory for sales for the year ending December 31, 2019, was 33,000. 3. Prepare the closing entries for Simkins Company as of June 30, 2019. 4. What would the net income have been if the perpetual inventory system had been used?arrow_forward
- The following transactions were completed by Nelsons Boutique, a retailer, during July. Terms on sales on account are 2/10, n/30, FOB shipping point. Required 1. Journalize the transactions for July in the cash receipts journal, the general journal (for the transaction on July 9th), or the cash payment journal as appropriate. Assume the periodic inventory method is used. 2. Total and rule the journals. 3. Prove the equality of debit and credit totals.arrow_forwardCarla Company uses the perpetual inventory system. The following information is available for January of the current year when Carla sold 1,600 units of inventory on January 14. Using the FIFO method, calculate Carlas cost of goods sold for January and its January 31 inventory.arrow_forwardSelected transactions for Niles Co. during March of the current year are listed in Problem 6-1B. Instructions Journalize the entries to record the transactions of Niles Co. for March using the periodic inventory system.arrow_forward
 Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub





