ESSENTIALS OF GENETICS-MODIFIED ACCESS
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780134190006
Author: KLUG
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 20PDQ
A woman who sought genetic counseling is found to be heterozygous for a chromosomal rearrangement between the second and third chromosomes. Her chromosomes, compared to those in a normal karyotype, are diagrammed here:
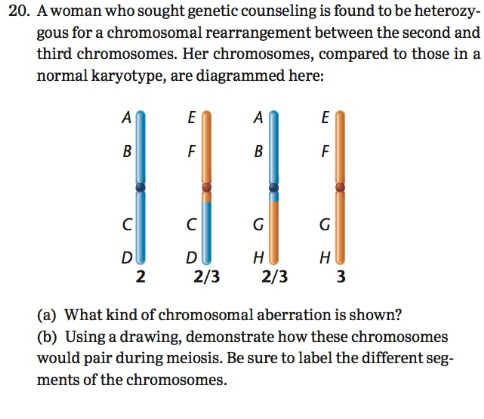
(a) What kind of chromosomal aberration is shown?
(b) Using a drawing, demonstrate how these chromosomes would pair during meiosis. Be sure to label the different segments of the chromosomes.
(c) This woman is phenotypically normal. Does this surprise you? Why or why not? Under what circumstances might you expect a
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Two phenotypically unaffected parents produce two children with familial Down syndrome. Regarding chromosome 14 and 21, what are the chromosomal composition of the parents?
A woman who sought genetic counseling is found to be heterozygousfor a chromosomal rearrangement between the second andthird chromosomes. Her chromosomes, compared to those in anormal karyotype, are diagrammed on the next page:(a) What kind of chromosomal aberration is shown?
A boy with Klinefelter syndrome (47,XXY) is born to a mother who is phenotypically normal and a father who has the X- linked skin condition called anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. The boy has patches of normal skin and patches of abnormal skin. Which of the following statemnets likely explains these observations?
The father contributed the extra X chromosome in the son as a result of a non-disjunction in meiosis I during spermatogenesis.
The mother contributed the extra X chromosome in the son as a result of a non-disjunction in meiosis II during oogenesis.
The mother contributed the extra X chromosome in the son as a result of a non-disjunction in meiosis I during oogenesis.
The father contributed the extra X chromosome in the son as a result of a non-disjunction in meiosis II during spermatogenesis.
Either parent could have contributed to the extra X chromosome in the son as a results of disjunction in either meiosis I or meiosis II during…
Chapter 6 Solutions
ESSENTIALS OF GENETICS-MODIFIED ACCESS
Ch. 6 - CASE STUDY| Fish tales Aquatic vegetation...Ch. 6 - CASE STUDY |Fish tales Aquatic vegetation...Ch. 6 - CASE STUDY |Fish tales
Aquatic vegetation...Ch. 6 - HOW DO WE KNOW? In this chapter, we focused on...Ch. 6 -
CONCEPT QUESTION
2. Review the Chapter Concepts...Ch. 6 -
3. Define these pairs of terms, and distinguish...Ch. 6 -
4. For a species with a diploid number of 18,...Ch. 6 - What explanation has been proposed to explain why...Ch. 6 - Contrast the fertility of an allotetraploid with...Ch. 6 -
7. Why do human monosomies most often fail to...
Ch. 6 -
8. Describe the origin of cultivated American...Ch. 6 - Predict how the synaptic configurations of...Ch. 6 - Inversions are said to “suppress crossing over.”...Ch. 6 -
11. Predict the genetic composition of gametes...Ch. 6 - Human adult hemoglobin is a tetramer containing...Ch. 6 -
13. The primrose, Primula kewensis, has 36...Ch. 6 - Certain varieties of chrysanthemums contain 18,...Ch. 6 - Drosophila may be monosomic for chromosome 4, yet...Ch. 6 - Mendelian ratios are modified in crosses involving...Ch. 6 -
17. Having correctly established the F2 ratio in...Ch. 6 -
18. In a cross between two varieties of corn,...Ch. 6 -
19. A couple planning their family are aware that...Ch. 6 -
20. A woman who sought genetic counseling is...Ch. 6 - The woman in Problem 20 has had two miscarriages....Ch. 6 -
22. In a recent cytogenetic study on 1021 cases...Ch. 6 -
23. A boy with Klinefelter syndrome (47,XXY) is...Ch. 6 - In a human genetic study, a family with five...Ch. 6 - A 3-year-old child exhibited some early indication...Ch. 6 - A normal female is discovered with 45 chromosomes,...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Assume that a meiotic-nondisjunction event causes trisomy 8 in a newborn. If two of the three copies of chromosome 8 are absolutely identical, at what point during meiosis did the nondisjunction event take place?arrow_forwardA boy with Klinefelter syndrome (47,XXY) is born to a mother who is phenotypically normal and a father who has the X-linked skin condition called anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. The mother’s skin is completely normal with no signs of the skin abnormality. In contrast, her son has patches of normal skin and patches of abnormal skin. (a) Which parent contributed the abnormal gamete? (b) Using the appropriate genetic terminology, describe the meiotic mistake that occurred. Be sure to indicate in which division the mistake occurred. (c) Using the appropriate genetic terminology, explain the son’s skin phenotype.arrow_forwardA wild-type chromosome has the following segments: A B C • D E F G H I Researchers have found individuals that are heterozygous for each of the following chromosome mutations. For each mutation, sketch how the wild-type and mutated chromosomes would pair in prophase I of meiosis, showing all chromosome strands. a. A B C • D E F D E F G H I b. A B C • D H I c. A B C • D G F E H I d. A B E D • C F G H Iarrow_forward
- A woman who sought genetic counseling is found to be heterozygousfor a chromosomal rearrangement between the second andthird chromosomes. Her chromosomes, compared to those in anormal karyotype, are diagrammed on the next page:(a) What kind of chromosomal aberration is shown? (b) Using a drawing, demonstrate how these chromosomeswould pair during meiosis. Be sure to label the differentsegments of the chromosomes.(c) This woman is phenotypically normal. Does thissurprise you? Why or why not? Under what circumstancesmight you expect a phenotypic effect of such arearrangement? The woman in above problem has had two miscarriages. Shehas come to you, an established genetic counselor, with thesequestions:(a) Is there a genetic explanation of her frequent miscarriages?arrow_forwardA woman who sought genetic counseling is found to be heterozygousfor a chromosomal rearrangement between the second andthird chromosomes. Her chromosomes, compared to those in anormal karyotype, are diagrammed on the next page:(a) What kind of chromosomal aberration is shown? (b) Using a drawing, demonstrate how these chromosomeswould pair during meiosis. Be sure to label the differentsegments of the chromosomes.(c) This woman is phenotypically normal. Does thissurprise you? Why or why not? Under what circumstancesmight you expect a phenotypic effect of such arearrangement? The woman in above problem has had two miscarriages. Shehas come to you, an established genetic counselor, with thesequestions:(a) If not, what is the chance that she could have a normalchild? Provide an informed response to her concernsarrow_forwardTwo phenotypically normal parents produce a phenotypically abnormal child in which chromosome 5 is missing part of its long arm but has a piece of chromosome 7 attached to it. The child also has one normal copy of chromosome 5 and two normal copies of chromosome 7. With regard to chromosomes 5 and 7, what do you think are the chromosomal compositions of the parents? Would it most likely be reciprocal translocation? It wouldn't be simple translocation because then the child would have the entirety of one chromosome and only some of the other, but in this case, there is only partial chromosome 5 and chromosome 7?arrow_forward
- A wild-type chromosome has the following segments: A B C • D E F G H I Researchers have found individuals that are heterozygous for each of the following chromosome mutations. For each mutation, sketch how the wild-type and mutated chromosomes would pair in prophase I of meiosis, showing all chromosome strands. Q. A B C • D H Iarrow_forwardA woman who sought genetic counseling is found to be heterozygousfor a chromosomal rearrangement between the second andthird chromosomes. Her chromosomes, compared to those in anormal karyotype, are diagrammed on the next page:(a) This woman is phenotypically normal. Does thissurprise you? Why or why not? Under what circumstancesmight you expect a phenotypic effect of such arearrangement?arrow_forwardA woman with no phenotype is known to have a 14:21 translocation. 1. With respect to only chromosomes 14 and 21, how many distinct chromosome combinations will happen in her eggs? What portion will be viable? 2. If she has children with a normal man (no translocations), what is the probability that they have a daughter with Down Syndrome or a son with no phenotype?arrow_forward
- For the following chromosome complements, what is the phenotypic sex of a person who has Q. XX with a copy of the SRY gene on an autosomal chromosome?arrow_forwardAssuming no other abnormalities, classify each of the following human sex chromosome complements as to whether or not individuals with that complement will be morphologically male or female. Three human sex chromosome complements will be classified as male and three will be classified as female. XXY XYY XXX XO XY XXarrow_forwardIf an organism has 15 pairs of homologous chromosomes, how many chromosomes will each daughter cell have after telophase of mitosis? In this same organism, how many chromosomes will each daughter cell have after telophase II of meiosis?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mitochondrial mutations; Author: Useful Genetics;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GvgXe-3RJeU;License: CC-BY