
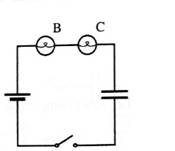
Suppose that instead of connecting the uncharged capacitor to the single bulb A. you connected it to the two-bulb circuit shown at right
1. Predict how the initial brightness of bulb B compares to the initial brightness of bulb C. Explain.
2. Predict how the initial brightness of bulb B compares to the initial brightness of bulb A above. Explain.
Discharge the capacitor and then set up the circuit with the uncharged capacitor and check your predictions. If your prediction is in conflict with your observation, how can you account for your observation?
3. Predict how the final charge on the capacitor compares to the final charge on the capacitor from part A.
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 6 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Introduction to Electrodynamics
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics (5th Edition)
- I need proper answer for the following ( understandable writing and well explained ) Why does a capacitor act as a short circuit at high frequencies? Plus, why does a capacitor act as an open circuit at low frequencies?arrow_forwardConsider the diagram at the right of a parallel circuit. Each light bulb has an identical resistance of R and the battery voltage is V. Use the labeled points on the diagram to answer the following questions. a. If the current at location A is I amperes, then the current at location B is ____ amperes. (Answer in terms of I.) b. If the current at location A is I amperes, then the current at location D is ____ amperes. (Answer in terms of I.) c. If the current at location A is I amperes, then the current at location L is ____ amperes. (Answer in terms of I.) d. If the voltage of the battery is doubled, then the current at location A would be ____ (two times, four times, one-half, one-fourth, etc.) the original value. e. If the voltage of the battery is doubled, then the current at location B would be ____ (two times, four times, one-half, one-fourth, etc.) the original value. f. If the voltage of the battery is doubled, then the current at location D would be ____ (two times, four times,…arrow_forwardWhat is the equivalent resistance of a Red-Green-Brown resistor in series with a parallel combination of Brown-Green-Red and Orange-Black-Red resistors? Show your work.arrow_forward
- Part D) Now apply the loop rule to loop 1 (the larger loop spanning the entire circuit). Sum the voltage changes across each circuit element around this loop going in the direction of the arrow. Express the voltage drops in terms of Vb, I1, I3, the given resistances, and any other given quantities. Answer=Σ(ΔV)=0= It is still saying incorrect because the correct answer does not depend on: I2, R2. Can you explain why that is and what the correct equation would be?arrow_forwardConsider the circuit diagram depicted in the figure. Part (a) If the current through the top branch is I2 = 0.025 A, what is the current through the bottom, I3, in amps?arrow_forward3question4 Show all work picture attatched Calculate the value of the resistance Rled in Circuit #1, to ensure that a GREEN LED will have a current of 10 mA Type your answer here or paste the image of your handwriting solution herearrow_forward
- Please fill out the template below with the work for this problem. Note that you need to have a picture, a list of knowns and unknowns, the general equation/s you will use, and the math steps to solve for the unknown, only plug in the numbers after you have solved for the unknown, and the answer with units included. Question 1: Suppose you have a 195 μF capacitor. What charge is stored in it when 102 V is applied to it, in millicoulombs?arrow_forward3question6 Show all work Picture attatched 6) Given three LEDs, connected in series as shown in the Circuit #2 (below), calculate the value of the resistance Rled_series to ensure that the current Itotal in the circuit is 10 mA. Type your answer here or paste the image of your handwriting solution herearrow_forwardA triangular array of resistors is shown in the figure on the right. What current will this array draw from a 35.0V battery having negligible internal resistance if we connect it across a.) ab; b.) bc and c.) ac?arrow_forward
- 1.in picture left why is PEi equal to 0?why is KEf is also equal zero?why Ri is too far away from Rf??? 2. The picture on the right,why PEf is equal to 0 instead of letting PEi equal to 0???? 3. what is the main words in the question helps us to decide which PE (PEf or PEi)equal to 0???arrow_forwardIdentical bulbs are shown in the circuit. 1) Is bulb A brighter, dimmer, or the same brightness as bulb B? Explain 2) Is the current through bulb D greater that or less that, or equal to the current through bulb F. Explain. 3) If bulb F is unscrewed from its socket, does bulb B become brighter, dimmer, or stay the same. Explain.arrow_forwardPartB5 Show all work Picture attatched Part B Given the following circuit Calculate the current through each Resistance R1 to R6 when its correspondent switch is closed (e.g. the current through R1 when the switch SW1 is closed, the current through R2 when the switch SW2 is closed, etc.) Type your solution of question 1) in RED or PASTE the image of your handwriting solution HERE If the value of the Fuse F1 is 1 Amperes, which different combinations of switches can you close together to ensure that will be the maximum current possible but the Fuse F1 will not blow apart? – Justify your answer with your calculations. Type your solution of question 2) in RED or PASTE the image of your handwriting solution HERE If the value of the Fuse F1 is 2 Amperes, which different combinations of switches can you close together to ensure that will be the maximum current possible but the Fuse F1 will not blow apart? – Justify your answer with your calculations. Type your solution of…arrow_forward
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
