
(a)
Interpretation:
The given substrates should be determined that whether they favor
Concept introduction:
Carbocation: it is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Carbocation stability order:
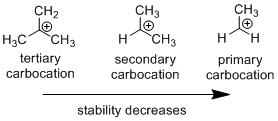
Carbo-cation Rearrangement:
Leaving group: it is a fragment that leaves substrate with a pair of electrons via heterolytic bond cleavage.
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Nucleophilic nature depends on the negative charge present in the molecule, the solvent in which it present and the electronegativity of the atom.
Solvent: it is substance which dissolves the chemical substrate. They are classified as polar protic and
Polar protic solvent: It contains at least one
Electropositive: The tendency of a metal to lose electrons readily in
(c)
Interpretation:
The given substrates should be determined that whether they favor
Concept introduction:
Carbocation: it is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Carbocation stability order:

Carbo-cation Rearrangement:
Leaving group: it is a fragment that leaves substrate with a pair of electrons via heterolytic bond cleavage.
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Nucleophilic nature depends on the negative charge present in the molecule, the solvent in which it present and the electronegativity of the atom.
Solvent: it is substance which dissolves the chemical substrate. They are classified as polar protic and polar aprotic solvent.
Polar protic solvent: It contains at least one
Electropositive: The tendency of a metal to lose electrons readily in chemical reaction.
(e)
Interpretation:
The given substrates should be determined that whether they favor
Concept introduction:
Carbocation: it is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Carbocation stability order:

Carbo-cation Rearrangement:
Leaving group: it is a fragment that leaves substrate with a pair of electrons via heterolytic bond cleavage.
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Nucleophilic nature depends on the negative charge present in the molecule, the solvent in which it present and the electronegativity of the atom.
Solvent: it is substance which dissolves the chemical substrate. They are classified as polar protic and polar aprotic solvent.
Polar protic solvent: It contains at least one
Electropositive: The tendency of a metal to lose electrons readily in chemical reaction.
(h)
Interpretation:
The given substrates should be determined that whether they favor
Concept introduction:
Carbocation: it is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Carbocation stability order:

Carbo-cation Rearrangement:
Leaving group: it is a fragment that leaves substrate with a pair of electrons via heterolytic bond cleavage.
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Nucleophilic nature depends on the negative charge present in the molecule, the solvent in which it present and the electronegativity of the atom.
Solvent: it is substance which dissolves the chemical substrate. They are classified as polar protic and polar aprotic solvent.
Polar protic solvent: It contains at least one
Electropositive: The tendency of a metal to lose electrons readily in chemical reaction.
(b)
Concept introduction:
Structure of the substrate plays an major role in the reactivity of
Leaving group: it is a fragment that leaves the chemical compound with pair of electrons in a heterolytic bond cleavage. The
Polar aprotic solvent: It does not contain
(d)
Concept introduction:
Structure of the substrate plays an major role in the reactivity of
Leaving group: it is a fragment that leaves the chemical compound with pair of electrons in a heterolytic bond cleavage. The
Polar aprotic solvent: It does not contain
(f)
Concept introduction:
Structure of the substrate plays an major role in the reactivity of
Leaving group: it is a fragment that leaves the chemical compound with pair of electrons in a heterolytic bond cleavage. The
Polar aprotic solvent: It does not contain
(g)
Concept introduction:
Structure of the substrate plays an major role in the reactivity of
Leaving group: it is a fragment that leaves the chemical compound with pair of electrons in a heterolytic bond cleavage. The
Polar aprotic solvent: It does not contain
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY GGC>CUSTOM<-TEXT
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





