
Concept explainers
Phoenix Company’s 2015
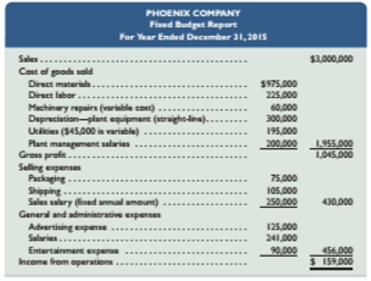
Required
- Classify all items listed in the fixed budget as variable or fixed. Also determine their amounts per unit or their amounts for the year, as appropriate.
- Prepare flexible budgets (See Exhibit 8.3) for the company at sales volumes of 14,000 and 16,000 units.
- The company’s business conditions are improving. One possible result is a sales volume of 18,000 units. The company president in confident that this volume is within the relevant range of existing capacity. How much would operating income increase over the 2015 budgeted amount of $159,000 if this level is reached without increasing capacity?
- An unfavorable change in business is remotely possible; in this case, production and sales volume for 2015 could fall to 12,000 units. How much income (or loss) from operations would occurs if sales volume falls to this level?
Concept introduction:
Fixed Budget:
A fixed budget, also known as static budget does not adjust throughout the budget period and is prepared on the assumption that specific amount of goods would be sold in the concerned period.
Requirement 1:
Classification of items of fixed budget as fixed or variable and their amounts per unit or their amounts for the year.
Answer to Problem 1PSA
Classification of fixed budget items as fixed or variable:
| Particulars | Total amount (In $) | Amount per unit (In $) |
| Variable costs: | ||
| Direct materials | 9, 75, 000 | 65 |
| Direct labor | 2, 25, 000 | 15 |
| Machinery repairs | 60, 000 | 4 |
| Utilities | 45, 000 | 3 |
| Packaging | 75, 000 | 5 |
| Shipping | 1, 05, 000 | 7 |
| Total variable costs | 99 | |
| Fixed costs: | ||
| Depreciation- Plant equipment | 3, 00, 000 | |
| Utilities | 1, 50, 000 | |
| Plant management salaries | 2, 00, 000 | |
| Sales salaries | 2, 50, 000 | |
| Advertising expense | 1, 25, 000 | |
| Salaries | 2, 41, 000 | |
| Entertainment expense | 90, 000 | |
| Total fixed costs | 13, 56, 000 |
Explanation of Solution
The items laid in fixed budget of the company in the given problem can be classified into variable or fixed based on their nature i.e. on the basis of their behavior and traceability as explained below:
Variable costs vary directly with the production level i.e. company’s variable cost increases as the production increases and vice-a-versa. Therefore, following costs would be classified as Variable:
- Direct materials: The direct materials would be relate to the amount paid for procurement of materials which would vary
- Direct labor: The payment made to direct labor would vary depending on the production
- Machinery repairs: The repairs done on machinery would be varied depending upon the usage of machinery for production of output
- Utilities: Utilities would be acquired depending on their requirement which would vary
- Packaging: The amount spent on packaging would be in relation to products produced which would vary
- Shipping: Expenses incurred on shipping would be incurred based on the number of products produced
Fixed costs do not vary with the level of production. They do not change with the amount of goods or services a company produces. Therefore, those costs which are fixed in nature would be covered under fixed costs as given below:
- Depreciation- Plant equipment: The depreciation charged on plants equipment would remain fixed and would not change with the level of production
- Utilities: Utilities other than variable in nature would be covered under fixed cost
- Plant management salaries: The salaries paid for managing would be fixed in nature
- Sales salaries: Salaries paid to sales staff would remain fixed in nature
- Advertising expense: The expenses on advertising would be covered under fixed cost
- Salaries: Salaries paid to staff would remain fixed in nature and would not change with the level of production
- Entertainment expense: Expenses on entertainment are fixed irrespective of the level of production
Further, it is given in the problem that sales volume is 15, 000 units and Sales are $3, 000, 0000. Therefore, calculation of Variable cost per unit has been calculated using the following formula:
Following would be the per unit amounts:
Thus, the total variable costs would be the following:
Also, fixed costs would include the following;
Therefore, classification of fixed budget items as asked in the given problem is shown below in the tabular manner:
Classification of fixed budget items as fixed or variable:
| Particulars | Total amount (In $) | Amount per unit (In $) |
| Variable costs: | ||
| Direct materials | 9, 75, 000 | 65 |
| Direct labor | 2, 25, 000 | 15 |
| Machinery repairs | 60, 000 | 4 |
| Utilities | 45, 000 | 3 |
| Packaging | 75, 000 | 5 |
| Shipping | 1, 05, 000 | 7 |
| Total variable costs | 99 | |
| Fixed costs: | ||
| Depreciation- Plant equipment | 3, 00, 000 | |
| Utilities | 1, 50, 000 | |
| Plant management salaries | 2, 00, 000 | |
| Sales salaries | 2, 50, 000 | |
| Advertising expense | 1, 25, 000 | |
| Salaries | 2, 41, 000 | |
| Entertainment expense | 90, 000 | |
| Total fixed costs | 13, 56, 000 |
Concept introduction:
Flexible Budget:
A flexible budget, also known as variation budget adjusts to changes in volume or activity. Flexible budgets are prepared for comparing actual to budgeted performances at many levels of activity during the previous year. In order to accurately predict the changes in costs, management identifies them into fixed or variable costs.
Fixed cost:
These costs do not vary with the level of production. They do not change with the amount of goods or services a company produces. They remain same even if the company does not produce any product or provide any service during an accounting period.
Variable cost:
These costs vary with the level of production. They are usually shown in the budget as either a percentage of total revenue or at a constant rate per unit produced.
Requirement 2:
Flexible budget for the company at sales volume of 14, 000 units and 16, 000 units.
Answer to Problem 1PSA
Flexible budget for the company for the year ended December 31, 2015 (Amount in $):
| Company | ||||
| Flexible budget | ||||
| For year ended December 31, 2015 | ||||
| Particulars | Flexible budget | Flexible budget for 14, 000 units sold | Flexible budget for 16, 000 units sold | |
| Variable amount per unit | Total fixed cost | |||
| Sales | 200 | 28, 00, 000 | 32, 00, 000 | |
| Variable costs: | ||||
| Direct materials | 65 | 9, 10, 000 | 10, 40, 000 | |
| Direct labor | 15 | 2, 10, 000 | 2, 40, 000 | |
| Machinery repairs | 4 | 56, 000 | 64, 000 | |
| Utilities | 3 | 42, 000 | 48, 000 | |
| Packaging | 5 | 70, 000 | 80, 000 | |
| Shipping | 7 | 98, 000 | 1, 12, 000 | |
| Total variable costs | 99 | 13, 86, 000 | 15, 84, 000 | |
| Contribution margin | 101 | 14, 14, 000 | 16, 16, 000 | |
| Fixed costs: | ||||
| Depreciation- Plant equipment | 3, 00, 000 | 3, 00, 000 | 3, 00, 000 | |
| Utilities | 1, 50, 000 | 1, 50, 000 | 1, 50, 000 | |
| Plant management salaries | 2, 00, 000 | 2, 00, 000 | 2, 00, 000 | |
| Sales salary | 2, 50, 000 | 2, 50, 000 | 2, 50, 000 | |
| Advertising expense | 1, 25, 000 | 1, 25, 000 | 1, 25, 000 | |
| Salaries | 2, 41, 000 | 2, 41, 000 | 2, 41, 000 | |
| Entertainment expense | 90, 000 | 90, 000 | 90, 000 | |
| Total fixed costs | 13, 56, 000 | 13, 56, 000 | 13, 56, 000 | |
| Income from operations | 58, 000 | 2, 60, 000 | ||
Explanation of Solution
For preparation of flexible budget of the company, following formulas would be used:
In the given problem, it is given that sales are $30, 00, 000 and sales volume is 15, 000 units.
Flexible budget has to be prepared at sales volume of 14, 000 and 16, 000 units. We have already calculated variable cost per unit of all the items. Now, calculations for variable cost have been made in the following manner:
| Particulars | Variable amount per unit (Amount in $) | For 14, 000 units sold | For 16, 000 units sold |
| Sales | 200 | $200*14, 000 = 28, 00, 000 | $200*16, 000 = 32, 00, 000 |
| Variable costs: | |||
| Direct materials | 65 | $65*14, 000 = 9, 10, 000 | $65*16, 000 = 10, 40, 000 |
| Direct labor | 15 | $15*14, 000 = 2, 10, 000 | $15*16, 000 = 2, 40, 000 |
| Machinery repairs | 4 | $4*14, 000 = 56, 000 | $4*16, 000 = 64, 000 |
| Utilities | 3 | $3*14, 000 = 42, 000 | $3*16, 000 = 48, 000 |
| Packaging | 5 | $5*14, 000 = 70, 000 | $5*16, 000 = 80, 000 |
| Shipping | 7 | $7*14, 000 = 98, 000 | $7*16, 000 = 1, 12, 000 |
| Total variable costs | 99 | 13, 86, 000 | 15, 84, 000 |
Further, contribution margin can be calculated using the below- mentioned formulas:
Thus, contribution margin would be:
Fixed costs would remain same irrespective of the changes in sales volume. Also, Income from operations can be computed using the following formula:
Therefore, flexible budget asked in the given problem at 14, 000 and 16, 000 units is given below:
Flexible budget for the company for the year ended December 31, 2015 (Amount in $):
| Company | ||||
| Flexible budget | ||||
| For year ended December 31, 2015 | ||||
| Particulars | Flexible budget | Flexible budget for 14, 000 units sold | Flexible budget for 16, 000 units sold | |
| Variable amount per unit | Total fixed cost | |||
| Sales | 200 | 28, 00, 000 | 32, 00, 000 | |
| Variable costs: | ||||
| Direct materials | 65 | 9, 10, 000 | 10, 40, 000 | |
| Direct labor | 15 | 2, 10, 000 | 2, 40, 000 | |
| Machinery repairs | 4 | 56, 000 | 64, 000 | |
| Utilities | 3 | 42, 000 | 48, 000 | |
| Packaging | 5 | 70, 000 | 80, 000 | |
| Shipping | 7 | 98, 000 | 1, 12, 000 | |
| Total variable costs | 99 | 13, 86, 000 | 15, 84, 000 | |
| Contribution margin | 101 | 14, 14, 000 | 16, 16, 000 | |
| Fixed costs: | ||||
| Depreciation- Plant equipment | 3, 00, 000 | 3, 00, 000 | 3, 00, 000 | |
| Utilities | 1, 50, 000 | 1, 50, 000 | 1, 50, 000 | |
| Plant management salaries | 2, 00, 000 | 2, 00, 000 | 2, 00, 000 | |
| Sales salary | 2, 50, 000 | 2, 50, 000 | 2, 50, 000 | |
| Advertising expense | 1, 25, 000 | 1, 25, 000 | 1, 25, 000 | |
| Salaries | 2, 41, 000 | 2, 41, 000 | 2, 41, 000 | |
| Entertainment expense | 90, 000 | 90, 000 | 90, 000 | |
| Total fixed costs | 13, 56, 000 | 13, 56, 000 | 13, 56, 000 | |
| Income from operations | 58, 000 | 2, 60, 000 | ||
Thus, the income from operations of company at sales volume of 14, 000 and 16, 000 units are $58, 000 and $2, 60, 000 respectively.
Concept introduction:
Fixed cost:
These costs do not vary with the level of production. They do not change with the amount of goods or services a company produces. They remain same even if the company does not produce any product or provide any service during an accounting period.
Variable cost:
These costs vary with the level of production. They are usually shown in the budget as either a percentage of total revenue or at a constant rate per unit produced.
Requirement 3:
Increase in operating income at 18, 000 units without increasing capacity.
Answer to Problem 1PSA
Increase in operating income at 18, 000 units without increasing capacity = $3, 03, 000
Explanation of Solution
Sales volume has been increased to 18, 000 units from 15, 000 units, thereby increasing 3, 000 units sold (18, 000 units- 15, 000 units). For calculating increase in operating income with existing capacity and fixed costs, firstly total contribution margin would be calculated using the following formula:
Contribution margin per unit has already been calculated as $101 per unit. Thus,
Total fixed costs are calculated as $13, 56, 000. Therefore, all the calculations have been shown in the table below:
| Particulars | Amount |
| Total contribution margin | $101* 18, 000 units = $18, 18, 000 |
| Less: Fixed costs | ($13, 56, 000) |
| Potential operating loss | $4, 62, 000 |
| Budgeted income of 2015 | ($1, 59, 000) |
| Increase in operational income | $3, 03, 000 |
Therefore, Increase in operating income at 18, 000 units without increasing capacity is coming out to be $3, 03, 000.
Concept introduction:
Fixed cost:
These costs do not vary with the level of production. They do not change with the amount of goods or services a company produces. They remain same even if the company does not produce any product or provide any service during an accounting period.
Variable cost:
These costs vary with the level of production. They are usually shown in the budget as either a percentage of total revenue or at a constant rate per unit produced.
Requirement 4:
Income (or loss) from operations if sales volume fall to 12, 000 units.
Answer to Problem 1PSA
Potential operating loss at sales volume of 12, 000 units = $1, 44, 000
Explanation of Solution
Sales volume has fallen to 12, 000 units from 15, 000 units, thereby decreasing 3, 000 units sold (15, 000 units- 12, 000 units). For calculating income (or loss) from operations, firstly total contribution margin would be calculated using the following formula:
Contribution margin per unit has already been calculated as $101 per unit. Thus,
Total fixed costs are calculated as $13, 56, 000. Therefore, all the calculations have been shown in the table below:
| Particulars | Amount |
| Total contribution margin | $101* 12, 000 units = $12, 12, 000 |
| Less: Fixed costs | ($13, 56, 000) |
| Potential operating loss | $1, 44, 000 |
Therefore, the potential operating loss at 12, 000 units is coming out to be $1, 44, 000.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING ACCT 2302 >IC<
- Before the year began, the following static budget was developed for the estimated sales of 100,000. Sales are sluggish and management needs to revise its budget. Use this information to prepare a flexible budget for 80,000 and 90,000 units of sales.arrow_forwardCarmichael Corporation is in the process of preparing next years budget. The pro forma income statement for the current year is as follows: Required: 1. What is the break-even sales revenue (rounded to the nearest dollar) for Carmichael Corporation for the current year? 2. For the coming year, the management of Carmichael Corporation anticipates an 8 percent increase in variable costs and a 60,000 increase in fixed expenses. What is the break-even point in dollars for next year? (CMA adapted)arrow_forwardStarburst Inc. has the following items and amounts as part of its master budget at the 10,000-unit level of sales and production: Determine the total dollar amounts for the above items that would appear in a flexible budget at the following volume levels, assuming that both levels are within the relevant range: a. 8,000-unit level of sales and production b. 12,000-unit level of sales and production (Hint: You must first determine the unit selling price and certain unit costs.)arrow_forward
- Shalimar Company manufactures and sells industrial products. For next year, Shalimar has budgeted the follow sales: In Shalimars experience, 10 percent of sales are paid in cash. Of the sales on account, 65 percent are collected in the quarter of sale, 25 percent are collected in the quarter following the sale, and 7 percent are collected in the second quarter after the sale. The remaining 3 percent are never collected. Total sales for the third quarter of the current year are 4,900,000 and for the fourth quarter of the current year are 6,850,000. Required: 1. Calculate cash sales and credit sales expected in the last two quarters of the current year, and in each quarter of next year. 2. Construct a cash receipts budget for Shalimar Company for each quarter of the next year, showing the cash sales and the cash collections from credit sales. 3. What if the recession led Shalimars top management to assume that in the next year 10 percent of credit sales would never be collected? The expected payment percentages in the quarter of sale and the quarter after sale are assumed to be the same. How would that affect cash received in each quarter? Construct a revised cash budget using the new assumption.arrow_forwardDigital Solutions Inc. uses flexible budgets that are based on the following data: Prepare a flexible selling and administrative expenses budget for October for sales volumes of 500,000, 750,000, and 1,000,000.arrow_forwardThe sales department of Macro Manufacturing Co. has forecast sales for its single product to be 20,000 units for June, with three-quarters of the sales expected in the East region and one-fourth in the West region. The budgeted selling price is 25 per unit. The desired ending inventory on June 30 is 2,000 units, and the expected beginning inventory on June 1 is 3,000 units. Prepare the following: a. A sales budget for June. b. A production budget for June.arrow_forward
- Review the completed master budget and answer the following questions: Is Ranger Industries expecting to earn a profit during the next quarter? If so, how much? Does the company need to borrow cash during the quarter? Can it make any repayments? Explain. (Carefully review rows 74 through 80.)arrow_forwardListed below are the budgeted factory overhead costs for 2011 for Moss Industries at a projected level of 2,000 units: Required: Prepare flexible budgets for factory overhead at the 1,000, 2,000, and 4,000 unit levels. (Hint: You must first decide which of the listed costs should be considered variable and which should be fixed.)arrow_forwardSales, production, direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead budgets King Tire Co.s budgeted unit sales for the year 2016 were: The budgeted selling price for truck tires was 200 per tire, and for passenger car tires it was 65 per tire. The beginning finished goods inventories were expected to be 2,000 truck tires and 5,000 passenger tires, for a total cost of 326,478, with desired ending inventories at 2,500 and 6,000, respectively, with a total cost of 400,510. There was no anticipated beginning or ending work-in- process inventory for either type of tire. The standard materials quantities for each type of tire were as follows: The purchase prices of rubber and steel were 2 and 3 per pound, respectively. The desired ending inventories for rubber and steel were 60,000 and 6,000 lb, respectively. The estimated beginning inventories for rubber and steel were 75,000 and 7,000 lb, respectively. The direct labor hours required for each type of tire were as follows: The direct labor rate for each department is as follows: Budgeted factory overhead costs for 2016 were as follows: Required: Prepare each of the following budgets for King for the year ended December 31, 2016: 1. Sales budget. 2. Production budget. 3. Direct material budget. 4. Direct labor budget. 5. Factory overhead budget. 6. Cost of goods sold budget.arrow_forward
- Using the following per-unit and total amounts, prepare a flexible budget at the 14,000-, 15,000-, and 16,000-unit levels of production and sales for Natural Products Inc.:arrow_forwardPrepare a flexible budgeted income statement for 47,000 units using the following information from a static budget for 45,000 units:arrow_forwardUsing the provided budgeted information for production of 10,000 and 15,000 units, prepare a flexible budget for 17,000 units.arrow_forward
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals Of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781337902571Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals Of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781337902571Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT





