
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
For the given reaction, the major product is to be determined. The complete, detailed mechanism is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
When the attacking species is an alcohol which is a weak base and weak nucleophile, it favors
Answer to Problem 9.81P
The complete, detailed mechanism and the major product for the given reaction is shown below:
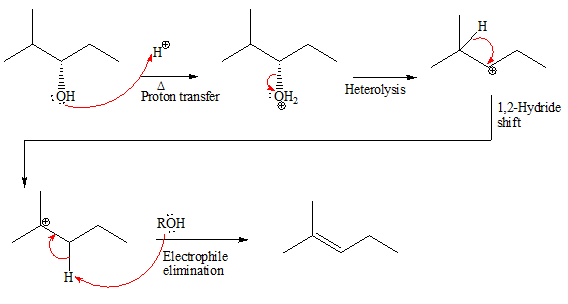
Explanation of Solution
The given reacting species are shown below:
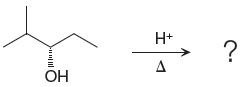
In the given reaction, attacking species is an alcohol which is a weak nucleophile. Also, the leaving group can be water under acidic conditions which is an excellent leaving group. Also, the solvent is an alcohol. Therefore, the given reaction favors

The complete, detailed mechanism and the major product for the given reaction is drawn on the basis of reacting species.
(b)
Interpretation:
For the given reaction, the major product is to be determined. The complete, detailed mechanism is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
When attacking species is an alcohol which is a weak base and weak nucleophile, it favors
Answer to Problem 9.81P
The complete, detailed mechanism and the major product for the given reaction is shown below:
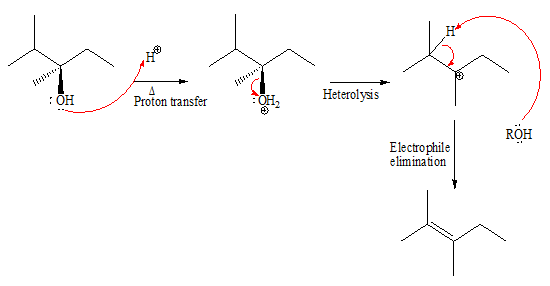
Explanation of Solution
The given reacting species are shown below,
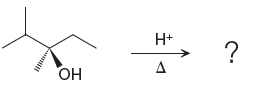
In the given reaction, attacking species is an alcohol which is a weak nucleophile. Also, the leaving group can be water under acidic conditions which is an excellent leaving group. Also, the solvent is an alcohol. Therefore, the given reaction favors

The complete, detailed mechanism and the major product for the given reaction are drawn on the basis of reacting species.
(c)
Interpretation:
For the given reaction, the major product is to be determined. The complete, detailed mechanism is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
When attacking species is an alcohol which is a weak base and weak nucleophile, it favors
Answer to Problem 9.81P
The complete, detailed mechanism and the major product for the given reaction is shown below:
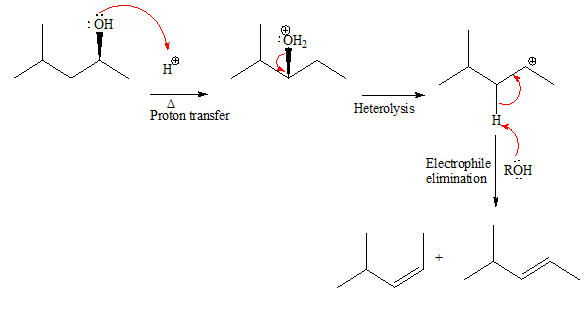
Explanation of Solution
The given reacting species are shown below,
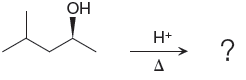
In the given reaction, attacking species is an alcohol which is a weak nucleophile. Also, the leaving group can be water under acidic conditions which is an excellent leaving group. Also, the solvent is an alcohol. Therefore, the given reaction favors 
The complete, detailed mechanism and the major product for the given reaction are drawn on the basis of reacting species.
(d)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction is to be determined. The complete, detailed mechanism is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
When attacking species is an alcohol which is a weak base and weak nucleophile, it favors
Answer to Problem 9.81P
The complete, detailed mechanism and the major product for the given reaction is shown below,
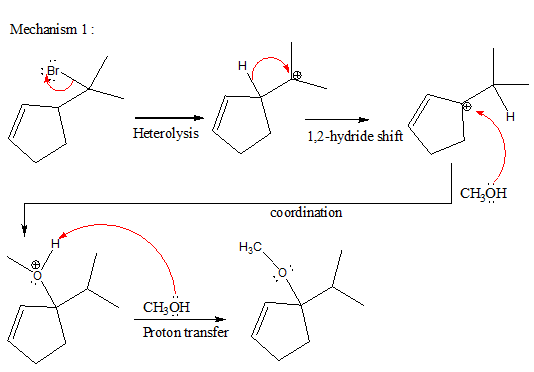
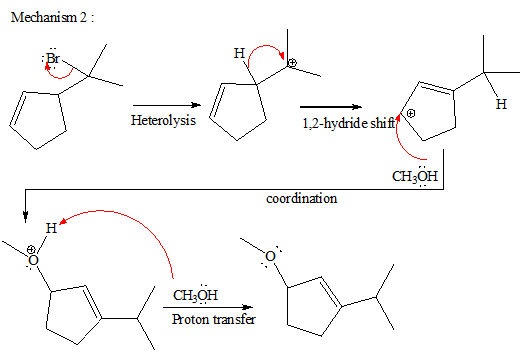
Explanation of Solution
The given reacting species are shown below,
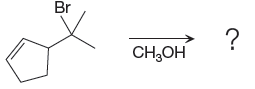
In the given reaction, attacking species is an alcohol which is a weak nucleophile. Also, the leaving group can be water under acidic conditions which is an excellent leaving group. Also, the solvent is an alcohol. Therefore, the given reaction favors


The complete, detailed mechanism and the major product for given reaction are drawn on the basis of reacting species.
(e)
Interpretation:
For the given reaction, the major product is to be determined. The complete, detailed mechanism is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The strong nucleophile and weak base favors
Answer to Problem 9.81P
The complete, detailed mechanism and product of the given reaction is as shown below:
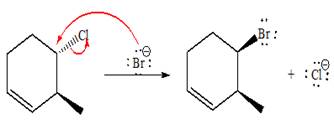
Explanation of Solution
The given reacting species are shown below,
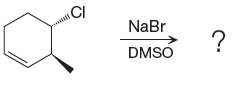
The Br- is a strong nucleophile but a weak base that favors
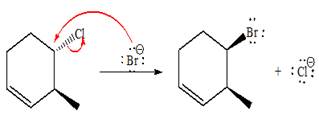
The complete, detailed mechanism and the major product for the given reaction are drawn on the basis of reacting species.
(f)
Interpretation:
For the given reaction, the major product is to be determined. The complete, detailed mechanism is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
If the attacking species is a strong bulky base but has low concentration it favors
Answer to Problem 9.81P
The complete, detailed mechanism and the products of the given reaction are shown below,
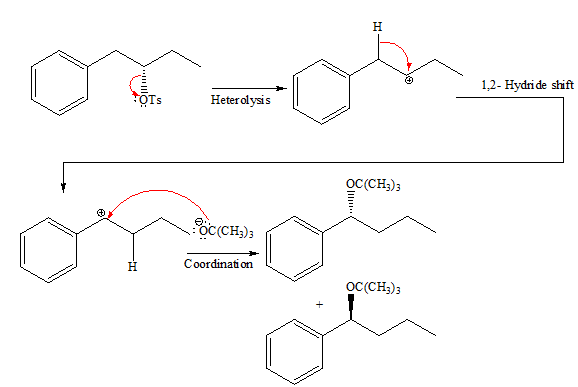
Explanation of Solution
The given reacting species are shown below,
In the given reaction, the attacking species is a strong bulky base so it favors

The complete, detailed mechanism and the major product for the given reaction is drawn on the basis of reacting species.
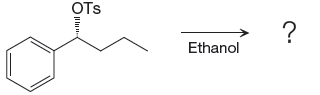
(g)
Interpretation:
For the given reaction, the major product is to be determined. The complete, detailed mechanism is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
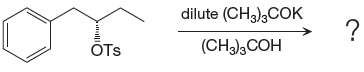
When attacking species is an alcohol which is a weak base and weak nucleophile, it favors
Answer to Problem 9.81P
The complete, detailed mechanism and the major product for the given reaction is shown below,
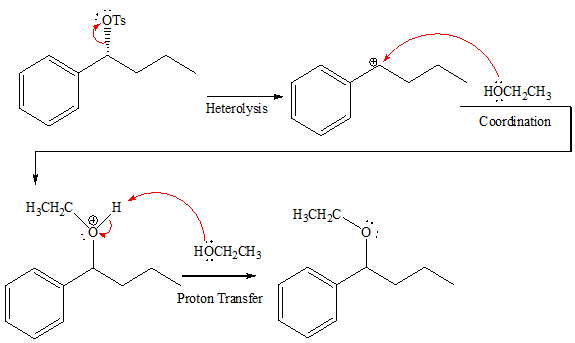
Explanation of Solution
The given reacting species are shown below:
In the given reaction, attacking species is a weak nucleophile and weak base. Also, the leaving group

The complete, detailed mechanism and the major product for the given reaction are drawn on the basis of reacting species.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
ORG.CHEM W/TEXT+SOLU.MANUAL
- Ochem help... What is the major product of the following reaction sequence? Provide the stepwise mechanism for each step (1, 2a, and 2b). (see attached image)arrow_forwardFor the following dehydrohalogenation (E2) reaction, draw the Zaitsev product(s) showing the stereochemistry clearly. If there is more than one organic product, both products can be drawn in the same box.arrow_forwardThe following reaction is done with a low concentration. What type of substitution mechanism will be favored: SN1 or SN2? Draw the product that will result.arrow_forward
- For each set of reactions, circle the mechanism (SN2 vs SN1), draw the main organic substitution/elimination product (for each reaction draw the product, though in some cases it may be equivalent) and indicate which reaction occurs at the faster rate.arrow_forwardis this an E1 or E2 mechanism for this reaction? What is the major product and mechanism for it?arrow_forwardWrite the mechanism of the following bromination reaction and explain the regioselectivity of the bromination reaction. Draw the mechanism, transition state, energy diagram, etc. The same reaction with chlorine is not much regioselective in Q1. Explain the decreased regioselectivity of the following chlorination reaction by comparing the bromination reaction in Q1. Draw the mechanism, transition state, energy diagram, etc.arrow_forward
- how do I draw this mechanism and determine if it’s sn1 sn2 e1 or e2arrow_forwardComplete the following reactions by providing the missing product(s). Determine what mechanism operates in each case (SN1, SN2, E1, or E2). Show the stereochemistry of the product(s) where appropriate. If more than one product is formed circle the major one.arrow_forwardDraw major elimination product and identify if it's E1 or E2arrow_forward
- Predict the correct mechanism and major product for the following reactionsarrow_forwardTu Identify the following mechanisms as SN1, SN2, E1, E2 and draw the final product for each reactionarrow_forwardIn the box to the left of each reaction below, write the mechanism by which it occurs (could be SN1, SN2, or E1, or even 2 of them). Then draw the product(s).arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
