
Consolidated Electric: Inventory Control
Joe Henry, the sole owner and president of the Consolidated Electric Company, reflected on his inventory management problems. He was a major wholesale supplier of equipment and supplies to electrical contractors, and his business hinged on the efficient management of inventories to meet his customers' needs. While Henry had built a very successful business, he was nearing retirement age and wanted to pass along a good inventory management system.
Henry's two sons-in-law were employed in the company. Carl Byerly, the older of the two, had a college degree in mathematics and was very interested in Inventory formulas and computers. The other son-in-law, Edward Wright, had a degree in biology and was manager of one of the company’s wholesale warehouses.
Joe Henry started the Consolidated Electric Company in the 1940s and built it Into a highly profitable business. In 2016 the company had achieved S10 million in sales and earned SI million in pretax profits. Consolidated Electric was currently the twelfth largest electrical wholesaler in the country.
Consolidated Electric operates through four warehouses in Iowa (Des Moines, Cedar Rapids, Sioux City, and Davenport). From these sites, contractors in Iowa, Minnesota, Nebraska, Wisconsin, Illinois, and Missouri are supplied with a wide range of electrical equipment, including wire, electrical boxes, connectors, lighting fixtures, and electrical controllers. The company stocks 20,000 separate line items In Its Inventory purchased from 200 different manufacturers. (A line Item is defined as a particular item carried at a particular location.) These items range from less than 1 cent each to several hundred dollars for the largest electrical controllers.
Of the 20,000 line items, a great many are carried to provide a full line of service. For example, the top 2,000 items account for 50 percent of the sales and the bottom 10,000 items for only 20 percent. The remaining 8,000 items account for 30 percent of the sales.
The company has continually purged its 20,000 inventory items to carry only those that are demanded at least once a year. As Henry says, “We live and die by good customer service at a reasonable selling price. If we do not meet this objective, the customer will go to another wholesaler or buy directly from the manufacturer.”
Henry explained that he currently managed inventory by using an "earn and turn" concept. According to this concept, the earnings margin multiplied by the inventory turn ratio must equal a constant value of 2.0. For example, if a particular electrical item costs $6 to purchase wholesale and is sold for $10, then the earnings margin is $4 and the earn ratio for this item is $4/$10 = .40. If this item has a turn ratio of 5 times a year (sales are 5 times the average inventory carried), then the product of earn and turn is .4(5) = 2.0. If another item earns more, it can turn slower; if it earns less, it must turn faster.
Each year, Henry sets a target earn-tum ratio for the entire business and a value for each product line. These targets are based on the estimated costs of operations and the return-on-investment goal for the company. As stated above, the current target ratio for the business is 2.0. The purchasing agents and inventory managers at each location are measured by their ability to meet the target earn-turn ratios on their product lines. The actual ratios are reported monthly.
Although earn-turn ratios work quite well in controlling profitability of the business and entire product lines, they do not work very well for individual inventory items. Some line items tend to be in excess supply, while others are often out of stock.
The inventory is currently managed by use of a small computer system. A record for each item is kept and a clerk posts transactions on the record as units are received or issued, thus keeping a running on-hand inventory balance. Periodically, a purchasing agent reviews the records for a particular supplier. Then, using the order point and quantity stored on the record, the purchasing agent places an order for all items that are below their reorder point.
If the total quantities of all items required from a supplier do not meet the purchase discount minimums or a truckload lot, additional items near their reorder points are added to the order. This is not done when the total order size is too far from the minimums, since excessive Inventories would build up.
The order quantity and reorder point on each record are based on judgment and past experience. Generally speaking, a three-month supply is ordered for low-cost items and as little as a one-month supply for expensive items. Most lines are reviewed on a weekly basis.
Consolidated Electric had been converting its inventory records to a new software system. At the present time, an on-hand balance is maintained on the computer, and an accurate history of all orders placed, receipts, and issues is kept.
A demand history for a typical item is shown in Appendix 1.
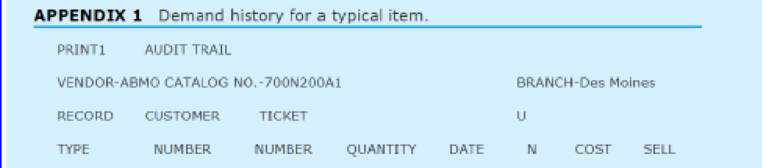
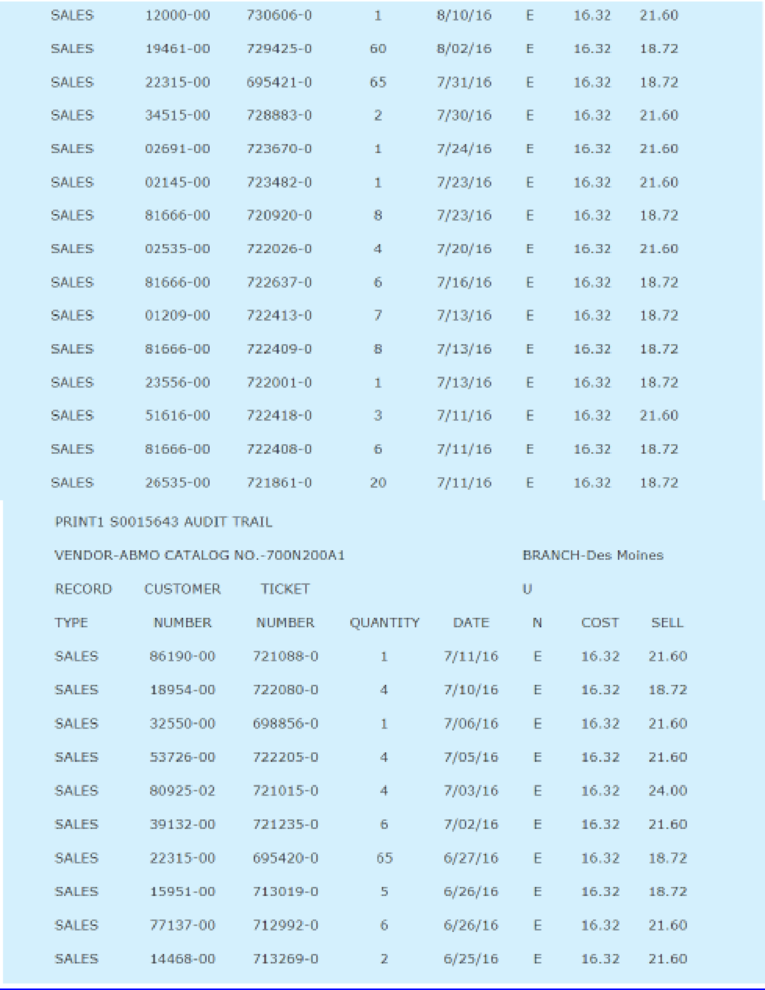
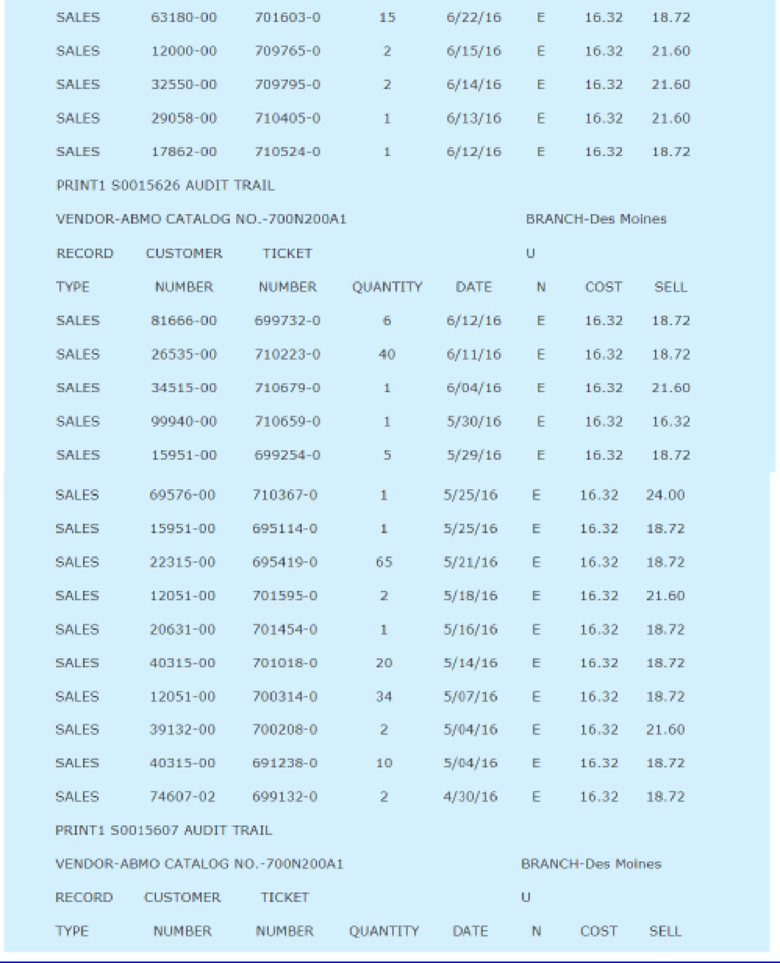
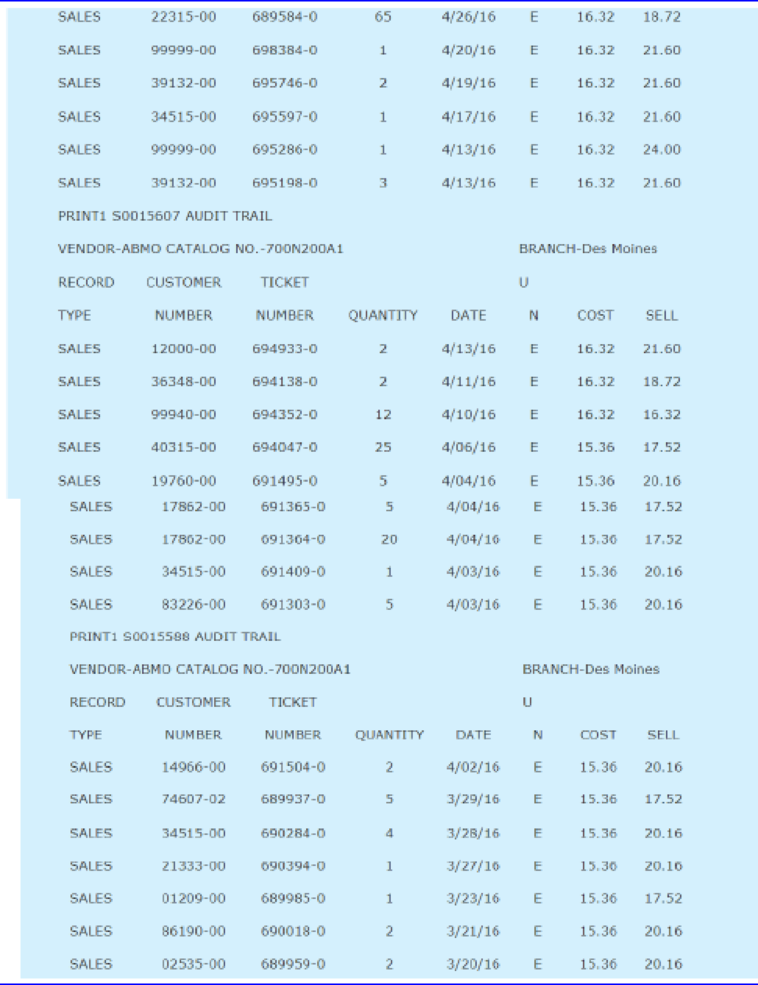
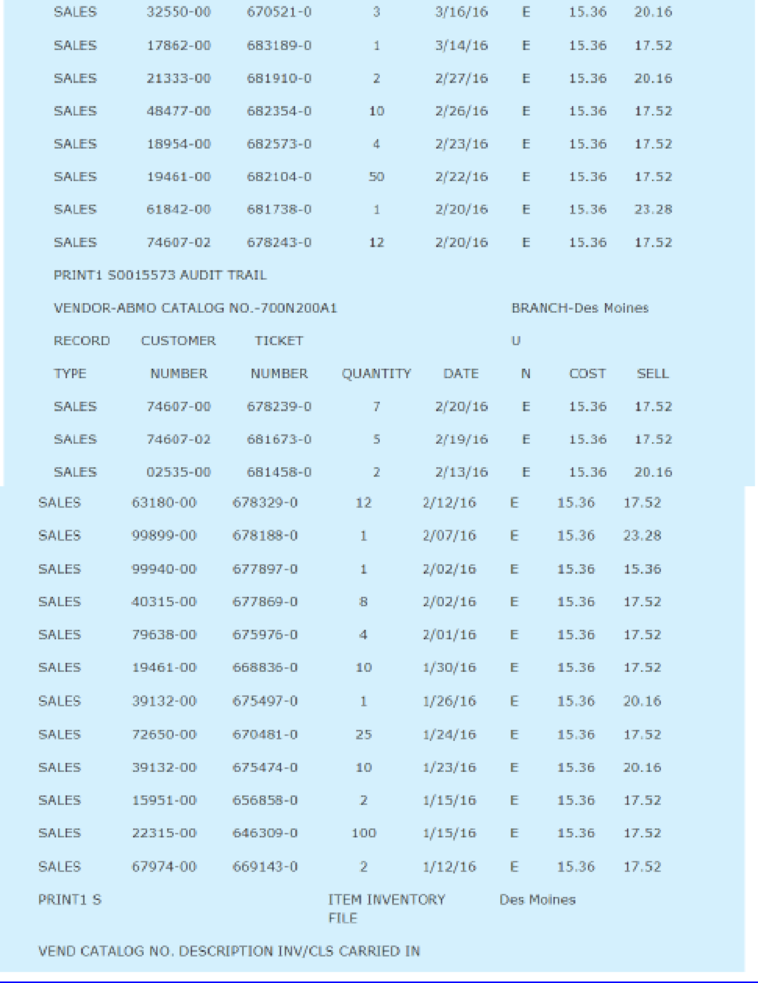
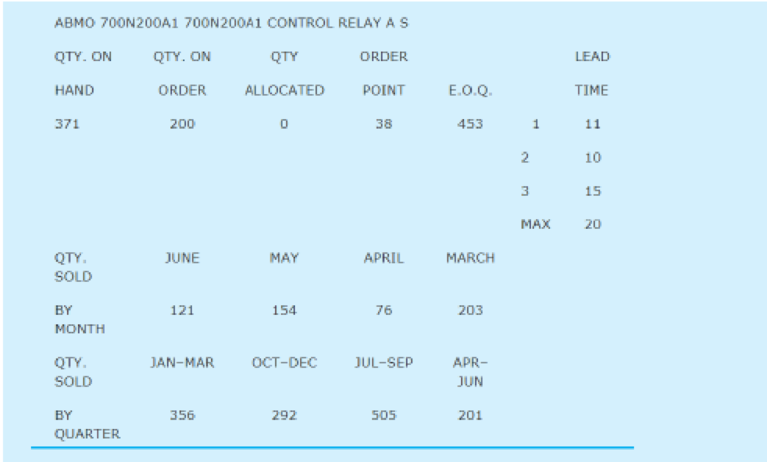
Henry was anxious to utilize the new system to calculate reorder points and order quantities, but he was unsure of the exact formulas to use. Using standard textbooks in the inventory field, Henry and Carl Byerly developed the formulas given in Exhibit 1. The EOQ formula utilizes a carrying cost of 28 percent and an ordering cost of $4.36 per order placed. These figures were based on past cost history at the company.
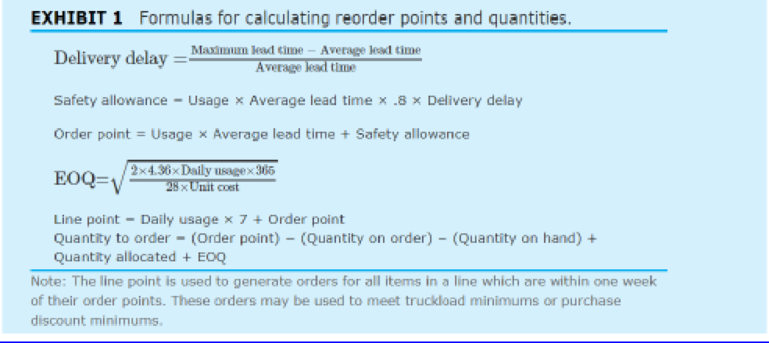
The formulas were programmed into the computer and tested on a pilot basis. For some Items the formulas seemed to work quite well, but for others they resulted in drastic departures from current practice and from common sense. For example, on one electrical box, the formulas would have ordered a two-year supply. Henry wanted to get the new software up as soon as possible, but he was not sure that the formulas would work properly. He wondered whether the formulas would meet the customer-service objectives of the business. Would they take advantage of truckload lots or purchase discounts whenever appropnate, and would the formulas result in reasonable inventory levels?
Discussion Questions
1. Design an inventory
2. Describe how the system you have designed will help the company meet customer-service and cost obiectives.
This case was prepared as a basis for class discussion, not to illustrate either effective or ineffective handling of an administrative situation.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter CS Solutions
OPERATIONS MANAGMENT IN...-ACCESS
- Scenario 3 Ben Gibson, the purchasing manager at Coastal Products, was reviewing purchasing expenditures for packaging materials with Jeff Joyner. Ben was particularly disturbed about the amount spent on corrugated boxes purchased from Southeastern Corrugated. Ben said, I dont like the salesman from that company. He comes around here acting like he owns the place. He loves to tell us about his fancy car, house, and vacations. It seems to me he must be making too much money off of us! Jeff responded that he heard Southeastern Corrugated was going to ask for a price increase to cover the rising costs of raw material paper stock. Jeff further stated that Southeastern would probably ask for more than what was justified simply from rising paper stock costs. After the meeting, Ben decided he had heard enough. After all, he prided himself on being a results-oriented manager. There was no way he was going to allow that salesman to keep taking advantage of Coastal Products. Ben called Jeff and told him it was time to rebid the corrugated contract before Southeastern came in with a price increase request. Who did Jeff know that might be interested in the business? Jeff replied he had several companies in mind to include in the bidding process. These companies would surely come in at a lower price, partly because they used lower-grade boxes that would probably work well enough in Coastal Products process. Jeff also explained that these suppliers were not serious contenders for the business. Their purpose was to create competition with the bids. Ben told Jeff to make sure that Southeastern was well aware that these new suppliers were bidding on the contract. He also said to make sure the suppliers knew that price was going to be the determining factor in this quote, because he considered corrugated boxes to be a standard industry item. As the Marketing Manager for Southeastern Corrugated, what would you do upon receiving the request for quotation from Coastal Products?arrow_forwardAvion, Inc. Susan Dey and Bill Mifflin, procurement managers at Avion, Inc., sat across from each other and reviewed a troubling performance report concerning a key supplier, Foster Technologies. The report detailed the deteriorating performance of Foster Technologies in the areas of material quality and on-time delivery. At this point, Kevin ODonnell, another procurement manager, entered the room. Explain the role of performance measurement in managing supply chain activities.arrow_forwardClassique Designs sells a variety of merchandise, including school shoes for girls. The business began the last quarter of 2013 with 30 pairs of the “Aerosoles” brand at a total cost of $54,000. The following transactions, relating to the “Aerosoles” brand were completed during the quarter: October 3 Purchased 45 pairs of shoes at a cost of $1,900 each. October 15 Sold 55 pairs to Casually Elegant Ltd at a unit price of $2,780 October 26 Purchased 70 pairs at a cost of $2,400 each but these were subject to a trade discount of 5%. November 10 Sold 60 pairs to Best City Store which yielded total sales revenue of $192,000. November 14 Owing to an increased demand for this brand, the manager of Classique purchased 80 additional pairs of the “Aerosole” brand at a unit cost of $2,500, but additionally there was freight charge of $100 on each pair. November 24 Sold 60 pairs of shoes to Big Buy Company at a price of $3,600 each. November 30 A physical…arrow_forward
- Relationship Between Order Management and Customer Service in the Broken Hill Proprietary Companyarrow_forwardJennifer has a small business mixing and selling essential oils. One product is a mixture of two oils, lavender and peppermint. She asked her assistant, Carmen, to check on two suppliers to determine the costs for her next batch. Carmen contacted the suppliers and got quotes from each for the order. She misplaced the number of ounces of each oil she needed to purchase. The information she has is: Supplier A: lavender: $5.80$5.80/ounce peppermint: $4.20$4.20/ounce Total cost: $128.40$128.40 Supplier B: lavender: $4.50$4.50/ounce peppermint: $5.00$5.00/ounce Total cost: $124$124 She decides to solve a system of equations to determine the number of ounces of lavender, LL and of peppermint, PP, she should order. What system of equations can Jennifer use to find LL and PP?arrow_forwardManaging Ashland multicomm services continuing its monitoring the upload speed firstarrow_forward
- Devan Co. began the year with $500 in office supplies. During the year, Devan used $2,800 worth of additional supplies. At the end of the year, Devan had $1,200 worth of supplies remaining. How many supplies did Devan purchase during the year? $2,300 $2,100 $3,500 $3,300arrow_forwardMalcolm Technology issued a new series of bonds on January 1, 1985. They were sold at par ($1,000) have a coupon rate of 10% and mature in 20 years. Coupon payments are made semi-annually. What was the price of the bond on January 1, 1995, when interest rates had fallen to 8%?arrow_forwardwhat is the purpose of SIMA, and how would SIMA be applicable to the Customs Act? Please answer minimum 800arrow_forward
- Vulcan Radio Manufacturing Inc. ("Vulcan") is a well-known manufacturer of radio broadcast equipment. Vulcan employs Thor on a full-time basis as an engineering sales representative in Ontario. In addition to working for Vulcan, Thor performs independent professional engineering consulting services for radio broadcasters. Thor's business cards read Thor, Audio Consulting Engineering Services. Thor's independent services include technical analyses of broadcast systems. As part of these services, Thor often makes recommendations for the selection and purchase of broadcast equipment by broadcasters. Sometimes, Thor recommends Vulcan's equipment to clients. Using PEO's Codes of Ethics and Code of Conduct as your guide. What approvals, licences, etc. must Thor obtain in order to be legally allowed to provide such consulting professional engineering services? Assuming that Thor has all the necessary licences, what should Thor tell his regular employer and clients about this work?…arrow_forwardPlease show formula and solution There are approximately 15,000 households in the Sampaloc, Manila. Over the 6-month lockdown, a number of households purchased one (1) unit of air conditioner. The breakdown of the brands purchased is as follows: Super Lamig - 4,688 households Frozen to Death - 1,456 households Feeling Airy - 2,355 households Typhoon - 3,899 households Based on the above data, what is the market penetration of air conditioning units in Sampaloc, Manila during the 6-month lockdown period?arrow_forward
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
