6.19 Consider the following cascade connection of isothermal reactors. A first-order reaction A B occurs in both reactors, with reaction rate constant k. The volumes of liquid in the reactors, V, are constant and equal; the flow rates Fo, F1, F2 and R are constant. Assume constant physical properties and a negligible time delay for the recycle line. Fo, Co R, C2 F1, C F2, C2 Figure E6.19 (a) Write a mathematical model for this process. (b) Derive a transfer function model relating the output con centration of A, C2 to the inlet concentration of A, Co- (c) Verify that, in the limit of no recycle (R 0), the transfer function derived in (b) is equivalent to the transfer function of the two tanks connected in series. (d) Show that when k 0 and a very large recycle flow rate is used (i.e., the limit as Ro), the transfer function derived in (b) becomes the transfer function of a single tank that has the volume eqto 2V and a gain of one. Hint: Recognize that F1 R+ F2 and Fo F2
6.19 Consider the following cascade connection of isothermal reactors. A first-order reaction A B occurs in both reactors, with reaction rate constant k. The volumes of liquid in the reactors, V, are constant and equal; the flow rates Fo, F1, F2 and R are constant. Assume constant physical properties and a negligible time delay for the recycle line. Fo, Co R, C2 F1, C F2, C2 Figure E6.19 (a) Write a mathematical model for this process. (b) Derive a transfer function model relating the output con centration of A, C2 to the inlet concentration of A, Co- (c) Verify that, in the limit of no recycle (R 0), the transfer function derived in (b) is equivalent to the transfer function of the two tanks connected in series. (d) Show that when k 0 and a very large recycle flow rate is used (i.e., the limit as Ro), the transfer function derived in (b) becomes the transfer function of a single tank that has the volume eqto 2V and a gain of one. Hint: Recognize that F1 R+ F2 and Fo F2
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P
Related questions
Question
B C and D ONLY!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
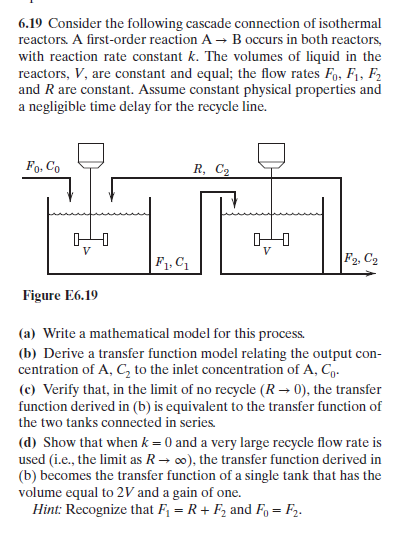
Transcribed Image Text:6.19 Consider the following cascade connection of isothermal
reactors. A first-order reaction A B occurs in both reactors,
with reaction rate constant k. The volumes of liquid in the
reactors, V, are constant and equal; the flow rates Fo, F1, F2
and R are constant. Assume constant physical properties and
a negligible time delay for the recycle line.
Fo, Co
R, C2
F1, C
F2, C2
Figure E6.19
(a) Write a mathematical model for this process.
(b) Derive a transfer function model relating the output con
centration of A, C2 to the inlet concentration of A, Co-
(c) Verify that, in the limit of no recycle (R 0), the transfer
function derived in (b) is equivalent to the transfer function of
the two tanks connected in series.
(d) Show that when k 0 and a very large recycle flow rate is
used (i.e., the limit as Ro), the transfer function derived in
(b) becomes the transfer function of a single tank that has the
volume eqto 2V and a gain of one.
Hint: Recognize that F1 R+ F2 and Fo F2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285061238
Author:
Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:
Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780072848236
Author:
Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Companies, The