The value of kcat for N-Ac-Phe-OC₂H5 is two-fold greater than that for the L-tryptophanyl analog and more than 10-fold greater than the value of kcat for the ester substrate N-Ac-Leu-OC2H5. Does this mean that N-Ac-Phe-OC2H5 exhibits greater specificity as a substrate than the other ester sub- strates? On what basis do you base your conclusion? Also, which kinetic parameters help to distin- guish between specificity (of substrate recognition) and affinity o0f a substrate when comparing a se- ries of substrates of an enzyme?
The value of kcat for N-Ac-Phe-OC₂H5 is two-fold greater than that for the L-tryptophanyl analog and more than 10-fold greater than the value of kcat for the ester substrate N-Ac-Leu-OC2H5. Does this mean that N-Ac-Phe-OC2H5 exhibits greater specificity as a substrate than the other ester sub- strates? On what basis do you base your conclusion? Also, which kinetic parameters help to distin- guish between specificity (of substrate recognition) and affinity o0f a substrate when comparing a se- ries of substrates of an enzyme?
Biochemistry
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Chapter26: Synthesis And Degradation Of Nucleotides
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 17P
Related questions
Question
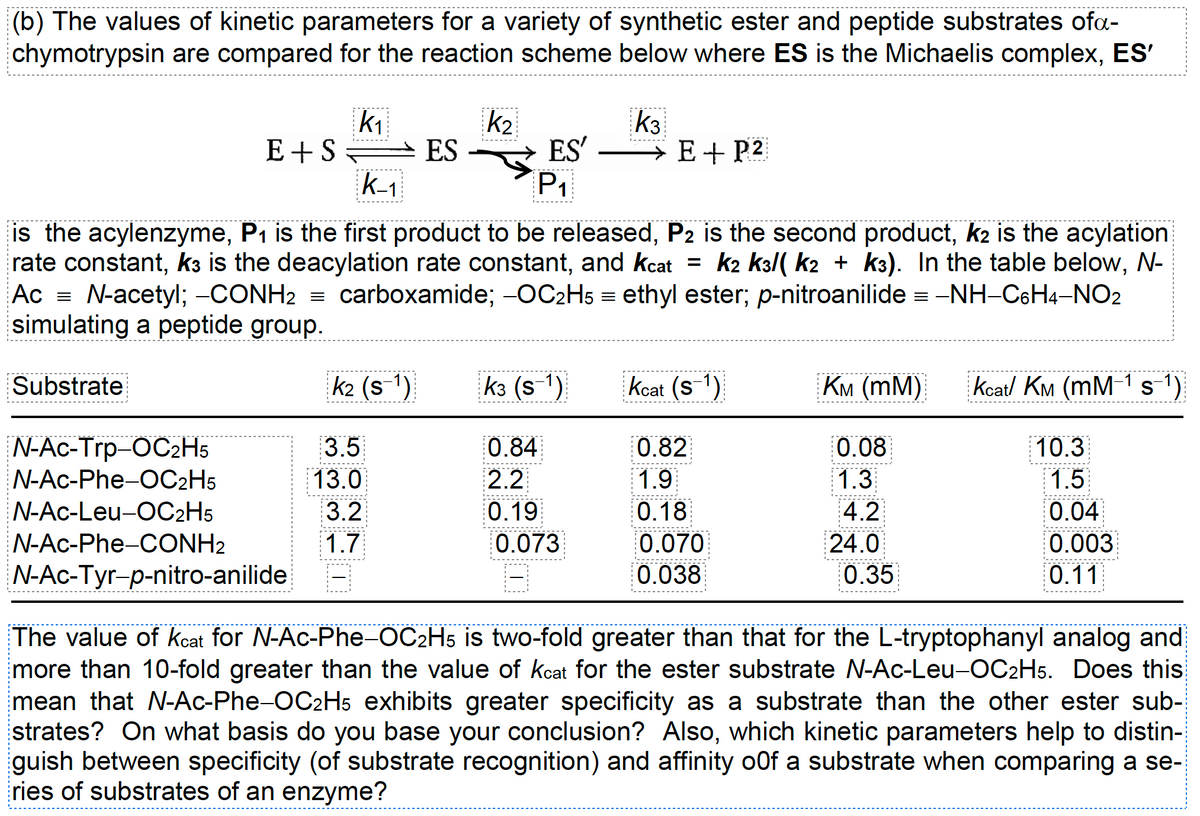
Transcribed Image Text:(b) The values of kinetic parameters for a variety of synthetic ester and peptide substrates ofa-
chymotrypsin are compared for the reaction scheme below where ES is the Michaelis complex, ES'
E+S
Substrate
K₁
N-Ac-Trp–OC₂H5
N-Ac-Phe-OC2H5
N-Ac-Leu-OC2H5
N-Ac-Phe-CONH2
N-Ac-Tyr-p-nitro-anilide
ES
K₂
3.5
13.0
3.2
1.7
K-₁
is the acylenzyme, P₁ is the first product to be released, P2 is the second product, k2 is the acylation
rate constant, k3 is the deacylation rate constant, and kcat = k2 k3/( k2 + k³). In the table below, N-
Ac = N-acetyl; -CONH₂ = carboxamide; -OC₂H5 = ethyl ester; p-nitroanilide = −NH-C6H4-NO2
simulating a peptide group.
ES'
K2 (S-¹) K3 (S-1)
0.84
2.2
0.19
P₁
K3
0.073
H
→ E+ P2
Kcat (S-1)
0.82
1.9
0.18
0.070
0.038
KM (MM)
0.08
1.3
4.2
24.0
0.35
1
Kcat/ KM (mM-¹ s¯¹)
10.3
1.5
0.04
0.003
0.11
The value of kcat for N-Ac-Phe-OC2H5 is two-fold greater than that for the L-tryptophanyl analog and
more than 10-fold greater than the value of kcat for the ester substrate N-Ac-Leu-OC2H5. Does this
mean that N-Ac-Phe-OC2H5 exhibits greater specificity as a substrate than the other ester sub-
strates? On what basis do you base your conclusion? Also, which kinetic parameters help to distin-
guish between specificity (of substrate recognition) and affinity o0f a substrate when comparing a se-
ries of substrates of an enzyme?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305961135
Author:
Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305961135
Author:
Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:
Cengage Learning