
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for the given molecule is to be completed.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structures involve only valence electrons. When drawing a Lewis structure, the first step is to calculate the total number of valence electrons. For a complete Lewis structure of a molecule, the atoms must complete their normal valency by bond formation and lone pairs of electrons. Maximum number of covalent bonds formed by any neutral atom with maximum number of lone pairs is
| Atom | Number of bond | Number of lone pairs |
| C | 4 | 0 |
| H | 1 | 0 |
| O | 2 | 2 |
| N | 1 | 1 |
| F | 1 | 3 |
Answer to Problem 1.46P
The complete Lewis structure for the given molecule is
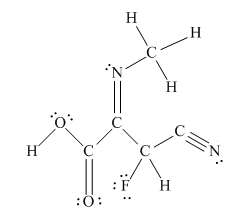
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is
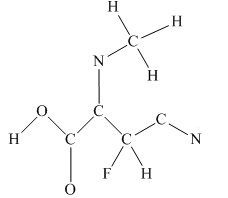
Total valence electron count for the given molecule is
The other oxygen atom has formed only one bond with carbon. This is converted to a double bond and two lone pairs are placed on the oxygen atom so that its octet is complete. A double bond is placed between C and N atom to complete the octet of carbon and a lone pair is placed in nitrogen to complete its octet.
A triple bond is placed between the other C and N to complete the octet of carbon and a lone pair is placed in the nitrogen to complete its octet.

This structure now accounts for all 54 electrons and the octet of each atom, except hydrogen, is complete. The duet for all hydrogens is complete.
The Lewis structure for the given molecule is completed from total valence electron count.
(b)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for the given molecule is to be completed.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structures involve only valence electrons. When drawing a Lewis structure, the first step is to calculate the total number of valence electrons. For a complete Lewis structure of a molecule, every carbon atom must form four covalent bonds whereas the hydrogen atom forms one bond.
Answer to Problem 1.46P
The complete Lewis structure for the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is
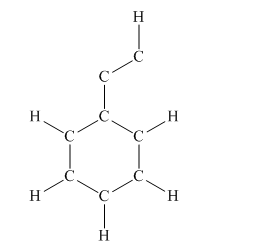
Total valence electron count for the given molecule must be

This structure now accounts for all 38 electrons and the octet of each atom, except hydrogen, is complete. The duet for all hydrogen atoms is complete.
The Lewis structure for the given molecule is completed from total valence electron count.
(c)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for the given molecule is to be completed.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structures involve only valence electrons. When drawing a Lewis structure, the first step is to calculate the total number of valence electrons. For a complete Lewis structure of a molecule, the atoms must complete their normal valency by bond formation and lone pairs of electrons. Maximum numbers of covalent bonds formed by any neutral atom with maximum number of lone pair are
| Atom | Number of bond | Number of lone pairs |
| C | 4 | 0 |
| H | 1 | 0 |
| O | 2 | 2 |
| N | 1 | 1 |
Answer to Problem 1.46P
The complete Lewis structure for the given molecule is
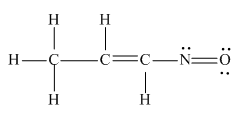
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is
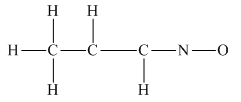
Total valence electron count for the given molecule is
The oxygen atom has formed only one bond with nitrogen. This is converted to a double bond and two lone pairs are placed on the oxygen atom so that its octet is complete. Another lone pair is placed on the nitrogen atom so that its octet is complete.
A double bond is placed between the C atoms attached to one hydrogen each. This completes the octet of both carbon atoms

This structure now accounts for all the 28 electrons, and the octet of each atom, except hydrogen, is complete. The duet for all hydrogen atoms is complete.
The Lewis structure for the given molecule is completed from total valence electron count.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY E-BOOK W/SMARTWORK5
- Choose the best lewis structure for NO3- Answer Choices in the attached picturearrow_forwardConsider the Lewis structure shown for thionitromethane. Draw the major resonance structure for the compound shown; include lone pairs of electrons, formal charges, and condensed hydrogen atoms (located in the More menu). Then draw curved arrows to show how this can be converted to the Lewis structure given.arrow_forwardFor each of the Lewis structures shown below, predict the Electron Geometry, Molecular Geometry and Bond Angle. Lastly, using the same format as shown in the last column of Table 1, draw a sketch (using wedges and dashes to show 3D if needed) of the Molecular Geometry.arrow_forward
- The molecule H2O2 (H-O-O-H) has: A. 4 bonding pairs and 3 lone pair. B. 3 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs. C. 3 bonding pairs and 3 lone pairs. D. 3 bonding pairs and 4 lone pair. E. some number of lone and bond pairs not described in 1-4.arrow_forwardFor the following three Lewis structures, list whether they are correct or incorrect: alt-text for image above: The first image shows a proposed Lewis structure for Freon-13, CClF3, that has a central carbon singly bonded to a three chlorine atoms and a fluorine atom. Each chlorine and the fluorine have 3 lone pairs of electrons around them. The second image shows a proposed lewis structure for the nitrite ion, NO2-, as a central nitrogen atom between two oxygen atoms. The O atom on the left has three lone pairs of electrons and then a single bond between the N. The right O atom has two lone pairs of electrons and a double bond with the N atom. The N atom has a single lone pair of electrons in addition to the double and single bonds with oxygen atoms. The third image shows diazomethane, CH2N2, and the proposed Lewis structure has a carbon singly bonded to two H atoms, then doubly bonded to a nitrogen. The nitrogen is doubly bonded to the second nitrogen, and the second nitrogen has…arrow_forward3-26 Table 3-2 shows the following ions of copper: Cu+ and Cu2+. Do these violate the octet rule? Explain.arrow_forward
- The following model is a representation of citric acid, the key substance in the so-called citric acid cycle, by which food molecules are metabolized in the body. Only the connections between atoms are shown; multiple bonds are not indicated. Complete the structure by indicating the positions of multiple bonds and lone-pair electrons (gray = C, red = O, ivory = H).arrow_forward3-58 In Section 2-3B, we saw that there are seven diatomic elements. (a) Draw Lewis structures for each of these diatomic elements. (b) Which diatomic elements are gases at room temperature? Which are liquids? Which are solids?arrow_forwardYou will not find “hydroxide” in the stockroom, but you will find sodium hydroxide (NaOH) andpotassium hydroxide (KOH). Lithium hydroxide (LiOH) is expensive and used in spacecraft airfilters since hydroxide reacts with carbon dioxide, and lithium is lighter than sodium or potassium.Cesium and francium hydroxides are very expensive and little used. Is this information consistentwith your answer to the previous question?arrow_forward
- 3-109 Until several years ago, the two chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) most widely used as heat transfer media in refrigeration systems were Freon-li (trichloro fluoromethane, CC13F) and Freon-12 (dichiorodi fluoromethane, CCl2F2). Draw a three-dimensional representation of each molecule and indicate the Direction of it.s polarity.arrow_forwardExplain in your own words, using 1-3 complete sentences and proper spelling and grammar, what holds the P atom to the F atom in a molecule of PF3? Be very specific. (Hint: is it a bond or a force? Which one?)arrow_forwardwhat is the generic formula (format for example, AX3E) and formal charge of Chlorine trifluoride?arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning



