
Concept explainers
Interpretation: The location of ozone in the Earth’s atmosphere needs to be explained.
Concept introduction: The layer/film of gases around our Earth is defined as an atmosphere. Life on Earth is impossible without it. On the basis of temperature, the atmosphere comprises four main layers which are mentioned below:
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
- Thermosphere
Answer to Problem 26A
The ozone layer is naturally formed by a reactive process in the stratosphere. The ozone layer is important because it protects our Earth from UV lights.
Explanation of Solution
90 % of ozone is located in the stratosphere. Above Earth's surface, the stratosphere about 10 to 16 kilometers long (on altitude). Excluding this, the stratosphere extends up to 50 kilometers (nearby). The ozone layer is naturally formed (or produced) in the stratosphere. The following image will help you to locate ozone in Earth’s atmosphere:
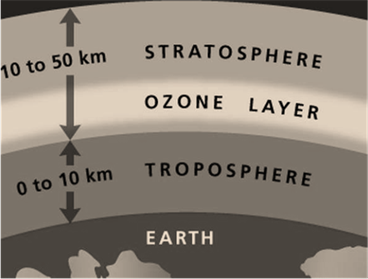
In the stratosphere, formation(by the reactive process) of the ozone layer is mentioned below:
Step 1: Solar ultraviolet radiation (or sunlight) breaks apart oxygen (O) molecule to form 2 separate oxygen atoms.
Step 2: Individually, the atom later undergoes a binding collision with another present oxygen molecule. This process forms an ozone molecule.
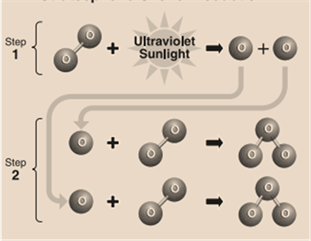
Step 3: After this process, 3 oxygen molecules plus sunlight react together to form 2 ozone molecules. This becomes the ozone layer. The reaction of this process is mentioned below:
The above reaction takes place in the presence of sunlight.
The ozone layer is a ring of protective gases which protects Earth from UV light.
Chapter 1 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: The Central Science (13th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Essential Organic Chemistry (3rd Edition)
Organic Chemistry (9th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (3rd Edition)
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





