
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
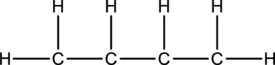
Lewis structure has to be completed from the skeletal structure given below and the bond angles around the central atoms in the given structure have to be predicted using the VSEPR model.
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structure is used for predicting the shape of molecules. From the steric number obtained in a Lewis structure, the molecular geometry can be predicted. VSEPR model can predict the shape of molecules considering their Lewis structure. Certain rules has to be followed in for the VSEPR model.
- The molecule will have a shape where there is minimal electrostatic repulsion between the valence‑shell electron pairs.
- The forces of repulsion between two lone pairs of electrons will be higher than the repulsion between lone pair and bond pair of electrons. This in turn will be higher than the bond pair‑bond pair of electrons.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Skeletal structure for the molecule given is shown;
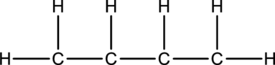
The Lewis structure can be drawn considering the valence electrons in the molecule. Total number of valence electrons is calculated as shown below;
Eighteen electrons are used up in the skeletal structure. One electron pair is added to the terminal carbon atom each. Thus the Lewis structure can be drawn as follows;
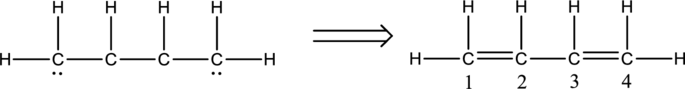
Bond Angles:
Central atoms present in the above structure are four carbon atoms. The bond angles can be predicted using the steric number.
Steric number for carbon atom C-1:
The number of lone pair of electrons on carbon atom is zero while the number of atoms that are bonded to carbon is three. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is three, the arrangement is trigonal planar and the bond angle will be
Steric number for carbon atom C-2:
The number of lone pair of electrons on carbon atom is zero while the number of atoms that are bonded to carbon is three. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is three, the arrangement is trigonal planar and the bond angle will be
Steric number for carbon atom C-3:
The number of lone pair of electrons on carbon atom is zero while the number of atoms that are bonded to carbon is three. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is three, the arrangement is trigonal planar and the bond angle will be
Steric number for carbon atom C-4:
The number of lone pair of electrons on carbon atom is zero while the number of atoms that are bonded to carbon is three. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is three, the arrangement is trigonal planar and the bond angle will be
(b)
Interpretation:
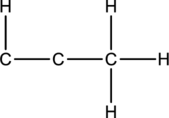
Lewis structure has to be completed from the skeletal structure given below and the bond angles around the central atoms in the given structure have to be predicted using the VSEPR model.
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Skeletal structure for the molecule given is shown;
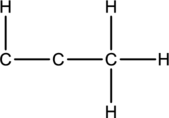
The Lewis structure can be drawn considering the valence electrons in the molecule. Total number of valence electrons is calculated as shown below;
Twelve electrons are used up in the skeletal structure. Two carbon atoms are added with a lone pair of electrons. Thus the Lewis structure can be drawn as follows;
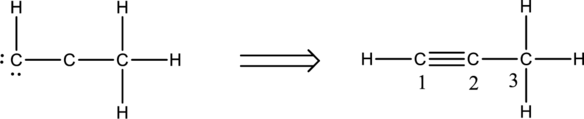
Bond Angles:
Central atoms present in the above structure are three carbon atoms. The bond angles can be predicted using the steric number.
Steric number for carbon atom C-1:
The number of lone pair of electrons on carbon atom is zero while the number of atoms that are bonded to carbon is two. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is two, the arrangement is linear and the bond angle will be
Steric number for carbon atom C-2:
The number of lone pair of electrons on carbon atom is zero while the number of atoms that are bonded to carbon is two. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is two, the arrangement is linear and the bond angle will be
Steric number for carbon atom C-3:
The number of lone pair of electrons on carbon atom is zero while the number of atoms that are bonded to carbon is four. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is four, the arrangement is tetrahedral and the bond angle will be
(c)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure has to be completed from the skeletal structure given below and the bond angles around the central atoms in the given structure have to be predicted using the VSEPR model.
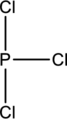
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Skeletal structure for the molecule given is shown;
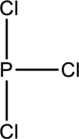
The Lewis structure can be drawn considering the valence electrons in the molecule. Total number of valence electrons is calculated as shown below;
Six electrons are used up in the skeletal structure. Three lone pair of electrons are placed on the chlorine atom each and a lone pair of electron is placed over the phosphorus atom. Thus the Lewis structure can be drawn as follows;
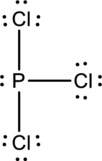
Bond Angles:
Central atom present in the above structure is a phosphorus. The bond angles can be predicted using the steric number.
Steric number for phosphorus:
The number of lone pair of electrons on phosphorus atom is one while the number of atoms that are bonded to phosphorus is three. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is four, the arrangement is tetrahedral and the bond angle will be
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
- Use the VSEPR model to predict the bond angles around each central atom in the following Lewis structures (benzene rings are frequently pictured as hexagons, without the letter for the carbon atom at each vertex). Note that the drawings do not necessarily depict the bond angles correctly.arrow_forward• identify sigma and pi bonds in a molecule and explain the difference between them.arrow_forwardIn each of the following molecules, a central atom is surrounded by a total of three atoms or unshared electron pairs: SnCl2, BCl3, SO2. In which of these molecules would you expect the bond angle to be less than 120? Explain your reasoning.arrow_forward
- Predict the molecular structure (including bond angles) for each of the following. (See Exercises 115 and 116.) a. ICl5 b. XeCl4 c. SeCl6arrow_forwardFor each of the following molecules, state the bond angle (or bond angles, as appropriate) that you would expect to see on the central atom based on the simple VSEPR model. Would you expect the actual bond angles to be greater or less than this? a CCl4 b SCl2 c COCl2 d AsH3arrow_forwardIdentify the type of hybridization, approximate bond angles for the N, C, and O atoms, and shortest carbon-to-oxygen bond length in alanine, an amino acid, whose Lewis structure isarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





