
(a)
Interpretation:
The electron dot formula and structural formula of
Concept introduction:
An electron dot formula is a way of representing the molecular structure in which electrons are represented by a dot. Structural formula is a way in which atoms are linked together through a solid line. This solid line represents the covalent bond. An electron dot structure is known as Lewis structure. Electron dot structure indicates the valence electrons of an atom which are involved in bonding.
Answer to Problem 38E
Electron dot structure of
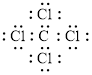
The structural formula of
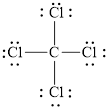
Explanation of Solution
In a molecule
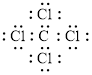
Figure 1

Figure 2
Each solid line, in Figure 2, between the carbon and chlorine atom is the covalent bond which is made up of two electrons. This bond is formed by sharing of electrons between the central atom carbon and the surrounding chlorine atom.
An electron dot structure and structural formula of
(b)
Interpretation:
The electron dot formula and structural formula of
Concept introduction:
An electron dot formula is a way of representing the molecular structure in which electrons are represented by a dot. Structural formula is a way in which atoms are linked together through a solid line. This solid line represents the covalent bond. An electron dot structure is known as Lewis structure. Electron dot structure indicates the valence electrons of an atom which are involved in bonding.
Answer to Problem 38E
Electron dot structure of
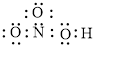
The structural formula of
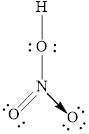
Explanation of Solution
In molecule
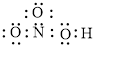
Figure 3

Figure 4
Each solid line, in Figure 4, between the nitrogen and oxygen atom is the covalent bond which is made up of two electrons. This bond is formed by sharing of electrons between the central atom nitrogen and the surrounding oxygen atom. Bond between oxygen and hydrogen is also a covalent bond. Bond between nitrogen and oxygen with red arrow is the coordinate bond. This shows the sharing of nitrogen electrons between the oxygen and the nitrogen.
An electron dot structure and structural formula of
(c)
Interpretation:
The electron dot formula and structural formula of
Concept introduction:
An electron dot formula is a way of representing the molecular structure in which electrons are represented by a dot. Structural formula is a way in which atoms are linked together through a solid line. This solid line represents the covalent bond. An electron dot structure is known as Lewis structure. Electron dot structure indicates the valence electrons of an atom which are involved in bonding.
Answer to Problem 38E
Electron dot structure
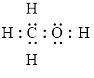
The structural formula of
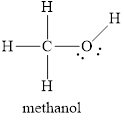
Explanation of Solution
In molecule
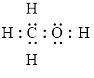
Figure 5

Figure 6
Each solid line, in Figure 6, between the carbon-hydrogen, carbon-oxygen and oxygen –hydrogen is the covalent bond which is made up of two electrons. This bond is formed by sharing of electrons between the two atoms present in that bond. Lone pair of oxygen is shown with
An electron dot structure and structural formula of
(d)
Interpretation:
The electron dot formula and structural formula of
Concept introduction:
An electron dot formula is a way of representing the molecular structure in which electrons are represented by a dot. Structural formula is a way in which atoms are linked together through a solid line. This solid line represents the covalent bond. An electron dot structure is known as lewis structure. Electron dot structure indicates the valence electrons of an atom which are involved in bonding.
Answer to Problem 38E
Electron dot structure of
![]()
The structural formula of
![]()
Explanation of Solution
In a molecule
![]()
Figure 7
![]()
Figure 8
Each solid line, in Figure 8, between the oxygen-hydrogen, carbon-oxygen and carbon –nitrogen is the covalent bond which is made up of two electrons. This bond is formed by sharing of electrons between the two atoms present in that bond. Lone pair of oxygen and nitrogen is shown with
An electron dot structure and structural formula of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY-STD.GDE.+SOL.MAN
- Write the structural formulas of 4 compounds with the formula C3H6Oarrow_forwarda. If A represents a group 5A element, what is the formal charge of A in the structure above? b. What is the shape of this molecule? c. Is this a polar molecule?arrow_forwardWhat are the chemical structure of the following?arrow_forward
- Give the electron dot diagram for N, O, S, H2O, and methane.arrow_forwardin the molecule PCI3 given the phosphorus has the electronegativity of 2.1 and the chlorine has an electronegativity of three point no we can conclude that this molecule isarrow_forwardBased on its Lewis structure, which molecule will have stronger oxygen-oxygen bonds, O2, or O3?arrow_forward
- Give a cation isoelectronic with fluoride ion______________________ 3.Arrange in increasingsize: sodiumion, nitride ion, magnesium ion, oxide ion, neon. (explain your rationale)______<______<______<_____<_____ Arrange in decreasingsize: sulfide ion, argon, potassium ion, calcium ion, chloride ion. (explain your rationale)______>______>______>_____>___arrow_forwardwhat is the formal charge on the singly bonded oxygen atoms in the lewis structure for the carbonate ion?arrow_forwardwhat is the lewis structure for SiH4S?arrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





