
Interpretation: The product formed after reaction of cyclohexane in the presence of
Concept introduction:
Molecules that have one unpaired electron are called free radicals.
Answer to Problem 1PP
Solution:

Explanation of Solution
Given information:
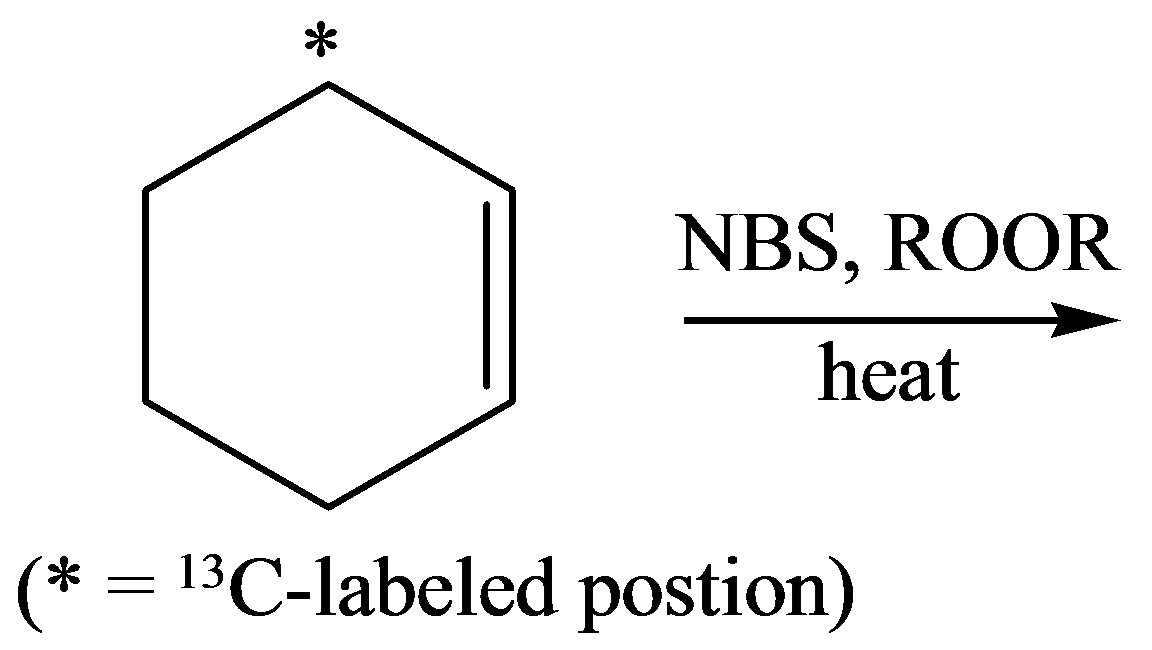
The reaction in the presence of
Allylic bromination is a free radical substitution reaction in which removal of hydrogen atom on carbon adjacent to a double bond with bromine.
Free radical substitution reaction takes place in the presence of
The structure of 3-bromocyclohexence is as follows:

The product formed after free radical substitution is 3-bromocyclohexence.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Bringing together your knowledge of the reaction chemistry of substituted benzenes, suggest a preparative route for conversion of compound A to compound B shown belowarrow_forward(a) Give a mechanism for this reaction, showing how the two products arise as aconsequence of the resonance-stabilized intermediate.(b) The bromination of cyclohexene using NBS gives only one major product, as shown onthe previous page. Explain why there is no second product from an allylic shift.arrow_forwardProvide a reasonable synthetic strategy for the synthesis of a racemic mixture of (1R,2R) and (1S,2S)-2-bromo-1-methylcyclopentanol from methylcyclopentanearrow_forward
- 3c)Referring to the intermediates you drew in problem below explain in detail why no meta product is obtained in the Friedel-Crafts alkylation of chlorobenzene. Draw all pertinent resonance structures to support your argument.arrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following reactions. Label the product as Zaitsev or Hofmann when relevant and indicate the stereochemical outcome when relevent.arrow_forwardmost of the additions of bromine to double bonds gave entirely antistereochemistry. Explain why the addition to phenanthrene gives a mixture of synand anti stereochemistry. When the product from (c) is heated, HBr is evolved and 9-bromophenanthrene results.Propose a mechanism for this dehydrohalogenation.arrow_forward
- Propose a plausible mechanism for the 1 to 2 conversion as shown, and explain the stereochemical result:arrow_forwardwe know that ethers, such as diethyl ether and tetrahydrofuran, are quite resistant to the action of dilute acids and require hot concentrated HI or HBr for cleavage. However, acetals in which two ether groups are linked to the same carbon undergo hydrolysis readily, even in dilute aqueous acid. How do you account for this marked difference in chemical reactivity toward dilute aqueous acid between ethers and acetals?arrow_forwardThe reaction of butan-2-ol with concentrated aqueous HBr goes with partial racemization, giving more inversion thanretention of configuration. Propose a mechanism that accounts for racemization with excess inversion.(b) Under the same conditions, an optically active sample of trans-2-bromocyclopentanol reacts with concentrated aqueous HBr to give an optically inactive product, (racemic) trans-1,2-dibromocyclopentane. Proposea mechanism to show how this reaction goes with apparently complete retention of configuration, yet withracemization. (Hint: Draw out the mechanism of the reaction of cyclopentene with Br2 in water to give thestarting material, trans-2- bromocyclopentanol. Consider how parts of this mechanism might be involved in thereaction with HBr.)arrow_forward
- Under basic conditions, the following substrates can undergo a [4+2] cycloaddition with regio- anddiastereo- control. Rationalize mechanistically how the reaction occurs as well as the regio- and stereochemical outcome with each base.arrow_forwardDraw the structure of the desired dibromide product H. ) Propose a reasonable arrow-pushing mechanism for formation of the byproduct I.Use your mechanism to justify the stereochemistry in molecule Iarrow_forwardIn another part of the project, an analogue of the protease inhibitor darunavir is further developed, as shown in structure 11.Enter the correct stereochemistry for all stereo centers and the double bonds that are relevant in 11. Answer sheets at the end of the problem set can be used.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
