
Interpretation:
The mechanism for the given reaction between 2,3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene and hydrogen bromide is to be determined. The reaction energy coordinate diagram that illustrates kinetic and thermodynamic pathways is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
舧 Electrophiles are electron-deficient species, which has positive or partially positive charge. Lewis acids are electrophiles, which accept electron pair.
舧 Nucleophiles are electron-rich species, which has negative or partially negative charge. Lewis bases are nucleophiles, which donate electron pair.
舧 Free radical is an atom, molecule, or ion that has an unpaired electron, which makes it highly chemically reactive.
舧 Substitution reaction: A reaction in which one of the hydrogen atoms of a hydrocarbon or a functional group is substituted by any other functional group is called substitution reaction.
舧 Elimination reaction: A reaction in which two substituent groups are detached and a double bond is formed is called elimination reaction.
舧 Addition reaction: It is the reaction in which unsaturated bonds are converted to saturated molecules by the addition of molecules.
舧 The reaction in which there is addition of hydrogen molecule is called hydrogenation reaction.
舧
舧 Hydrogenation with platinum as a catalyst is used to convert unsaturated carbohydrates to saturated hydrocarbons
舧 Oxidation of
舧 Ozonolysis helps convert the carbon – carbon double bonds to carbon – oxygen double bond (carbonyl compounds).
舧 Dimethyl sulfide is used as a reducing agent that decomposes the intermediate formed into the carbonyl group.
舧 NBS (nitro-bromo succinimide) is a special reagent used for bromination of allylic carbocations.
舧 Bromine replaces the hydrogen attached to the carbon adjacent to the carbon bearing double bond.
舧 This method of using NBS can produce allylic bromides without bromine reacting with the double bond.
舧 Dehydration of a primary alcohol in the presence of a mineral acid like concentrated sulfuric acid results in the formation of alkene via E2 elimination.
舧 1,2–addition of hydrohalogenation (HX) to a diene is the addition of hydrogen to the carbon designated as 1 and halogen to the carbon designated as 2. The positions of carbon as 1 and 2 are not according to the IUPAC numbering of the molecule, but as a conjugated diene. The mechanism is similar to 1,4-addition. The mechanism of 1,2-addition and 1,4-addition of hydrohalogenation is given below:
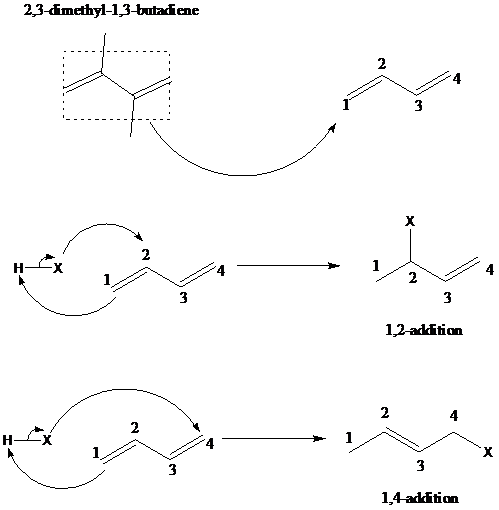
舧 When conjugated diene is attacked by an electrophile, the resultant products are formed via 1,2-addition and 1,4-addition reaction mechanism. Kinetics and
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Propose a mechanism for this isomerization.arrow_forwardPropose a mechanism for the following reaction, an important step in the laboratory synthesis of proteins:arrow_forwardThis is a transesterification reaction. It mechanistically is the same as a Fischer Esterification. Write a mechanism for the reaction. Include all lone pairs and formal charges present throughout the mechanism.arrow_forward
- Outline a detailed mechanism for the problem below. No other reagents other than those given are necessary. Use arrows to explain the flow of electrons and show all intermediates.arrow_forwardProvide a detailed mechanism for the following (Hint:halohydrin reaction). Use arrows to show electron flow and show intermediates.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

