
(a)
Interpretation:
The numbers of chlorination products obtained from radical chlorination of methyl cyclohexane has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
In a halogenation reaction, one or more halogen atoms are introduced into an organic compound. Generally, these reactions are initiated in the presence of light or heat.
Chlorination:
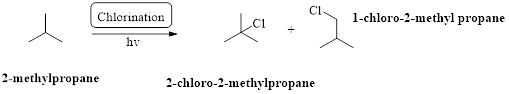
2-methylpropane undergoes radical chlorination which yields the 2-chloro-2-methylpropane and 1-chloro-2-methylpropane.
The mechanism of monochlorination of ethane (as an example) includes three steps,
- (i) Initiation
- (ii) Propagation
- (iii) Termination
The mechanism of monochlorination of ethane is shown below,
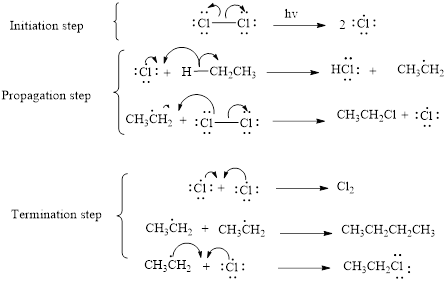
In a halogenation reaction, one or more halogen atoms are introduced into an organic compound. Generally, these reactions are initiated in the presence of light or heat
(b)
Interpretation:
The number of monochlorination products obtained from the radical chlorination of methyl cyclohexane should be given when all stereoisomers are included.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
In a halogenation reaction, one or more halogen atoms are introduced into an organic compound. Generally, these reactions are initiated in the presence of light or heat.
Chlorination:
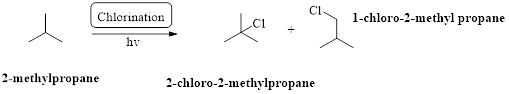
2-methylpropane undergoes radical chlorination which yields the 2-chloro-2-methylpropane and 1-chloro-2-methylpropane.
The mechanism of monochlorination of ethane (as an example) includes three steps,
- (i) Initiation
- (ii) Propagation
- (iii) Termination
The mechanism of monochlorination of ethane is shown below,

In a halogenation reaction, one or more halogen atoms are introduced into an organic compound. Generally, these reactions are initiated in the presence of light or heat
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-superimposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-superimposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Total number of stereoisomers = 2n
Where n is the number of chiral centers.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry (3rd Edition)
- When HBr adds to a conjugated diene, what is the product-determining step?arrow_forwardExplain the importance of Pericyclic Reactions? Why should we study ?arrow_forwardAlkane chlorination can occur at any position in the alkane chain. Draw and name all monochloro products you might obtain from radical chlorination of 3-methylpentane.arrow_forward
- Free-radical chlorination of pentane can produce up to__________ different monochloropentanes. one two three four fivearrow_forwardWhy do these two dienes react at different temperatures?arrow_forwarda) Write the name of three steps of free-radical halogenation of methane?b) Give the mechanism of formation of dichloromethane from chloromethane?c) Explain why free-radical halogenation usually gives mixture of products.arrow_forward
- How many total isomers are possible from the mono-chlorination of methylcyclohexane, via radical halogenation?arrow_forwardAn electrophilic addition reaction of a conjugated diene that produces more than two organic productsarrow_forward2. In the bromination reactions, what is the function of CCl4? Why can it fulfil its role?3. Bromination proceeds by either free radical substitution or electrophillic addition. Based on Table 3, which mechanism is followed by alkanes? by alkenes? by alkynes?4. For which hydrocarbon type is light necessary for bromination to take place?5. What is the function of light in the bromination reaction? Why are alkenes and alkynes not included as samples?arrow_forward
- What are the Steps of Radical Halogenation ?arrow_forwardBased on the hydrogenation and the bromination reaction information, how many different alkene structures can you draw that could be Compound X? (If enantiomers are possible, count each pair of enantiomers as one structure.)arrow_forwardDraw all the different monochlorinated products one would obtain by the radical chlorination of 2-methylbutane.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
