
(a)
Interpretation:
The mechanism for the given reaction is to be drawn, and the major product is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 17.47P
The mechanism for the given reaction is drawn below:
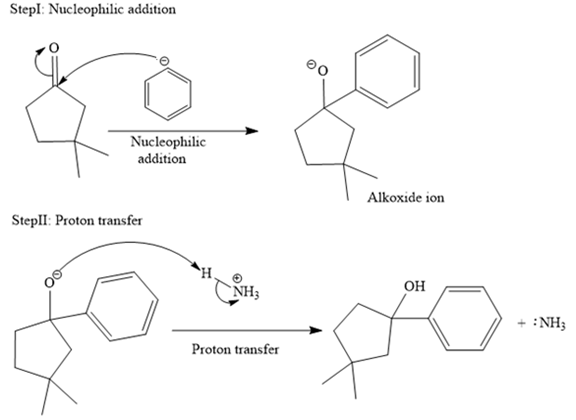
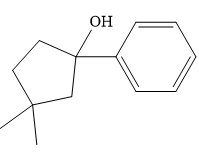
The major product of the given reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
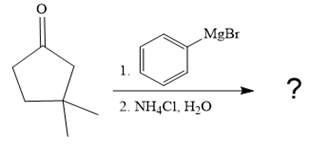
In the given reaction, the starting material is a cyclic
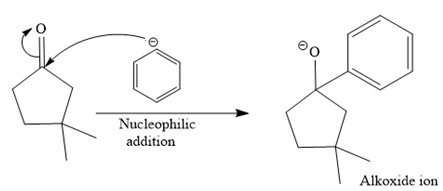
An alkoxide ion, on acid workup, forms uncharged alcohol as the final product.
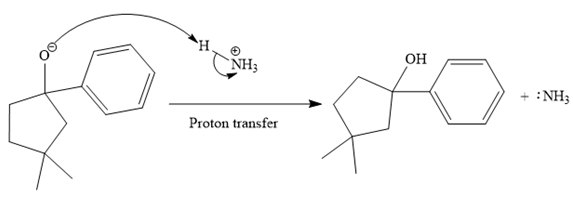
Thus, the major product of the given reaction is

Ketones, when treated with Grignard reagent, produce tertiary alcohol as the final product.
(b)
Interpretation:
The mechanism for the given reaction is to be drawn, and the major product is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Organometallic compounds have a polar covalent
Answer to Problem 17.47P
The mechanism for the given reaction is drawn below:
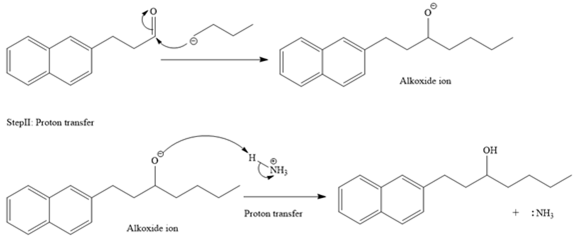
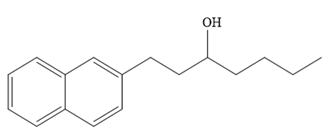
The major product of the given reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
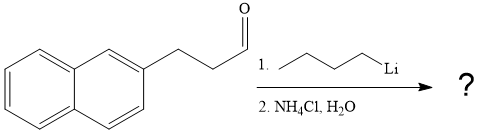
In the given reaction, the starting material is an
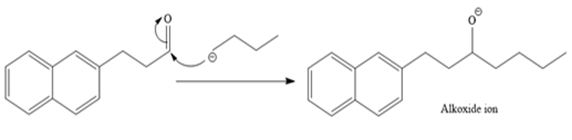
An alkoxide ion, on acid workup, forms uncharged alcohol as the final product.
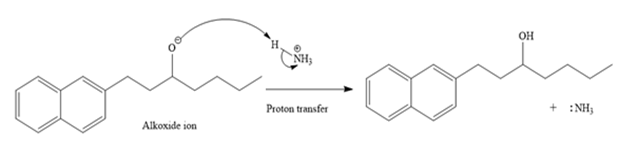
Thus, the major product of the given reaction is
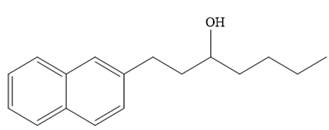
Ketones, when treated with Grignard reagent, produce tertiary alcohol as the final product.
(c)
Interpretation:
The mechanism for the given reaction is to be drawn, and the major product for the same reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Although
Answer to Problem 17.47P
The mechanism for the given reaction is drawn below:
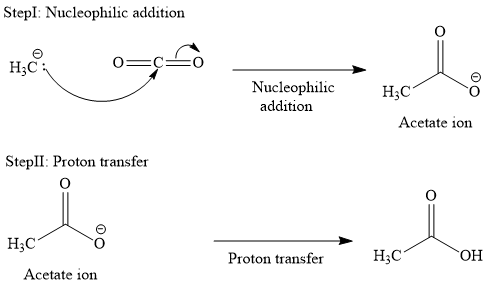
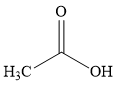
The major product of the given reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
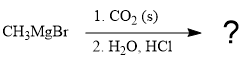
Each
The first step of the reaction is the attack of the nucleophile
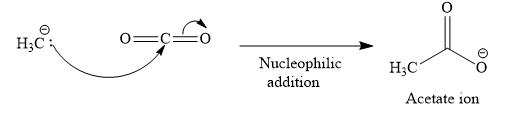
The immediate product of carboxylation is a carboxylate ion, which is subsequently protonated through an acid workup to yield a carboxylic acid.
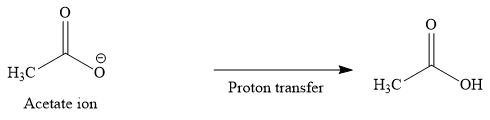
Thus, the major product of the given reaction is
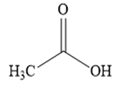
The Grignard reagent adds across the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY E-BOOK W/SMARTWORK5
- Draw the mechanism and major product of the following reactionarrow_forwardDraw the complete mechanism and the major organic product for each of the following reactions.arrow_forwardPlease explain B, C, and D. Draw the mechanism and the major product(s) of each of the following reaction.arrow_forward
- Please explain A, B, and C. Draw the mechanism and the major product(s) of each of the following reactions. Thanks!arrow_forwardDraw a complete mechanism and predict the major product in the following reactionarrow_forwardDraw a detailed mechanism for the following reaction and include the major productarrow_forward
- Draw the products and mechanism of the following reactionarrow_forwardDraw the mechanism and the major organic product for each of the following reactions. Please show all work with arrowsarrow_forwardDraw the complete, detailed mechanism for each of the following reactions and predict the major products.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





