
(a)
Interpretation:
From the given compounds from E to H, a compound containing a primary amine and a primary amide needs to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Amine − is an organic N compounds formed by replacing one or more H atoms of
Amide- is an organic compound contains the group of
Answer to Problem 31P
Structure H.
Explanation of Solution
Amines are formed by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms of ammonia with alkyl groups.
Furthermore,
In the below structure, bond that is indicated in red color is the single
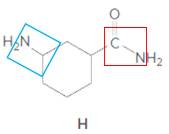
Hence, structure H is a compound that contains a
(b)
Interpretation:
From the given compounds from E to H, a compound containing a primary amine and a secondary amide needs to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Amine − is an organic N compounds formed by replacing one or more H atoms of
Amide- is an organic compound contains the group of
Answer to Problem 31P
Structure F.
Explanation of Solution
Amines are formed by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms of ammonia with alkyl groups.
Furthermore,
In the below structure, bonds that are indicated in red color are the two
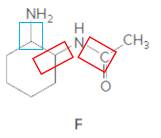
Hence, structure F is a compound that contains a
(c)
Interpretation:
From the given compounds from E to H, a compound containing a secondary amine and a tertiary amide needs to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Amine − is an organic N compounds formed by replacing one or more H atoms of
Amide- is an organic compound contains the group of
Answer to Problem 31P
Structure E.
Explanation of Solution
Amines are formed by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms of ammonia with alkyl groups.
Furthermore,
In the below structure, bonds that are indicated in red color are the three
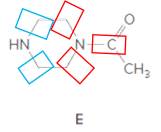
Hence, structure E is a compound that contains a
(d)
Interpretation:
From the given compounds from E to H, a compound containing a tertiary amine and a tertiary amide needs to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Amine − is an organic N compounds formed by replacing one or more H atoms of
Amide- is an organic compound contains the group of
Answer to Problem 31P
Structure G.
Explanation of Solution
Amines are formed by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms of ammonia with alkyl groups.
Furthermore,
In the below structure, bonds that are indicated in red color are the three
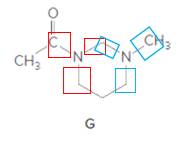
Hence, structure G is a compound that contains a
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- Which type of amine is phentermine? a) a primary aliphatic amine b) a primary aromatic amine c) a tertiary aliphatic amine d) a tertiary aromatic aminearrow_forwardDraw a structural formula for each amine and amine derivative. Q.) trans-2-Aminocyclohexanolarrow_forward1. Which of the following DOES NOT belong to the group? * A. Amine B. Nitrile C. Amide D. Acyl Halide 2. What is the IUPAC name of the compound? (Please refer to the first image attached.) A. 4,4-Dibromobutane B. 1,1-Dibromobutane C. 1-Butyl-2,2-dibromine D. Butyl-2,2-Dibromobutane E. None of the choices 3. What is the IUPAC name of the compound (Please refer to the second image attached.) A. 1-Cyclohexyl-1-cyclopropylcyclohexane B. 1-Cyclopropyl-1-cyclohexylcyclohexane C. Cycloropyl-1,1-dicyclohexane D. 1,2-Dicyclohexyl-1-cyclopropane E. None of the choicesarrow_forward
- N-p-hydroxyphenylethanamide is commonly known as a. acetaminophen b. acetamide c. acetanilide d. formamide High molar mass amines have __________ odor. a.strong ammoniacal b.fruity c.fishy d.obnoxious Trimethyl amine has _________ odor. a.obnoxious b.fishy c. ammoniacal d. fruityarrow_forwardWhich type of amine is (s)-methamphetamine? a) a primary aliphatic amine b) a primary aromatic amine c) a secondary aliphatic amine d) a secondary aromatic aminearrow_forwardWhat amine is formed by reduction of each amide?arrow_forward
- What are the functional groups present in this antibacterial antibiotic? A. Amide, thioether, aldehyde, phenol, carboxylic acid B. Amide, thioether, ketone, amine, phenol, carboxylic acid C. Amide, thioether, ketone, phenol, carboxylic acid D. Thioether, ketone, amine, phenol, carboxylic acid A brief explanation would be highly appreciated + upvotearrow_forwardGive an acceptable name for each amine.arrow_forwardAromatic amines are _________ neutral because of the polarity are unique as they do not behave like any of the other amines acidic, but stronger than the aliphatic amines basic, but weaker than aliphatic aminesarrow_forward
- Draw a structural formula for each amine and amine derivative. Q.) Benzylaminearrow_forwardWhich statement is true regarding following compound? [CH3CH2NH3]+ Cl- Question 10 options: This compound is an ammonium salt. This compound is a primary amine. This compound is a secondary amine. This compound is a tertiary amine.arrow_forwardDraw a structural formula for each amine and amine derivative. Q.) tert-Butylaminearrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





