
Interpretation: The structure of three salts formed needs to be determined if 0.27 g of octahedral complex of Cr reacts with strong dehydrating agent and lost mass of 0.036 g. Reaction of 270 mg of second salt with same dehydrating agent show mass loss of 18 mg. The 3rd salt did not lose any mass while treating with dehydrating agent.
Given:
Concept Introduction:
Crystal field theory is the theory given to explain the bonding in the coordination complexes. As ligand approaches towards the metal ion, the d-orbital of metal ion divide according to the energy of metal ion. On the basis of energy and degeneracy, the d-orbital can be classified as
In octahedral complex, the
Answer to Problem 84AE
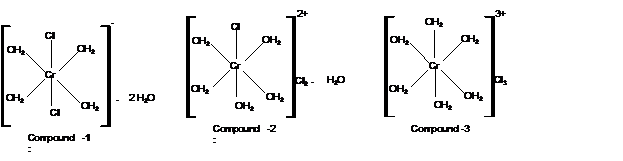
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Addition of excess of aqueous silver nitrate to 100.0 mL portion of 0.100 M solution of each salt forms silver chloride,
- 1st solution= 1430 mg AgCl
- 2nd solution = 2870 mg AgCl
- 3rd solution = 4300 mg AgCl
Two salts are green and one is violet here.
Compound 1:
Calculate moles of water of hydration:
With 2 moles of water; the formula must be
Mass of AgCl = 1430 mg
Check the mass of Cl in
Calculate moles of water of hydration:
With 1 moles of water; the formula must be
Mass of AgCl = 2870 mg
Check the mass of Cl in
Compound 3:
Moles of water of hydration is 0 as no water lose is there. Thus the formula must be
Mass of AgCl = 4300 mg
Check the mass of Cl in
Hence the structure of complexes should be:
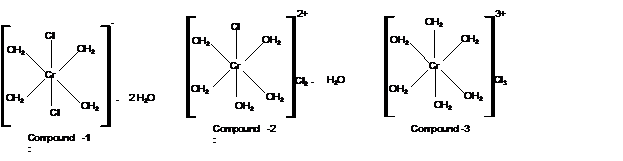
Thus,
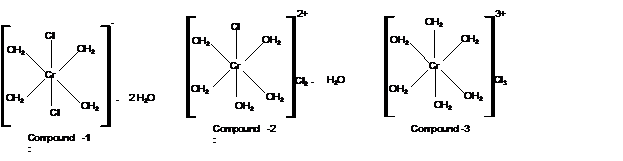
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Chemical Principles
- Calculate the molar absorptivity and absorbance of a 1.00 x 104 M solution, which has atransmittance of 32.1% , when the path length is 2.5 cm at 650 nm. (arrow_forwardThe standard curve was made by spectrophotographic analysis of equilibrated iron(III) thiocyanate solutions of known concentration. You are asked to analyze a Fe(SCN)2+Fe(SCN)2+ solution with an unknown concentration and an absorbance value of 0.4150.415 . The slope-intercept form of the equation of the line is ?=4558.4?+0.0147y=4558.4x+0.0147 . The unknown was analyzed on the same instrument as the standard curve solutions at the same temperature. What is the Fe3+Fe3+ concentration of the unknown solution?arrow_forwardPredict whether the following complexes would show Jahn-Teller distortion: Ammonium pentachlorooxidochromate(V), meff = 1.8 mB Potassium hexaiodidomanganate(IV), meff = 3.8 mB Potassium hexachoridocuprate(II), meff = 1.8 mB Hexaaquamanganese(II) chloride, meff = 6.0 mBarrow_forward
- The absorbance of a 0.00105% m/v solution of tolbutamide in methanol when measured in a 1 cm path length cell was found to be 0.796 at 228 nm. Calculate the specific absorbance.arrow_forwardWhat would be a reasonable guess for the wavelength of maximum absorbance for FD&C Orange 2?arrow_forwardThe accuracy of a spectrophotometer can be evaluated by preparing a solution of 60.06-ppm K2Cr2O7 in 0.0050 M H2SO4 and measuring its absorbance at a wavelength of 350 nm using a cell with a pathlength of 1.00 cm. The absorbance should be 0.640. What is the molar absorptivity of K2Cr2O7 at this wavelength?arrow_forward
- If the apparent molar absorptivity of cefuroxime sodium is 2.046 × 103 L mol−1 cm−1 in a 1-cm cuvette, at what concentration should the standard and sample solutions be prepared to result to an ideal absorbance value of 0.500? Show your solution.arrow_forwardAtomic absorption spectroscopy with graphite furnace atomization is an extremely sensitive technique. The standard addition method is used with this technique to determine the concentration of copper in urine. A 20.00 mL sample of urine is spiked with 1.00 mL of 300. ppb Cu²+ and this mixture gives a response of 0.168. Another 1.00 mL aliquot of 300. ppb Cu²+ is added to this mixture and gives a reading of 0.235Determine the concentration of copper in the urine samplearrow_forwardThe absorbance values observed during the determination of the complex stoichiometry with the Job method using the spectroscopic method were plotted and the following correct equations were obtained. According to this, what is the n value of the compound formed by Fe + 3 and SCN- ions?1. Line equation: y = 2.6188x + 0.1608 2. Line equation: y = -2.5963x + 2.7203arrow_forward
- The absorbance of a 1.05x10-5 M Fe+3 determined at 580 nm using a 2.50-cm cell was said to be 0.200. What is the molar absorptivity of this solution in liters/mole cm?arrow_forwardExplain the role of potassium hexacyanoferrate(II), K4[Fe(CN)6] as a component of the Benedict’s reagent for the Estimation of Glucosearrow_forwardLead is determined by atomic absorption at 283.3 nm, whereas it is determined at 405.8 nm by flame emission. Explain why the most sensitive line is different for these two methods.arrow_forward
 Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning

