
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Given uncharged molecule is to be identified as polar or nonpolar, using its electrostatic potential map. If the molecule is polar, the direction of its net molecular dipole moment it to be determined.
Concept introduction:
A polar bond is one in which the bond pair is unequally shared by the two atoms.
A partial positive charge is developed on the less electronegative atom while and an equal but negative partial charge is developed on the more electronegative atom.
Molecules that contain more than one polar bond may or may not have a net dipole moment. The dipole moment is a vector quantity. The net molecular dipole moment is the result of the vector addition of all the individual dipole moments. Depending on the symmetry of the molecule, the individual bond dipoles can partly or completely cancel or reinforce each other.
A bond dipole or a molecular dipole is represented by an arrow pointing from the atom or region with a partial positive charge toward an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Electrostatic potential maps of molecules show the distribution of electron density in different parts of the molecule. The electron density is represented by different colors, ranging from blue to red. Blue color indicates a low electron density, an atom or region with a partial positive charge. Red color indicates high electron density, an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Answer to Problem 2.40P
The electrostatic potential map shows that the molecule is nonpolar.
Explanation of Solution
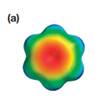
The electrostatic potential map shows the molecule with a negative charge concentrated at the center, with positive charge distributed symmetrically around the center. This shows that the individual bond dipoles are all of equal magnitude, and they all point toward the center. The vector addition of these dipoles will be zero because of their symmetric distribution. Therefore, the molecule is nonpolar.
The net dipole moment of a molecule is the vector sum of the individual bond dipoles.
(b)
Interpretation:
Given uncharged molecule is to be identified as polar or nonpolar, using its electrostatic potential map. If the molecule is polar, the direction of its net molecular dipole moment it to be determined.
Concept introduction:
A polar bond is one in which the bond pair is unequally shared by the two atoms.
A partial positive charge is developed on the less electronegative atom while and an equal but negative partial charge is developed on the more electronegative atom.
Molecules that contain more than one polar bond may or may not have a net dipole moment. The dipole moment is a vector quantity. The net molecular dipole moment is the result of the vector addition of all the individual dipole moments. Depending on the symmetry of the molecule, the individual bond dipoles can partly or completely cancel or reinforce each other.
A bond dipole or a molecular dipole is represented by an arrow pointing from the atom or region with a partial positive charge toward an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Electrostatic potential maps of molecules show the distribution of electron density in different parts of the molecule. The electron density is represented by different colors, ranging from blue to red. Blue color indicates a low electron density, an atom or region with a partial positive charge. Red color indicates high electron density, an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Answer to Problem 2.40P
The electrostatic potential map shows that the molecule is nonpolar.
Explanation of Solution
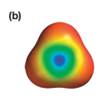
The electrostatic potential map shows a molecule with a negative charge concentrated at the center, with positive charge distributed symmetrically around the center. This shows that the individual bond dipoles are all of equal magnitude, and they all point toward the center. The vector addition of these dipoles will be zero because of their symmetric distribution. Therefore, the molecule is nonpolar.
The net dipole moment of a molecule is the vector sum of the individual bond dipoles.
(c)
Interpretation:
The given uncharged molecule is to be identified as polar or nonpolar, using its electrostatic potential map. If the molecule is polar, the direction of its net molecular dipole moment it to be determined.
Concept introduction:
A polar bond is one in which the bond pair is unequally shared by the two atoms.
A partial positive charge is developed on the less electronegative atom while and an equal but negative partial charge is developed on the more electronegative atom.
Molecules that contain more than one polar bond may or may not have a net dipole moment. The dipole moment is a vector quantity. The net molecular dipole moment is the result of the vector addition of all the individual dipole moments. Depending on the symmetry of the molecule, the individual bond dipoles can partly or completely cancel or reinforce each other.
A bond dipole or a molecular dipole is represented by an arrow pointing from the atom or region with a partial positive charge toward an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Electrostatic potential maps of molecules show the distribution of electron density in different parts of the molecule. The electron density is represented by different colors, ranging from blue to red. Blue color indicates a low electron density, an atom or region with a partial positive charge. Red color indicates high electron density, an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Answer to Problem 2.40P
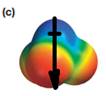
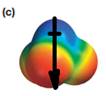
The electrostatic potential map shows that the molecule is polar.
The direction of the net molecular dipole is downward as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
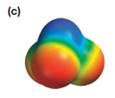
The electrostatic potential map shows a molecule with an asymmetric charge distribution. The positive charge is concentrated on the atom at the top, while the negative charge is distributed on three atoms at the bottom. The individual bond dipoles will therefore not cancel completely. Therefore, the molecule is polar.
The direction of the molecular dipole will be downward, as shown below by the black arrow.
The net dipole moment of a molecule is the vector sum of the individual bond dipoles.
(d)
Interpretation:
The given uncharged molecule is to be identified as polar or nonpolar, using its electrostatic potential map. If the molecule is polar, the direction of its net molecular dipole moment it to be determined.
Concept introduction:
A polar bond is one in which the bond pair is unequally shared by the two atoms.
A partial positive charge is developed on the less electronegative atom while and an equal but negative partial charge is developed on the more electronegative atom.
Molecules that contain more than one polar bond may or may not have a net dipole moment. The dipole moment is a vector quantity. The net molecular dipole moment is the result of the vector addition of all the individual dipole moments. Depending on the symmetry of the molecule, the individual bond dipoles can partly or completely cancel or reinforce each other.
A bond dipole or a molecular dipole is represented by an arrow pointing from the atom or region with a partial positive charge toward an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Electrostatic potential maps of molecules show the distribution of electron density in different parts of the molecule. The electron density is represented by different colors, ranging from blue to red. Blue color indicates a low electron density, an atom or region with a partial positive charge. Red color indicates high electron density, an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Answer to Problem 2.40P
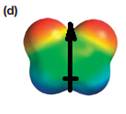
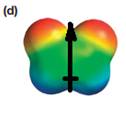
The electrostatic potential map shows that the molecule is polar.
The direction of the net molecular dipole is upward, as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
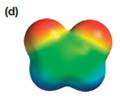
The electrostatic potential map shows a molecule with a negative charge distributed on two atoms at the top and the positive charge distributed on two atoms at the bottom. This shows that the individual bond dipoles both point approximately upward and slightly away from the center line. The vector addition of these dipoles will be nonzero. Therefore, the molecule is polar.
The direction of the net dipole moment will be upward as shown below.
The net dipole moment of a molecule is the vector sum of the individual bond dipoles.
(e)
Interpretation:
The given uncharged molecule is to be identified as polar or nonpolar, using its electrostatic potential map. If the molecule is polar, the direction of its net molecular dipole moment it to be determined.
Concept introduction:
A polar bond is one in which the bond pair is unequally shared by the two atoms.
A partial positive charge is developed on the less electronegative atom while and an equal but negative partial charge is developed on the more electronegative atom.
Molecules that contain more than one polar bond may or may not have a net dipole moment. The dipole moment is a vector quantity. The net molecular dipole moment is the result of the vector addition of all the individual dipole moments. Depending on the symmetry of the molecule, the individual bond dipoles can partly or completely cancel or reinforce each other.
A bond dipole or a molecular dipole is represented by an arrow pointing from the atom or region with a partial positive charge toward an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Electrostatic potential maps of molecules show the distribution of electron density in different parts of the molecule. The electron density is represented by different colors, ranging from blue to red. Blue color indicates a low electron density, an atom or region with a partial positive charge. Red color indicates high electron density, an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Answer to Problem 2.40P
The electrostatic potential map shows that the molecule is polar.
The direction of the net molecular dipole is upward as shown below.
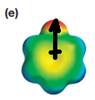
Explanation of Solution
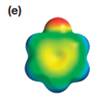
The electrostatic potential map shows a molecule with a negative charge concentrated on the atom at the top center, with positive charge distributed over atoms on the side and at the bottom. This shows that the individual bond dipoles are not symmetrically distributed and will not cancel out completely. Therefore, the molecule is polar.
The direction of the net molecular dipole will be upward because of the concentration of negative charge at the top and a symmetrical distribution of the positive charge in the rest of the molecule.
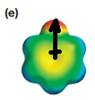
The net dipole moment of a molecule is the vector sum of the individual bond dipoles.
(f)
Interpretation:
The given uncharged molecule is to be identified as polar or nonpolar, using its electrostatic potential map. If the molecule is polar, the direction of its net molecular dipole moment it to be determined.
Concept introduction:
A polar bond is one in which the bond pair is unequally shared by the two atoms.
A partial positive charge is developed on the less electronegative atom while and an equal but negative partial charge is developed on the more electronegative atom.
Molecules that contain more than one polar bond may or may not have a net dipole moment. The dipole moment is a vector quantity. The net molecular dipole moment is the result of the vector addition of all the individual dipole moments. Depending on the symmetry of the molecule, the individual bond dipoles can partly or completely cancel or reinforce each other.
A bond dipole or a molecular dipole is represented by an arrow pointing from the atom or region with a partial positive charge toward an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Electrostatic potential maps of molecules show the distribution of electron density in different parts of the molecule. The electron density is represented by different colors, ranging from blue to red. Blue color indicates a low electron density, an atom or region with a partial positive charge. Red color indicates high electron density, an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Answer to Problem 2.40P
The electrostatic potential map shows that the molecule is nonpolar.
Explanation of Solution
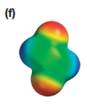
The electrostatic potential map shows a charge distribution that is symmetric about the center of the molecule with two negative regions opposite each other across the center as well as two positive regions across the center. The individual bond dipoles will therefore cancel out completely. Therefore, the net dipole moment will be zero, and the molecule will be nonpolar.
The net dipole moment of a molecule is the vector sum of the individual bond dipoles.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY E-BOOK W/SMARTWORK5
- Construct, fully label, and populate a MO diagram for the nitrosonium anion, NO+. Based on the diagram, state which of NO+ or NO you expect to have a stronger bond.arrow_forwardWhich of the following would be the more stable (lower in energy) of these resonance structures, and would be most representative of the molecule?arrow_forwardGive a clear handwritten answer with explanation....given below some compounds choose which compound is contains sp2 hybridized carbon atom...?arrow_forward
- Question:What is the significance of the LUMO (Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital) in organic chemistry, and how does it contribute to chemical reactions?arrow_forwardDraw a bond-line structure that best matches the given 3D representation?arrow_forwardPlease construct the MO diagrams of NH3 and NH4+and use their MO’s toexplain the protonation (acid-base reaction) of NH3arrow_forward
- Give a clear handwritten answer with explanation...give detailed answer.....given below some options in which choose the best answer that converts the bond line diagram below the given structure.arrow_forwardThe molecule shown on the right in the example in the right column is the amino acid histidine, and the five-membered ring is known as aromatic. An aromatic ring has 2, 6, 10, 14, etc., electrons placed in 2p orbitals around a ring. Indicate which of the following statements must therefore be true. 1. There are a total of six electrons in the pi system (defined as electrons in 2p orbitals), including the lone pair on the ring N that is not circled. 2. There are a total of six electrons in the pi system, including the lone pair on the ring N atom that is circled. 3. The lone pair on the ring N atom that is not circled resides in an sp2 orbital on an sp2 hybridized nitrogen atom. 4. Statements 2 and 3 are both truearrow_forwardThat answer is incorrect. Is there another possible solution? Preferably in a cyclopentane shapearrow_forward
- BRIEFLY, explain why can you use litmus paper to distinguish between H2SO4 and (NH4)2SO4?arrow_forwardConsider structure A, which other strucutre shown is the same as molecule A? and whyarrow_forwardIn the spaces provided, indicate the type of bond, and the hybridized orbitals that overlap to form the bond.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
